carbonyl group → karbonilna skupina
Carbonyl group is a functional group common to all ketones and aldehydes.
carboxylate group → karboksilna skupina
Carboxylate group (-COOH) is a functional group which is common to all carboxylic acids.
glycosyl group → glikozidna skupina
The structure obtained by removing the hydroxy group from the hemiacetal function of a monosaccharide.
groups in periodic system of elements → skupine periodnog sustava
Periodic system of elements is divided into 18 groups of chemical elements. Elements belonging to the same group have a same number of valence electrons and similar chemical properties. Elements of main groups are in 1., 2., and in groups 13. to 18. Different groups of elements can be named according to the first element in the group (elements of boron group, elements of carbon group), or they have some special names (noble gases, halogenic elements, halyde elements, earthalkali and alkali metals).
acetal → acetal
Acetals are organic compounds having the structure R2C(OR’)2 (R’ ≠ H). They are organic compounds formed by addition of alcohol molecules to aldehyde or ketone molecules. Originally, the term was confined to derivatives of aldehydes (one R = H), but it now applies equally to derivatives of ketones (neither R = H ). Mixed acetals have different R’ groups. The formation of acetals is reversible; acetals can be hydrolysed back to aldehydes (ketone) in acidic solutions.
Acetal, 1,1-diethoxyethane (CH3CH(OC2H5)2), is an organic compound, pleasant smelling, formed by addition of ethyl alcohol to ethanal (acetaldehyde). It is used as a solvent and in synthetic organic chemistry.
glucose → glukoza
Glucose (grape sugar, blood sugar), C6H12O6, is an aldohexose (a monosaccharide sugar having six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group). An older common name for glucose is dextrose, after its dextrorotatory property of rotating plane polarized light to the right. Glucose in free (in sweet fruits and honey) or combined form (sucrose, starch, cellulose, glycogen) is is probably the most abundant organic compound in nature. During the photosynthesis process, plants use energy from the sun, water from the soil and carbon dioxide gas from the air to make glucose. In cellular respiration, glucose is ultimately broken down to yield carbon dioxide and water, and the energy from this process is stored as ATP molecules (36 molecules of ATP across all processes).
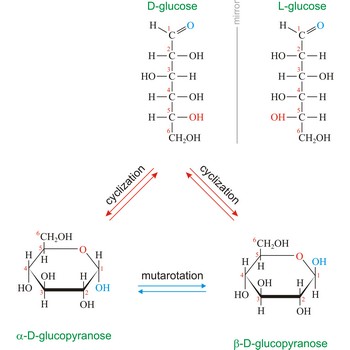
Naturally occurring glucose is D isomers (OH group on the stereogenic carbon farthest from the aldehyde group, C-5, is to the right in the Fischer projection). Although often displayed as an open chain structure, glucose and most common sugars exist as ring structures. In the α form, the hydroxyl group attached to C-1 and the CH2OH attached to C-5 are located on opposite sides of the ring. β-glucose has these two groups on the same side of the ring. The full names for these two anomers of glucose are α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-glucopyranose.
hemiacetal → poluacetal
Hemiacetals are organic compounds having the general formula R2C(OH)OR’ (R’ ≠ H), derived from aldehydes or ketones by formal addition of an alcohol to the carbonyl group. Hemiacetals are generally unstable compounds. In some cases however, stable cyclic hemiacetals can be readily formed, especially when 5- and 6-membered rings are possible. In this case an intramolecular OH group reacts with the carbonyl group. Glucose and many other aldoses exist as cyclic hemiacetals whereas fructose and similar ketoses exist as cyclic hemiketals. Originally, the term was confined to derivatives of aldehydes (one R = H), but it now applies equally to derivatives of ketones (neither R = H).
monosaccharide → monosaharid
Monosaccharides are carbohydrates, with the general formula Cn(H2O)n, that cannot be decomposed to a simpler carbohydrates by hydrolysis.
Depending on whether the molecule contains an aldehyde group (-CHO) or a ketone group (-CO-) monosaccharide can be a polyhydroxy aldehyde (aldose) or a polyhydroxy ketone (ketose). These aldehyde and ketone groups confer reduction properties on monosaccharides. They are also classified according to the number of carbon atoms they contain: trioses have three carbon atoms, tetroses four, pentoses five, hexoses six, heptoses seven, etc. These two systems of classification are often combined. For example, a six-carbon polyhydroxy aldehyde such as D-glucose is an aldohexose, whereas a six-carbon polyhydroxy ketone such as D-fructose is a ketohexose.
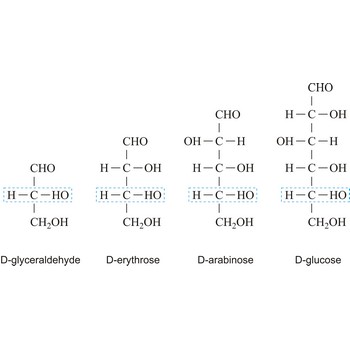
The notations D and L are used to describe the configurations of carbohydrates. In Fischer projections of monosaccharides, the carbonyl group is always placed on top (in the case of aldoses) or as close to the top as possible (in the case of ketoses). If the OH group attached to the bottom-most asymmetric carbon (the carbon that is second from the bottom) is on the right, then the compound is a D-sugar. If the OH group is on the left, then the compound is an L-sugar. Almost all sugars found in nature are D-sugars.
Monosaccharides can exist as either straight-chain or ring-shaped molecules. During the conversion from straight-chain form to cyclic form, the carbon atom containing the carbonyl oxygen, called the anomeric carbon, becomes a chiral center with two possible configurations (anomers), α and β. When the stereochemistry of the first carbon matches the stereochemistry of the last stereogenic center the sugar is the α-anomer when they are opposite the sugar is the β-anomer.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Karbonilna skupina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table