smoke → dim
Smoke is a fine suspension of solid particles in a gas. In general smoke particles range downward from about 5 μm in diameter to less than 01 μm in diameter. Smoke generally refers to a visible mixture of products given off by the incomplete combustion of an organic substance such as wood, coal, fuel oil etc. This airborne mixture general contains small particles (dusts) of carbon, hydrocarbons, ash etc. as well as vapors such as carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and water vapor.
sodium → natrij
Sodium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1807. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word natrium meaning sodium carbonate. It is soft silvery-white metal. Fresh surfaces oxidize rapidly. Reacts vigorously, even violently with water. Reacts with water to give off flammable gas. Burns in air with a brilliant white flame. Sodium is obtained by electrolysis of melted sodium chloride (salt), borax and cryolite. Metallic sodium is vital in the manufacture of organic compounds. Sodium chloride (NaCl) is table salt. Liquid sodium is used to cool nuclear reactors.
sol → sol
Sols are dispersions of small solid particles in a liquid. The particles may be macromolecules or may be clusters of small molecules. Lyophobic sols are those in which there is no affinity between the dispersed phase and the liquid (e.g. silver chloride dispersed in water). Lyophobic sols are inherently unstable, in time the particles aggregate, and form a precipitate. Lyiophilic sols, on the other hand, are more like true solutions in which the solute molecules are large and have an affinity for the solvent (e.g. starch in water). Association colloids are systems in which the dispersed phase consists of clusters of molecules that have lyophobic and lyophilic parts (e.g. soap in water).
solid state → čvrsto agregatno stanje
Solid state is characterised by a constant shape and volume. Particles are placed very close to one another and have efect one on another with great attraction forces. Solid bodies do not assume the shape of the container in which they are put.
spin → spin
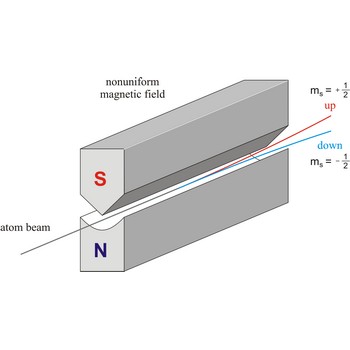
Spin is the intrinsic angular momentum of an elementary particle, or system of particles such as nucleus, that is also responsible for the magnetic moment; or, a particle or nucleus possessing such a spin. The spins of nuclei have characteristic fixed values. Pairs of neutrons and protons align to cancel out their spins, so that nuclei with an odd number of neutrons and/or protons will have a net non-zero rotational component characterized by a non-zero quantum nuclear spin number.
Stern-Gerlach experiment: a beam of silver atoms is split into two beams when it traverses a nonuniform magnetic field. Atoms with spin quantum number ms=+1/2 follow one trajectory, and those with ms=+1/2 follow another.
sulfur → sumpor
Sulfur has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Sanskrit word sulvere meaning sulphur; also from the Latin word sulphurium meaning sulphur. It is pale yellow, odourless, brittle solid, which is insoluble in water but soluble in carbon disulfide. Sulfur is found in pure form and in ores like cinnabar, galena, sphalerite and stibnite. Pure form is obtained from underground deposits by the Frasch process. Used in matches, gunpowder, medicines, rubber and pesticides, dyes and insecticides. Also for making sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
superoxide → superoksid
Superoxides are binary compounds containing oxygen in the -½ oxidation state. Sodium superoxide (NaO2) can be prepared with high oxygen pressures, whereas the superoxides of rubidium, potassium, and cesium can be prepared directly by combustion in air. These compounds are yellow to orange paramagnetic solids. Superoxide ion, O2-, has an unpaired electron, is not particularly stable, and spontaneously decomposes into peroxide over time.
They are strong oxidising agents that vigorously hydrolyze (react with water) to produce superoxide and oxygen gas.
vacuum filtration → vakuum filtracija
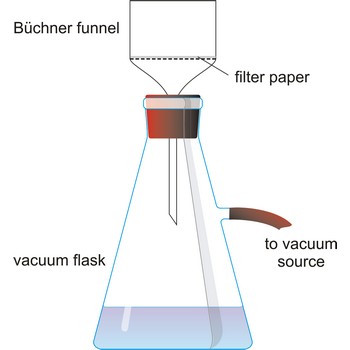
Vacuum filtration is a technique for separating a solid product from a liquid. The mixture of solid and liquid is poured through a filter paper in a Buchner funnel. The solid is trapped by the filter and the liquid is drawn through the funnel into the flask below, by a vacuum.
velocity → brzina
If a point-like object moves so that its position vector changes from being ri to rf, than the displacement Δr of object is
If a point-like object undergoes a displacement, Δr, in time Δt, its average velocity, v is defined as
The instantaneous velocity, v, is obtained from the average velocity by shrinking the time interval Δt towards zero. The average velocity approaches a limiting value, which is the velocity of a given instant:
Velocity is a vector quantity. If we plot the path of a moving particle as a curve in a coordinate system, the instantaneous velocity is always tangent to that curve.
SI unit for velocity is m s-1.
work → rad
Work is the energy required to move an object against an opposing force. Work is usually expressed as a force times a displacement.
When a constant force F acts on a point-like object while the object moves through a displacement s, the force does work W on the object. If force and displacement are at a constant angle Θ to each other, the work is expressed by the scalar product of these two vectors:
When the force F on a point-like object is not constant that is, it depends on the position of the object, the work done by force while object moves from initial position with coordinates (xi, yi, zi) to final position with coordinates (xf, yf, zf)is given by expression:
Where Fx, Fy and Fz are scalar components of the force.
SI unit for work is joule (J); 1 J = 1 Nm = 1 kg m2 s-2. The electron-volt (eV) is commonly used in atomic and nuclear physics.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Elementarna čestica." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table