ruthenium → rutenij
Ruthenium was discovered by Karl Karlovich Klaus (Russia) in 1844. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word Ruthenia meaning Russia. It is rare, extremely brittle, silver-grey metal. Unaffected by air, water or acids. Reacts with very hot (molten) alkalis. Ruthenium is found in pentlandite and pyroxinite. Used to harden platinum and palladium. Aircraft magnetos use platinum alloy with 10 % ruthenium.
scandium → skandij
Scandium was discovered by Lars Fredrik Nilson (Sweden) in 1879. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word Scandia meaning Scandinavia. It is fairly soft, silvery-white metal. Burns easily. Tarnishes readily in air. Reaction with water releases hydrogen. Reacts with air and halogens. Scandium occurs mainly in the minerals thortveitile (~34 % scandium) and wiikite. Also in some tin and tungsten ores. Pure scandium is obtained as a by-product of uranium refining. Scandium metal is used in some aerospace applications. Scandium oxide (Sc2O2) is used in the manufacture of high-intensity electric lamps. Scandium iodide (ScI3) is used in lamps that produce light having a colour closely matching natural sunlight.
semiconductor → poluvodič
Semiconductor is a material in which the highest occupied energy band (valence band) is completely filled with electrons at T = 0 K, and the energy gap to the next highest band (conduction band) ranges from 0 to 4 or 5 eV. With increasing temperature electrons are excited into the conduction band, leading to an increase in the electrical conductivity.
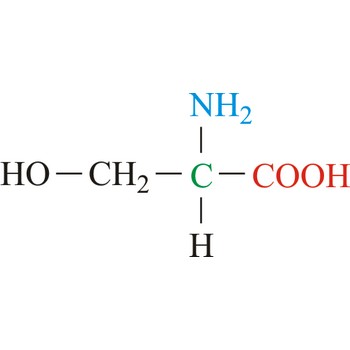
serine → serin
Serine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It is one of two hydroxyl amino acids. Both are commonly considered to by hydrophilic due to the hydrogen bonding capacity of the hydroxyl group. Serine often serves as a nucleophile in many enzyme active sites, and is best known for its role in the serine proteases. Serine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine.
- Abbreviations: Ser, S
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO3
- Molecular weight: 105.09 g/mol
square pyramidal molecular geometry → kvadratna piramidalna geometrija molekule
Square pyramidal is a molecular shape that results when there are five bonds and one lone pair on the central atom in the molecule. Bromine pentafluoride (BrF5) has the geometry of a square pyramid, with fluorine atoms occupying five vertices, one of which is above the plane of the other four. This molecule is made up of six equally spaced sp3d2 (or d2sp3) hybrid orbitals arranged at 90° angles. The shape of the orbitals is octahedral. Because of the high symmetry of the octahedral arrangement, all six positions are equivalent, so it does not matter in which position in the drawing we put the lone pair. The remaining four atoms connected to the central atom give the molecule a square planar shape.
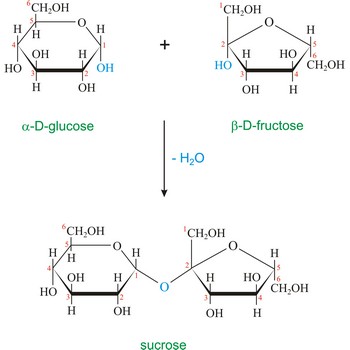
sucrose → saharoza
Sucrose (saccharose), or ordinary table sugar, is a disaccharide in which α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-fructofuranose are joined at their anomeric carbons by a glycosidic bond. There are no hemiacetals remaining in the sucrose and therefore sucrose is not a reducing sugar and does not exhibit mutarotation. Sugar is a white crystalline sweet compound found in many plants and extracted from sugar cane and sugar beet. It is used as a sweetening agent in food and drinks. If heated to 200 °C, sucrose becomes caramel. When sucrose is hydrolyzed it forms an equimolar mixture of glucose and fructose. This mixture of monosaccharides is called invert sugar. Honeybees have enzymes called invertases that catalyze the hydrolysis of sucrose. Honey, in fact, is primarily a mixture of glucose, fructose, and sucrose.
sugar → šećer
Sugar is any of a group of water-soluble carbohydrates of relatively low molecular weight and typically having a sweet taste. The group comprises mainly monosaccharides (glucose, fructose, galactose), disaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose), and trisaccharides (raffinose). Many monosaccharides and disaccharides fairly commonly found in nature bear names reflecting the source from which they were first isolated. For example, glucose is also known as grape sugar, lactose as milk sugar, and maltose as malt sugar. In everyday usage, the name is often used to refer specifically to sucrose (table sugar, cane sugar, beet sugar).
supercritical fluid chromatography → superkritična fluidna kromatografija
Supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) is a hybrid of gas and liquid chromatography. SFC is of importance because it permits the separation and determination of a group of compounds that are not conveniently handled by either gas or liquid chromatography. These compounds are either nonvolatile or thermally labile so that gas chromatography cannot be used and they do not contain functional groups that make possible detection by liquid chromatography. SFC has been applied to a wide variety of materials including natural prodcuts, drugs, foods, pesticides and herbicides, fossil fuels, explosives and propellants.
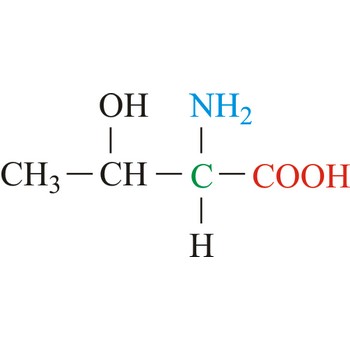
threonine → treonin
Threonine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It differs from serine by having a methyl substituent in place of one of the hydrogens on the β carbon. Threonine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Thr, T
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H9NO3
- Molecular weight: 119.12 g/mol
transition metal → prijelazni element
This group of metals is distinguished from other metals not by their physical properties, but by their electronic structure. Transition metals are elements characterized by a partially filled d subshell. The First Transition Series comprises scandium (Sc), titanium (Ti), vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni) and copper (Cu). The Second and Third Transition Series include the lanthanides and actinides, respectively.
The transition metals are noted for their variability in oxidation state. Thus, manganese has two electrons in its outside shell and five electrons in the next shell down, and exhibits oxidation states of +1, +2, +3, +4, +5, +6, and +7.
They are also characterised by the fact that well into the series, going from left to right, the properties of the succeeding metals do not differ greatly from the preceding ones.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Karboksilna skupina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table