Geiger counter → Geigerov brojač
Geiger counter (Geiger-Muller counter) is a device used to detect and measure ionising radiation. It consists of a tube containing a low-pressure gas (usually argon or neon with methane) and a cylindrical hollow cathode through the centre of which runs a fine-wire anode. A potential difference of about 1 000 V is maintained between the electrodes. An ionising particle or photon passing through a window into the tube will cause an ion to be produced and the high potential will accelerate it towards its appropriate electrode, causing an avalanche of further ionisations by collision. The consequent current pulses can be counted in electronic circuits or simply amplified to work a small loudspeaker in the instrument. It was first devised in 1908 by the German physicist Hans Geiger (1882-1945). Geiger and W. Muller produced an improved design in 1928.
glucose → glukoza
Glucose (grape sugar, blood sugar), C6H12O6, is an aldohexose (a monosaccharide sugar having six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group). An older common name for glucose is dextrose, after its dextrorotatory property of rotating plane polarized light to the right. Glucose in free (in sweet fruits and honey) or combined form (sucrose, starch, cellulose, glycogen) is is probably the most abundant organic compound in nature. During the photosynthesis process, plants use energy from the sun, water from the soil and carbon dioxide gas from the air to make glucose. In cellular respiration, glucose is ultimately broken down to yield carbon dioxide and water, and the energy from this process is stored as ATP molecules (36 molecules of ATP across all processes).
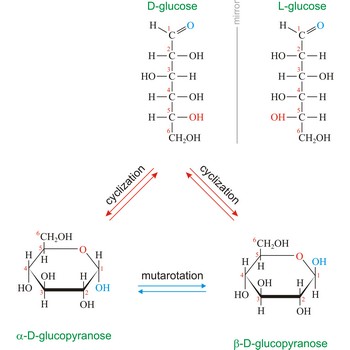
Naturally occurring glucose is D isomers (OH group on the stereogenic carbon farthest from the aldehyde group, C-5, is to the right in the Fischer projection). Although often displayed as an open chain structure, glucose and most common sugars exist as ring structures. In the α form, the hydroxyl group attached to C-1 and the CH2OH attached to C-5 are located on opposite sides of the ring. β-glucose has these two groups on the same side of the ring. The full names for these two anomers of glucose are α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-glucopyranose.
half-life → vrijeme poluraspada
For a simple radioactive decay process, half-life, t1/2, is defined as the time required for the activity of a given radioactive isotopes to decrease to half its value by that process.
The half-life is a characteristic property of each radioactive isotope and is independent of its amount or condition.
high fructose corn syrup → visoko fruktozni kukuruzni sirup
High fructose corn syrup (HFCS) is commonly used in place of sugar in foods and drinks. Corn starch is hydrolyzed to glucose, which is then treated with glucose isomerase to produce a fructose-rich mixture. HFCS is available in a number of forms, named according to the percentage of fructose they contain, HFCS-55 for instance contains 55 % fructose and 45 % glucose. The enhanced sweetness, low cost and ease of use are the main reasons why manufacturers now prefer to use high fructose corn syrup instead of sugar.
monosaccharide → monosaharid
Monosaccharides are carbohydrates, with the general formula Cn(H2O)n, that cannot be decomposed to a simpler carbohydrates by hydrolysis.
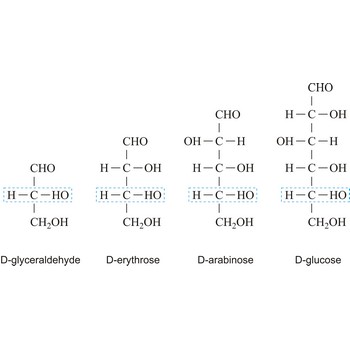
Depending on whether the molecule contains an aldehyde group (-CHO) or a ketone group (-CO-) monosaccharide can be a polyhydroxy aldehyde (aldose) or a polyhydroxy ketone (ketose). These aldehyde and ketone groups confer reduction properties on monosaccharides. They are also classified according to the number of carbon atoms they contain: trioses have three carbon atoms, tetroses four, pentoses five, hexoses six, heptoses seven, etc. These two systems of classification are often combined. For example, a six-carbon polyhydroxy aldehyde such as D-glucose is an aldohexose, whereas a six-carbon polyhydroxy ketone such as D-fructose is a ketohexose.
