carbohydrate → ugljikohidrat
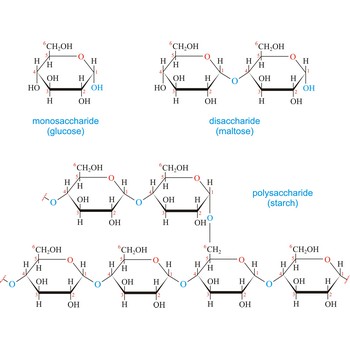
Carbohydrates (often called carbs for short) are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, or substances that yield such compounds on hydrolysis. They are also known as saccharides, a term derived from the Latin word saccharum for sugar. Carbohydrates are the most abundant class of compounds in the biological world, making up more than 50 % of the dry weight of the Earth’s biomass. Every type of food we eat can have its energy traced back to a plant. Plants use carbon dioxide and water to make glucose, a simple sugar, in photosynthesis. Other carbohydrates such as cellulose and starch are made from the glucose. Light from the sun is absorbed by chlorophyll and this is converted to the energy necessary to biosynthesize carbohydrates
The term carbohydrate was applied originally to monosaccharides, in recognition of the fact that their empirical composition can be expressed as Cx(H2O)y. Later structural studies revealed that these compounds were not hydrates but the term carbohydrate persists.
Carbohydrates are generally classed as either simple or complex. Simple sugars, or monosaccharides, are carbohydrates that can’t be converted into smaller subunits by hydrolysis. Complex carbohydrates are made of two (disaccharides) or more (oligosaccharides, polysaccharides) simple sugars linked together by acetal (glycosidic) bonds and can be split into the former by hydrolysis.
change of state → promjena stanja
Change of state is a physical change which appears when a substance crosses from one state into another. This usually happens because of the change of energy of particles provoked by heating or cooling.
Glauber’s salt → Glauberova sol
Glauber’s salt is sodium sulphate decahydrate (Na2SO4·10H2O). Loses water of hydration at 100 °C. Energy storage capacity is more than seven times that of water.
heat transfer → prijenos topline
From observations and experiments it has been found that heat energy can be transferred from one position to another through three different modes: conduction, convection and radiation.
chemical potential → kemijski potencijal
For a mixture of substances, the chemical potential of constituent B (μB) is defined as the partial derivative of the Gibbs energy G with respect to the amount (number of moles) of B, with temperature, pressure, and amounts of all other constituents held constant.
Also called partial molar Gibbs energy. Components are in equilibrium if their chemical potentials are equal.
chlorophyll → klorofil
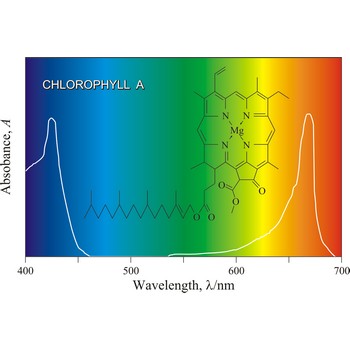
Chlorophyll is a green pigment present in green plants and cyanobacteria. Chlorophyll is essential in the transformation of light energy to chemical energy in photosynthesis. Chlorophyll absorbs light mostly in the blue and red ends of the visible spectrum, and very little in the green wavelengths. That green light is reflected, giving us the leaf colour we see.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Energija kristalne rešetke." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table