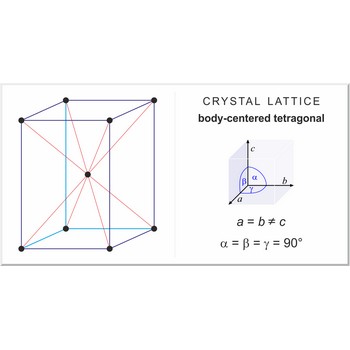
body-centered tetragonal lattice → prostorno centrirana tetragonska rešetka
Body-centered tetragonal lattice (tetragonal-I), like all lattices, has lattice points at the eight corners of the unit cell plus an additional points at the center of the cell. It has unit cell vectors a=b≠c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
Born-Haber cycle → Born-Haberov kružni proces
Born-Haber cycle is a cycle of reactions used for calculating the lattice energies of ionic crystalline solids. For a compound MX, the lattice energy is the enthalpy of the reaction
The standard enthalpy of formation of the ionic solid is the enthalpy of the reaction
The cycle involves equating this enthalpy (which can be measured) to the sum of the enthalpies of a number of steps proceeding from the elements to the ionic solid. The steps are:
1) Atomization of the metal
2) Atomization of the nonmetal
3) Ionisation of the metal
This is obtained from the ionisation potential.
4) Ionisation of the nonmetal
This is electron affinity.
5) Formation of the ionic solids
Equation of the enthalpies gives
from which ΔHL can be found.
carbonization → karbonizacija
Carbonization begins when you heat organic substances like wood, sugar or meat with no presence of air; they go black because of secreted carbon.
cementation → cementacija
Cementation is any metallurgical process in which the surfaces of a metal is impregnated by some other substance, especially an obsolete process for making steel by heating bars of wrought iron to red heat for several days in a bed of charcoal.
chemical → kemikalija
Chemicals are a common name for all chemical products or substances prepared by means of chemical-technologic processes.
chemical compound → kemijski spoj
Some substance is a compound only if it can be decomposed into two or more different substances by means of a chemical reaction. If two or more substances react, thus creating a new substance, that new substance is called a chemical compound.
chemical element → kemijski element
Chemical element is a type of matter of which elementary matter is composed. Chemical element is composed of atoms with the same core charge.
boron → bor
Boron compounds have been known for thousands of years, but the element was not discovered until 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy (England) and independently by Joseph-Louis Gay-Lussac (France) and L. J. Thenard (France). The origin of the name comes from the Arabic word buraq and the Persian word burah meaning boraks. It is hard, brittle, lustrous black semimetal. Unreactive with oxygen, water, alkalis or acids. Combines with most metals to form borides. Boron is obtained from kernite, a kind of borax (Na2B4O7·10H2O). High purity boron is produced by electrolysis of molten potassium fluroborate and potassium chloride (KCl). Amorphous boron is used in pyrotechnic flares to provide a distinctive green color and in rockets as an igniter.
Bragg angle → Braggov kut
Bragg angle (Θ) is the angle between an incident X-ray beam and a set of crystal planes for which the secondary radiation displays maximum intensity as a result of constructive interference. British physicist Sir William Henry Bragg and his son Sir William Lawrence Bragg developed a simple relation for scattering angles, now call Bragg’s law.
which relates the angle θ between a crystal plane and the diffracted X-ray beam, the wavelength λ of the x-rays, the crystal plane spacing d, and the diffraction order n (any integer).
The diffraction experiment as presently considered is intended to provide quantitative information on the lattice constant and shape characteristics of the unit cell.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kristalna tvar." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table