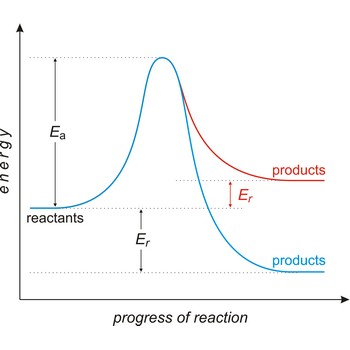
activation energy → energija aktivacije
Activation energy (Ea) is the energy that must be added to a system in order for a process to occur, even though the process may already be thermodynamically possible. In chemical kinetics, the activation energy is the height of the potential barrier separating the products and reactants. It determines the temperature dependence on the reaction rate.
adenosine triphosphate → adenozin trifosfat
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is nucleotide that is of fundamental importance as a carrier of chemical energy in all living organisms. It consists of adenin linked to D-ribose).
Allihn condenser → Allihnovo hladilo
Allihn condenser or bulb condenser consists of an outer water jacket and the inner glass tube with a series of spherical bubbles to maximize the thermal contact with the cooling water. It is named after its inventor, the German chemist Felix Richard Allihn (1854-1915).
allotrope → alotrop
Allotropes are the elements which exist in two or more different forms in the same physical state. Allotropes generally differ in physical properties and may also differ in chemical activity.
Diamond, graphite and fullerenes are three allotropes of the element carbon. Graphite is a soft, black, slippery substance; by contrast, diamond is one of the hardest substances known. The different properties of the allotropes arise from their chemical structures. Diamonds typically crystallize in the cubic crystal system and consist of tetrahedrally bonded carbon atoms. Graphite crystallizes in the hexagonal system. In the fullerenes, the carbon atoms taking the form of a hollow sphere, ellipsoid, or tube.
In some cases, the allotropes are stable over a temperature range, with a definite transition point at which one changes into the other. For instance, tin has two allotropes: white (metallic) tin stable above 13.2 °C and grey (nonmetallic) tin stable below 13.2 °C.
The term allotropes may also be used to refer to the molecular forms of an element. Ozone is a chemically active triatomic allotrope of the element oxygen.
allotropy → alotropija
Allotropy (Gr. allos, other, and tropos, manner) is the phenomenon of an element existing in two or more physical forms in the same physical state. The difference between the forms involves either crystaline structure (white, red and black phosphorus), the number of atoms in the molecule of a gas (diatomic oxygen and triatomic ozone), or the molecular structure of a liquid (liquid helium an helium II).
In some cases, the allotropes are stable over a temperature range, with a definite transition point at which one changes into the other. For instance, tin has two allotropes: white (metallic) tin stable above 13.2 °C and grey (nonmetallic) tin stable below 13.2 °C. This form allotropy is called enantiotropy. Form of allotropy, in which there is no transition temperature at which the two are in equilibrium, is called monotropy.
Allotropy does not apply to the substance existing in different physical states as, for example, when ice melts and changes from solid ice to liquid water.
Allotropy is generally restricted to describing polymorphic behaviour in elements, while polymorphism may refer to any material having multiple crystal structures.
amount concentration → količinska koncentracija
Amount concentration (also called molar concentration and in older literature molarity) is the amount of a given substance in a stated unit of a mixture, solution, or ore. The common unit is mole per cubic decimetre (moldm−3) or mole per litre (molL-1) sometimes denoted by M.
The concentration of an atom, ion, or molecule in a solution may be symbolised by the use of square brackets, as [Ca2+].
argon → argon
Argon was discovered by Lord Raleigh and Sir William Ramsay (Scotland) in 1894. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word argos meaning inactive. It is colourless and odourless noble gas. Chemically inert. It is the third most abundant element in the earth’s atmosphere and makes up about 1 %. Argon is continuously released into the air by decay of radioactive potassium-40. Pure form is obtained from fractional distillation of liquid air. Used in lighting products. It is often used in filling incandescent light bulbs. Some is mixed with krypton in fluorescent lamps. Crystals in the semiconductor industry are grown in argon atmospheres.
chemical → kemikalija
Chemicals are a common name for all chemical products or substances prepared by means of chemical-technologic processes.
aromatic compounds → aromatski ugljikovodici
Aromatic compounds are a major group of unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons containing one or more rings, typified by benzene, which has a 6-carbon ring containing three double bonds. All the bonds in benzene (C6H6) are the same length intermediate between double and single C-C bonds. The properties arise because the electrons in the p-orbitals are delocalised over the ring, giving extra stabilization energy of 150 kJ/mol over the energy of Kekulé structure. Aromatic compounds are unsaturated compounds, yet they do not easily partake in addition reactions.
Historical use of the term implies a ring containing only carbon (e.g., benzene, naphthalene), but it is often generalized to include heterocyclic structures such as pyridine and thiophene.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kemijsko staklo." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table