The notations D and L are used to describe the configurations of carbohydrates. In Fischer projections of monosaccharides, the carbonyl group is always placed on top (in the case of aldoses) or as close to the top as possible (in the case of ketoses). If the OH group attached to the bottom-most asymmetric carbon (the carbon that is second from the bottom) is on the right, then the compound is a D-sugar. If the OH group is on the left, then the compound is an L-sugar. Almost all sugars found in nature are D-sugars.
Monosaccharides can exist as either straight-chain or ring-shaped molecules. During the conversion from straight-chain form to cyclic form, the carbon atom containing the carbonyl oxygen, called the anomeric carbon, becomes a chiral center with two possible configurations (anomers), α and β. When the stereochemistry of the first carbon matches the stereochemistry of the last stereogenic center the sugar is the α-anomer when they are opposite the sugar is the β-anomer.
nerve poison → živčani bojni otrov
Nerve poison (nerve gas, agents) have had an entirely dominant role since the Second World War. Nerve poisons acquired their name because they affect the transmission of nerve impulses in the nervous system. All nerve poisons belong chemically to the group of organo-phosphorus compounds. They are stable and easily dispersed, highly toxic and have rapid effects both when absorbed through the skin and via respiration. Nerve poisons can be manufactured by means of fairly simple chemical techniques. The raw materials are inexpensive and generally readily available.
The most important nerve agents included in modern chemical weapons arsenals are:
| Tabun | (o-ethyl dimethylamidophosphorylcyanide) |
| Sarin | (isopropyl methylphosphonofluoridate) |
| Soman | (pinacolyl methylphosphonofluoridate) |
| GF | (cyclohexyl methylphosphonofluoridate) |
| VX | (o-ethyl S-diisopropylaminomethyl methylphosphonothiolate) |
Nerve poisons are colorless, odorless, tasteless liquids of low volatility. Antidotes are atropine sulfate and pralidoxime iodide.
organic → organski
1. Organic refers to any chemical compound based on carbon (C) with the exception of some of the simple compounds of carbon, such as carbon dioxide, which are frequently classified as inorganic compounds. Additional elements that are commonly found in organic compounds are hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), phosphorus (P) and sulfur (S).
2. Organic or organically-grown foods are grown or raised without synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, growth stimulators, or antibiotics and other drugs. Pests are controlled by cultivation techniques and the use of pesticides derived from natural sources and the use of natural fertilizers. In addition, organically grown foods must also be stored without the use of chemicals such as artificial additives and preservatives, and without food irradiation.
polysaccharide → polisaharid
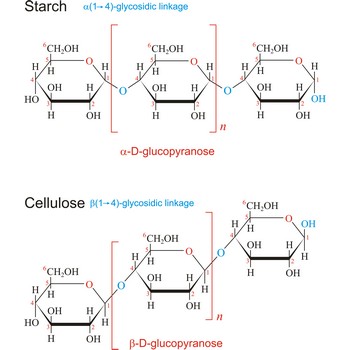
Polysaccharides are compounds consisting of a large number of simple sugars (monosaccharides) linked together by glycosidic bonds. When polysaccharides are composed of a single monosaccharide building block, they are termed homopolysaccharides. Heteropolysaccharides contain two or more different types of monosaccharide. Polysaccharides may have molecular weights of up to several million and are often highly branched. Since they have only the one free anomeric -OH group at the end of a very long chain, polysaccharides aren’t reducing sugars and don’t show noticeable mutarotation. The most common polysaccharides are cellulose, starch, and glycogen.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Jednostavna sol." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table