activated complex → aktivirani kompleks
Activated complex is an intermediate structure formed in the conversion of reactants to products. The activated complex is the structure at the maximum energy point along the reaction path; the activation energy is the difference between the energies of the activated complex and the reactants.
complexometry → kompleksometrija
Complexometry is a volumetric analytic method which is based on titration of metal ion solutions with a substance that, combined with metal ions yields complex compounds, e.g. EDTA. The stoichiometric ratio of EDTA-metal in complexometric analyses is always 1:1, whatever the valency of the metal
aluminate → aluminat
Aluminate is a salt formed when aluminium hydroxide or y-alumina is dissolved in solutions of strong bases, such as sodium hydroxide. Aluminates exist in solutions containing the aluminate ion, commonly written [Al(OH)4]-. In fact the ion probably is a complex hydrated ion and can be regarded as formed from a hydrated Al3+ ion by removal of four hydrogen ions:
Other aluminates and polyaluminates, such as [Al(OH)6]3- and [(HO)3AlOAl(OH)3]2-, are also present.
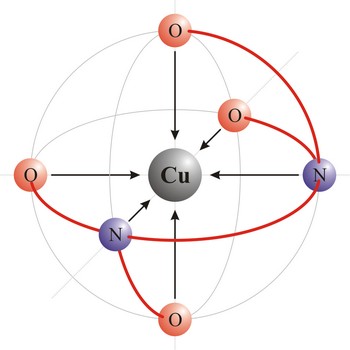
chelate → kelat
Chelate is a compound characterized by the presence of bonds from two or more bonding sites within the same ligand to a central metal atom. For example, copper complexes with EDTA to form a chelate. Chelate complexes are more stable than complexes with the corresponding monodentate ligands.
chelating agent → kelatni agens
Chelating agent is ligand that binds to a metal using more than one atom; a polydentate ligand.
cyanide process → cijanidni postupak
Cyanide process is a method for separating a metal from an ore. Crushed ore is treated with cyanide ion to produce a soluble metal cyanide complex. The complex is washed out of the ore and reduced to metallic form using an active metal (usually zinc).
ionophore → ionofore
Ionophore is a relatively small hydrophobic molecule that facilitates the transport of ions across lipid membranes. Most ionophores are produced by microorganisms. There are two types of ionophores: channel formers, which combine to form a channel in the membrane through which ions can flow; and mobile ion carriers, which transport ions across a membrane by forming a complex with the ion.
ligand field theory → teorija ligandnog polja
Ligand field theory is a description of the structure of crystals containing a transition metal ion surrounded by nonmetallic ions (ligands). It is based on the construction of molecular orbitals involving the d-orbitals of the central metal ion and combinations of atomic orbitals of the ligands.
monodentate ligand → monodentantni ligand
Monodentate ligand is a ligand that has only one atom that coordinates directly to the central atom in a complex. For example, ammonia and chloride ion are monodentate ligands of copper in the complexes [Cu(NH3)6]2+ and [CuCl6]2+.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kompleks." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table