Born-Haber cycle → Born-Haberov kružni proces
Born-Haber cycle is a cycle of reactions used for calculating the lattice energies of ionic crystalline solids. For a compound MX, the lattice energy is the enthalpy of the reaction
The standard enthalpy of formation of the ionic solid is the enthalpy of the reaction
The cycle involves equating this enthalpy (which can be measured) to the sum of the enthalpies of a number of steps proceeding from the elements to the ionic solid. The steps are:
1) Atomization of the metal
2) Atomization of the nonmetal
3) Ionisation of the metal
This is obtained from the ionisation potential.
4) Ionisation of the nonmetal
This is electron affinity.
5) Formation of the ionic solids
Equation of the enthalpies gives
from which ΔHL can be found.
crystal water → kristalna voda
Crystal water is water contained in certain salt crystals. It can be removed by heating. Crystals that contain crystal water are called hydrated and their salts hydrates.
diffraction grating → difrakcijska rešetka
Diffraction grating is a series of slits used to separate an incident wave into its component wavelengths by directionally separating their diffraction maxima.
cubic crystal system → kubični kristalni sustav
Cubic crystal system is also known as the isometric system. The Isometric crystal system characterizes itself by its three equivalent crystallographic axes perpendicular to each other.
a = b = c
α = β = γ = 90°
crystal system → kristalni sustav
Crystal system is a method of classifying crystalline substances on the basis of their unit cell. There are seven unique crystal systems. The simplest and most symmetric, the cubic (or isometric) system, has the symmetry of a cube. The other six systems, in order of decreasing symmetry, are hexagonal, tetragonal, rhombohedral (also known as trigonal), orthorhombic, monoclinic and triclinic.
|
Crystal system
|
Unit-cell
|
Conditions on unit-cell edges and angles |
|
cubic |
 |
a=b=c α=β=γ=90° |
|
hexagonal |
 |
a≠c α=γ=90° β=120° |
|
tetragonal |
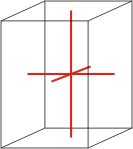 |
a=b≠c α=β=γ=90° |
|
rhombohedral |
 |
a=b=c α=β=γ≠90° |
|
orthorhombic |
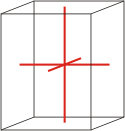 |
a≠b≠c α=β=γ=90° |
|
monoclinic |
 |
a≠b≠c α=γ=90°≠β |
|
triclinic |
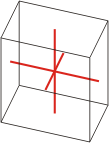 |
a≠b≠c α≠β≠γ≠90° |
law of conservation of energy → zakon o očuvanju energije
Law of conservation of energy: In an isolated system energy can be transferred from one form to another but the total energy of the system remains constant.
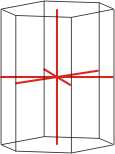
hexagonal crystal system → heksagonski kristalni sustav
Hexagonal crystal system is based on four crystallographic axes. The system of crystallographic axes of the hexagonal crystal system consists of three equivalent horizontal (equatorial) axes of which the positive ends make an angle of 120°. These axes are sometimes denoted as a, b and d axes. The fourth axis is (c) is perpendicular to and shorter or longer than the other three.
mass-energy equivalence → ekvivalencija mase i energije
In the special theory of relativity Einstein demonstrated that neither mass nor energy were conserved separately, but that they could be traded one for the other and only the total "mass-energy" was conserved. The relationship between the mass and the energy is contained in what is probably the most famous equation in science,
Where m is the mass of the object and c is the velocity of light. Cockcroft and Walton (1932) are routinely credited with the first experimental verification of mass-energy equivalence.
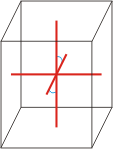
monoclinic crystal system → monoklinski kristalni sustav
Minerals of the monoclinic crystal system are referred to three unequal axes. Two of these axes (a and c) are inclined toward each other at an oblique angle; these are usually depicted vertically. The third axis (b) is perpendicular to the other two and is called the ortho axis. The two vertical axes therefore do not intersect one another at right angles, although both are perpendicular to the horizontal axis.
a ≠ b ≠ c
α = γ = 90° ≠ β
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Energija kristalne rešetke." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table



