phase diagram → fazni dijagram
Phase diagram is a graphic representation of the equilibrium relationships between phases (such as vapour-liquid, liquid-solid) of a chemical compound, mixture of compounds, or solution.
The figure shows a typical phase diagram of an element or a simple compound. The stability of solid, liquid and gas phases depends on the temperature and the pressure. The three phases are in equilibrium at the triple point. The gas and liquid phases are separated by a phase transition only below the temperature of the critical point.
potentiometric titration → potenciometrijska titracija
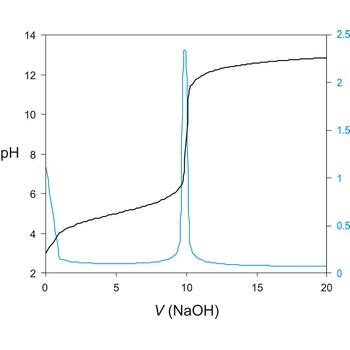
Potentiometric titration is a volumetric method in which the potential between two electrodes is measured (referent and indicator electrode) as a function of the added reagent volume. Types of potentiometric titrations for the determination of analytes in photoprocessing solutions include acid-base, redox, precipitation, and complexometric.
Potentiometric titrations are preferred to manual titrations, since they are more accurate and precise. They are also more easily adapted to automation, where automated titration systems can process larger volumes of samples with minimal analyst involvement.
A titration curve has a characteristic sigmoid curve. The part of the curve that has the maximum change marks the equivalence point of the titration. The first derivative, ΔE/ΔV, is the slope of the curve, and the endpoint occurs at the volume, V', where ΔE/ΔV has the maximum value.
qualitative analysis → kvalitativna analiza
Qualitative analysis involves determining the nature of a pure unknown compound or the compounds present in a mixture. Qualitative inorganic analysis is used to separate and detect cations and anions in a sample substance. According to their properties, cations are usually classified into six groups. Each group has a common reagent which can be used to separate them from the solution.
Soxhlet extractor → Soxhletov ekstraktor
Soxhlet extractor is a laboratory apparatus designed to extract substances with a low solubility in the extracting solvent. The method described by the German chemist Franz von Soxhlet (1848-1926) in 1879 is the most commonly used example of a semi-continuous method applied to extraction of lipids from foods. In the Soxhlet extractor, the sample soaks in hot solvent that is periodically siphoned off, distilled and returned to the sample. During each cycle, a portion of the non-volatile compound dissolves in the solvent. After many cycles the desired compound is concentrated in the distillation flask. The solvent in the flask is then evaporated and the mass of the remaining lipid is measured.
standard → standard
Standards are materials containing a known concentration of an analyte. They provide a reference to determine unknown concentrations or to calibrate analytical instruments.
The accuracy of an analytical measurement is how close a result comes to the true value. Determining the accuracy of a measurement usually requires calibration of the analytical method with a known standard. This is often done with standards of several concentrations to make a calibration or working curve.
A primary standard is a reagent that is extremely pure, stable, has no waters of hydration, and has a high molecular weight.
A secondary standard is a standard that is prepared in the laboratory for a specific analysis. It is usually standardised against a primary standard.
standard deviation → standardna devijacija
Standard deviation (σ) is a measure of the dispersion of a set of data from its mean. Standard deviation is a statistical term that measures the amount of variability or dispersion around an average
Suppose there are many measurements of a quantity presumed to be similar, like the size of peas in a pod. If the number of readings for each size were plotted, a bell-shaped curve would probably result, with a few small and large peas and most clustered around the average size. Around two-thirds of all measurements fall in the range spanned by the standard deviation, a measure of the spread.
supercritical fluid → superkritični fluid
Supercritical fluid is any substance above its critical temperature and critical pressure (see phase diagram). It shows unique properties that are different from those of either gases or liquids under standard conditions. A supercritical fluid has both the gaseous property of being able to penetrate anything, and the liquid property of being able to dissolve materials into their components. Solublity increases with increasing density (i.e. with increasing pressure). An example of this is naphthalene which is practically insoluble in low pressure carbon dioxide. At 100 bar the solubility is 10 g/L and at 200 bar it is 50 g/L. Rapid expansion of supercritical solutions leads to precipitation of a finely divided solid.
velocity → brzina
If a point-like object moves so that its position vector changes from being ri to rf, than the displacement Δr of object is
If a point-like object undergoes a displacement, Δr, in time Δt, its average velocity, v is defined as
The instantaneous velocity, v, is obtained from the average velocity by shrinking the time interval Δt towards zero. The average velocity approaches a limiting value, which is the velocity of a given instant:
Velocity is a vector quantity. If we plot the path of a moving particle as a curve in a coordinate system, the instantaneous velocity is always tangent to that curve.
SI unit for velocity is m s-1.
Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation → Heyrovsky-Ilkovičeva jednadžba
The Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation describes the entire current-potential curve (polarographic wave) of a reversible redox system in polarography
where R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, F is the Faraday constant, n denotes the number of electrons taking part in the electrode reaction. E1/2 is a unique potential (for a given reaction and supporting electrolyte) termed the half-wave potential.
In order to obtain E1/2 from the above equation, we plot a graph of ln[(id-i)/i] against E. The intercept on the x-axis gives then an accurate value of E1/2. The slope of the obtained straight line is equal to nF/RT from which n is determined.
Chitosan → Kitozan
Chitosan is a linear polysaccharide composed of randomly distributed N-acetyl D-glucosamine and D-glucosamine units. It can be easily derived from partial deacetylation of natural polymer chitin. At a minimum deacetylization level of 60 % (amount of free amino groups in the polymer) it is considered to be chitosan. Thanks to the amino groups of D-glucosamine, chitosan can be protonated and turned into polycation, which is one of the sources of unique properties of chitosan as biopolymer, like aqueous solubility, antibacterial properties, biodegradability with non-toxic residues and biocompatibility.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Krivulja topljivosti." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table