critical point → kritična točka
In general, critical point is the point on the phase diagram of a two-phase system at which the two coexisting phases have identical properties and therefore represent a single phase. At the liquid-gas critical point of a pure substance, the distinction between liquid and gas vanishes, and the vapour pressure curve ends. The coordinates of this point are called the critical temperature and critical pressure. Above the critical temperature it is not possible to liquefy the substance.
EDTA → EDTA
Ethyldiaminetetraacetic acid (C10H16N2O8) or shortened EDTA is a hexadentant ligand, and it forms chelates with both transition-metal ions and main-group ions. EDTA is used as a negative ion - EDTA4-. The diagram shows the structure of the ion with the important atoms picked out. The EDTA ion entirely wraps up a metal ion using all 6 of the positions. The co-ordination number is again 6 because of the 6 co-ordinate bonds being formed by the central metal ion.
EDTA is frequently used in soaps and detergents, because it forms a complexes with calcium and magnesium ions. These ions are in hard water and interfere with the cleaning action of soaps and detergents. EDTA is also used extensively as a stabilizing agent in the food industry and as an anticoagulant for stored blood in blood banks. EDTA is the most common reagent in complexometric titration.
electrode of the second kind → elektroda drugog reda
Electrodes of the second kind are metal electrodes assembly with the equilibrium potential being a function of the concentration of an anion in the solution. Typical examples are the silver/silver-chloride electrode and the calomel electrode. The potential of the metal is controlled by the concentration of its cation in the solution, but this, in turn, is controlled by the anion concentration in the solution through the solubility product of the slightly soluble metal salt. Contrast with electrode of the first kind and electrode of the third kind.
unsaturated solution → nezasićena otopina
Unsaturated solution is a solution that contains less than the maximum possible equilibrium concentration of a solute.
electrode of the third kind → elektroda trećeg reda
Electrode of the third kind is a metal electrode assembly with the equilibrium potential being a function of the concentration of a cation, other than the cation of the electrode metal, in the solution. The assembly consists of a metal in contact with two slightly soluble salts (one containing the cation of the solid metal, the other the cation to be determined, with both salts having a common anion) immersed in a solution containing a salt of the second metal (e.g., zinc metal--zinc oxalate--calcium oxalate--calcium salt solution). The potential of the metal is controlled by the concentration of its cation in the solution, but this is controlled by the anion concentration in the solution through the solubility product of the slightly soluble metal salt, which, in turn is controlled by the concentration of the cation of the second slightly soluble salt. These electrodes are very sluggish and unstable due to a series of equilibria to be established to produce a stable potential.
extraction → ekstrakcija
Extraction is the separation of a component from its mixture by selective solubility. When a solution of one substance in one solvent is brought in with another solvent dissolved substance will distribute between the two solutants because of different solubility. Extraction is an efficient and fast method used for separating and concentrating matters. Extraction is best done several times in a succession, with smaller amount of solvent in it the matter is better dissolved. For example, caffeine can be separated from coffee beans by washing the beans with supercritical fluid carbon dioxide; the caffeine dissolves in the carbon dioxide, but flavour compounds do not. Vanillin can be extracted from vanilla beans by shaking the beans with an organic solvent, like ethanol.
fatty acid → masna kiselina
Fatty acids are aliphatic monocarboxylic acids characterized by a terminal carboxyl group (R-COOH). The higher members of this series of acids occur in nature in the combined form of esters of glycerol (fats), and hence all acids of this family are called fatty acids. Natural fatty acids commonly have a chain of 4 to 28 carbons (usually unbranched and even-numbered), which may be saturated or unsaturated. The most important of saturated fatty acids are butyric (C4), lauric (C12), palmitic (C16), and stearic (C18). The most common unsaturated acids are oleic, linoleic, and linolenic (all C18).
The physical properties of fatty acids are determined by the chain length, degree of unsaturation, and chain branching. Short-chain acids are pungent liquids, soluble in water. As the chain length increases, melting points are raised and water-solubility decreases. Unsaturation and chain branching tend to lower melting points.
glutamic acid → glutaminska kiselina
Glutamic acid is an electrically charged amino acids. It is one of the two amino acids that contain a carboxylic acid group in its side chains. These acids play important roles as general acids in enzyme active centers, as well as in maintaining the solubility and ionic character of proteins. Glutamic acid is commonly referred to as glutamate, because its carboxylic acid side chain will be deprotonated and thus negatively charged in its anionic form at physiological pH. Glutamic acid is referred to as a non-essential amino acid because a healthy human can synthesize all the glutamic acid needed for normal body function from other amino acids.
- Abbreviations: Glu, E
- IUPAC name: 2-aminopentanedioic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H9NO4
- Molecular weight: 147.13 g/mol
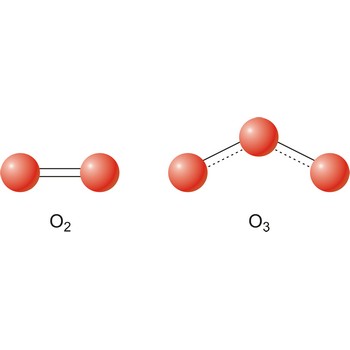
oxygen → kisik
Oxygen was discovered by Joseph Priestley (England) in 1774. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words oxy genes meaning acid and forming (acid former). It is colourless, odourless gas; pale blue liquid. Extremely reactive. Forms oxides with nearly all other elements except noble gases. It is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust and makes up almost 21 % of the atmosphere. Oxygen is obtained primarily from liquid air by fractional distillation. Small amounts are made in the laboratory by electrolysis of water. Used in steel making, welding and supporting life. Naturally occurring ozone (O3) in the upper atmosphere shields the earth from ultraviolet radiation.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Krivulja topljivosti." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table