bathymetry → batimetrija
Bathymetry (from the Greek word bathus, deep) is the science of measuring the depths of the oceans, seas, lakes, etc. or the topographic maps of the sea floor that result from such measurements. Bathymetric charts are designed to present accurate, measurable description and visual presentation of the submerged terrain.
benzene → benzen
Benzene is a colourless liquid hydrocarbon, C6H6, b.p. 80 °C. It is now made from petroleum by catalytic reforming (formerly obtained from coal tar). Benzene is the archetypal aromatic compound. It has an unsaturated molecule, yet will not readily undergo addition reactions. On the other hand, it does undergo substitution reactions in which hydrogen atoms are replaced by other atoms or groups.
In 1865, Friedrich August Kekulé purposed the benzene molecule structure as a hexagonal ring which consists of six carbon atoms with alternate carbon-carbon single and carbon-carbon double bond. But such a structure should be highly reactive, and so didn't account for the unreactive nature of benzene. We now know that the best representation for the structure of benzene is indeed, hexagonal, with each C-C bond distance being identical and intermediate between those for a single and double bond. The π-orbitals from each neighbouring carbon atom overlap to form a delocalised molecular orbital which extends around the ring, giving added stability and with it, decreased reactivity. That is the reason the structural formula of benzene represents as a hexagon with a circle in the center which represents the delocalized electrons.
carboxylic acids → karboksilne kiseline
Carboxylic acids are organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more RC(=O)OH groups (the carboxyl group). In the systematic chemical nomenclature carboxylic acids names end in the suffix -oic (e.g. ethanoic acids, CH3COOH). The carbon of the terminal group being counted as part of the chain. They are generally weak acids. Carboxylic acids include a large and important class of fatty acids and may be either saturated or unsaturated. There are also some natural aromatic carboxylic acids (benzoic, salicylic).
crystal → kristal
Crystal is a solid with a regular geometric shape, having a characteristic internal structure and enclosed by symmetrically arranged plane surfaces, intersecting at definite and characteristic angles. In crystals the particles (atoms, ions, or molecules) have a regular three-dimensional repeating arrangement in space. This is called the crystal structure. The crystal lattice is the arrangement of points in space at which the particles are positioned.
fluorescence → fluorescencija
Fluorescence is a luminescence phenomenon in which electron returns to it's ground state almost instantaneously (less than 10-8 second), and in which emission from a luminescent substance ceases when the exciting source is removed. Fluorescence is characterized by radiation emission in all directions.
hydrophilic → hidrofilan
Hydrophilic is having a strong tendency to bind or absorb water, which results in swelling and formation of reversible gels. This property is characteristic of carbohydrates.
hydrophobic → hidrofoban
Hydrophobic is antagonistic to water, incapable of dissolving in water. This property is characteristic of oils, fats, waxes, and many resins.
cellulose → celuloza
Cellulose, (C6H10O5)n, is a polysaccharide that consists of a long unbranched chain of glucose units linked by (1→4)-β-glycoside bonds. Nature uses cellulose primarily as a structural material to impart strength and rigidity to plants. Leaves, grasses, and cotton are primarily cellulose. The fibrous nature of extracted cellulose has led to its use in textile industry for the production of cotton, artificial silk, etc. Cellulose also serves as raw material for the manufacture of cellulose acetate, known commercially as acetate rayon, and cellulose nitrate, known as guncotton. Gunncotton is the major ingredient in smokeless powder, the explosive propellant used in artillery shells and in ammunition for firearms.
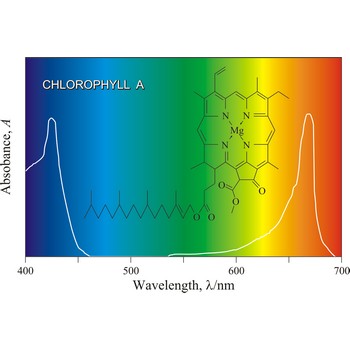
chlorophyll → klorofil
Chlorophyll is a green pigment present in green plants and cyanobacteria. Chlorophyll is essential in the transformation of light energy to chemical energy in photosynthesis. Chlorophyll absorbs light mostly in the blue and red ends of the visible spectrum, and very little in the green wavelengths. That green light is reflected, giving us the leaf colour we see.
colloid → koloid
Colloids are systems in which there are two or more phases, with one (the dispersed phase) distributed in the other (the continuous phase). Moreover, at least one of the phases has small dimensions, in the range between 1 nm and 1 μm (10-9 m – 10-6 m). Dimension, rather than the nature of the material, is characteristic. In this size range, the surface area of the particle is large with respect to its volume so that unusual phenomena occur, e.g., the particles do not settle out of the suspension by gravity and are small enough to pass through filter membranes. Macromolecules (proteins and other high polymers) are at the lower limit of this range; the upper limit is usually taken to be the point at which the particles can be resolved in an optical microscope.
Colloidal particles may be gaseous, liquid, or solid, and occur in various types of suspensions:
Sols - dispersions of small solid particles in a liquid.
Emulsions - colloidal systems in which the dispersed and continuous phases are both liquids.
Gels - colloids in which both dispersed and continuous phases have a three-dimensional network throughout the material.
Aerosols - colloidal dispersions of liquid or solid particles in a gas.
Foams - dispersions of gases in liquids or solids.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Karat." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table