Acheson process → Achesonov proces
Acheson process is an industrial process to synthesize graphite and silicon carbide (carborundum), named after its inventor the American chemist Edward Goodrich Acheson (1856-1931). In this process, a solid-state reaction between pure silica sand (SiO2) and petroleum coke (C) at very high temperature (more than 2500 °C) leads to the formation of silicon carbide under the general reaction:
While studying the effects of high temperature on carborundum, Acheson had found that silicon vaporizes at about 4150 °C, leaving behind graphitic carbon.
activated charcoal → aktivni ugljen
Activated charcoal or activated carbon is charcoal that has been activated for adsorption by steaming or by heating in a vacuum. Charcoal is obtained by burning wood, nutshells, coconut husks or other materials. Charcoal becomes activated by heating it with steam to approximately 1000 °C in the absence of oxygen.
The chemical nature of amorphous carbon, combined with a high surface area makes it an ideal medium for the adsorption of organic chemicals. A single gram of such material can have 400 m2 to 1 200 m2 square meters of surface area. Activated charcoal is widely used to decolorize liquids, recover solvents, and remove toxins from water and air.
alkaloid → alkaloid
Alkaloids are basic nitrogen organic compounds (mostly heterocyclic) derived from plants and having diverse pharmacological properties. Alkaloids include morphine, cocaine, atropine, quinine, and caffeine, most of which are used in medicine as analgesics or anaesthetics. Some alkaloids are poisonous, e.g. strychnine and coniine, and colchicine inhibit cell division.
blast furnace → visoka peć
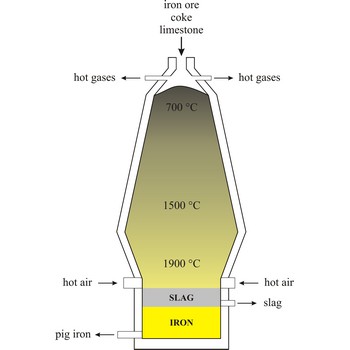
Blast furnace is a furnace for smelting of iron from iron oxide ores (hematite, Fe2O3 or magnetite, Fe3O4). Coke, limestone and iron ore are poured in the top, which would normally burn only on the surface. The hot air blast to the furnace burns the coke and maintains the very high temperatures that are needed to reduce the ore to iron. The reaction between air and the fuel generates carbon monoxide. This gas reduces the iron(III) oxide in the ore to iron.
Because the furnace temperature is in the region of 1500 °C, the metal is produced in a molten state and this runs down to the base of the furnace.
The production of iron in a blast furnace is a continuous process. The furnace is heated constantly and is re-charged with raw materials from the top while it is being tapped from the bottom. Iron making in the furnace usually continues for about ten years before the furnace linings have to be renewed.
coal gas → ugljeni plin
Coal gas is a gas produced by the destructive distillation of coal, and contains approximately 50 % hydrogen, 35 % methane and 8 % carbon monoxide. The by-products of the production of coal gas are coal tar and coke.
pit coal → kameni ugljen
Pit coal is natural black coal that has a carbon content of 75 %-90 %. It is an important raw material in organic industry
carbon → ugljik
Carbon has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word carbo meaning charcoal. Graphite form of carbon is a black, odourless, slippery solid. Graphite sublimes at 3825 °C. Diamond form is a clear or colored; an extremely hard solid. C60 is Buckminsterfullerine. Carbon black burns readily with oxidants. Carbon is made by burning organic compounds with insufficient oxygen. There are close to ten million known carbon compounds, many thousands of which are vital to organic and life processes. Radiocarbon dating uses the carbon-14 isotope to date old objects.
graphite → grafit
Graphite is an allotrope of carbon. The atoms are arranged in layers as a series of flat, hexagonal rings. Graphite is a good conductor of heat and electricity. The layers cleave easily, making graphite useful as a solid lubricant. A process to make pure synthetic graphite was invented by the American chemist Edward Goodrich Acheson (1856–1931). The process consists of heating a mixture of clay (aluminum silicate) and powdered coke (carbon) in an iron bowl. The reaction involves the production of silicon carbide, which loses silicon at 4150 °C to leave graphite.
hydrogen → vodik
Hydrogen was discovered by Sir Henry Cavendish (England) in 1766. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words hydro and genes meaning water and generate. It is colourless, odourless gas, burns and forms explosive mixtures in air. Reacts violently with oxidants. Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. Commercial quantities of hydrogen are produced by reacting superheated steam with methane or carbon. In lab work from reaction of metals with acid solutions or electrolysis. Most hydrogen is used in the production of ammonia and in metal refining. Also used as fuel in rockets. Its two heavier isotopes (deuterium and tritium) used respectively for nuclear fusion.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Koks." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table