electroplating → galvaniziranje
Electroplating (also called electrodeposition) is the deposition of a metallic coating onto an object by putting a negative charge onto the object and immersing it into a solution which contains a salt of the metal to be deposited. The metallic ions of the salt carry a positive charge and are attracted to the part. When they reach it, the negatively charged part provides the electrons to reduce the positively charged ions to metallic form.
Typically, a brass or nickel object is coated with a layer of silver by making use of electrolysis of a silver solution, using the object to be coated as the cathode. The anode consist of pure silver, and the cathode is the object to be plated. The electrolyte is a mixure of silver nitrate with potassium cyanide. The reactions are:
The cyanide ensures a low concentration of silver ions, a condition for providing the best plating results.
white light → bijela svjetlost
White light is a mixture of lights of all colours. If white light is passed through a glass prism or an optical lattice, it is separated into several colours (the visible light spectrum).
erbium → erbij
Erbium was discovered by Carl Gustaf Mosander (Sweden) in 1843. Named after Ytterby, a village in Sweden. It is soft, malleable, silvery metal. Reacts slowly with water. Dissolves in acids. Metal ignites and burns readily. Erbium is found with other heavier rare earths in xenotime and euxenite. Erbium oxide is used in ceramics to obtain a pink glaze. Also a few uses in the nuclear industry and as an alloying agent for other exotic metals.
Erlenmeyer flask → Erlenmeyerova tikvica
Erlenmeyer flask is a glass container which has a narrow, cylindrical mouth and a cone-shaped main body that ends in a wide, flat bottom. It was named after its inventor, a German chemist Richard Erlenmeyer (1825-1909). Erlenmeyer flasks are most often used in titrations to hold the liquid that is being titrated.
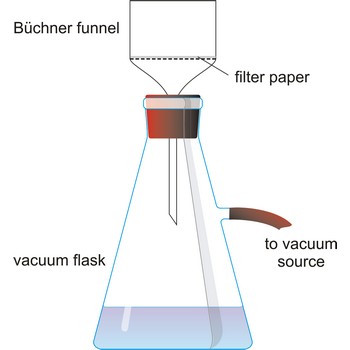
filter flask → boca za odsisavanje
Filter flask, also known as a vacuum flask, is a flask with a side arm to which a vacuum can be applied. It usually have heavy side walls to withstand high vacuum.
fume hood → digestor
Fume hood is a type of local exhaust ventilation system (engineering control). A typical fume hood is cabinet with a moveable front sash (window) made out of safety glass. Air is drawn into the hood under and through the opened sash and is exhausted through openings in the rear and top of the cabinet to a remote point such as an exhaust stack on the roof of the building. A properly used and properly functioning fume hood exhausts hazardous gases, dusts, mists, and vapors from a confined location and helps protect workers from inhalation exposure.
gas washing bottle → boca ispiralica
Gas washing bottle or Drechsel bottle provide an inexpensive but effective method for washing or drying gases. The gas enters the bottle through the top of the central vertical tube, the lower end of which is below the surface of the washing medium. To maximize surface area contact of the gas to the liquid, a gas stream is slowly blown into the vessel through the fritted glass tip so that it breaks up the gas into many tiny bubbles. After bubbling through the medium, the gas rises to the top and exits through the side tube. It is named after the German chemist Edmund Drechsel (1843-1897).
germanium → germanij
Germanium was discovered by Clemens Winkler (Germany) in 1886. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word Germania meaning Germany. It is greyish-white semi-metal. Unaffected by alkalis and most (except nitric) acids. Stable in air and water. Germanium is obtained from refining copper, zinc and lead. Widely used in semiconductors. It is a good semiconductor when combined with tiny amounts of phosphorus, arsenic, gallium and antimony.
global warming → globalno zatopljenje
Global warming or greenhouse effect is an effect occurring in the atmosphere because of the presence of certain gases (greenhouse gases) that absorb infrared radiation. Light and ultraviolet radiation from the sun is able to penetrate the atmosphere and warm the Earth’s surface. This energy is re-radiated as infrared radiation which because of its longer wavelength, is absorbed by such substances as carbon dioxide. The overall effect is that the average temperature of the Earth and its atmosphere is increasing (so-called global Warming). The effect is similar to that occurring in a greenhouse, where light and long-wavelength ultraviolet radiation can pass through the glass into greenhouse but the infrared radiation is absorbed by the glass and part of it is re-radiated into the greenhouse.
The greenhouse effect is seen as a major environmental hazard. Average increases in temperature could change weather patterns and agricultural output. It might also lead to melting of the polar ice caps and a corresponding rise in sea level. Carbon dioxide, from fossil-fuel power stations and car exhausts, is the main greenhouse gas. Other contributory pollutants are nitrogen oxides, ozone, methane, and chloroflourocarbons.
Kirchoff, Gustav → Kirchoff, Gustav
Gustav Kirchoff (1824-1887) was a German physicist who, with the chemist Robert Bunsen (1811-1899), laid the foundations of spectral analysis. He realized that the Fraunhofer lines in the Sun's spectrum were due to light from the photosphere being absorbed at those specific wavelengths by elements in the solar atmosphere. He also found that incandescent solids, liquids, and compressed gases emit a continuous spectrum. Use of the Bunsen burner in conjunction with a glass prism led to the development of the spectroscope in collaboration with the Bunsen and to the spectroscopic discovery of the elements rubidium (1860) and cesium (1861).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kalijevo staklo." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table