electrical current → električna struja
Electrical current is a flow of electric charges. The SI unit of electric current is the ampere (A).
electrical double layer → električni dvosloj
Electrical double layer is the structure of charge accumulation and charge separation that always occurs at the interface when an electrode is immersed into an electrolyte solution. The excess charge on the electrode surface is compensated by an accumulation of excess ions of the opposite charge in the solution. The amount of charge is a function of the electrode potential. This structure behaves essentially as a capacitor. There are several theoretical models that describe the structure of the double layer. The three most commonly used ones are the Helmholtz model, the Gouy-Chapman model, and the Gouy-Chapman-Stern model.
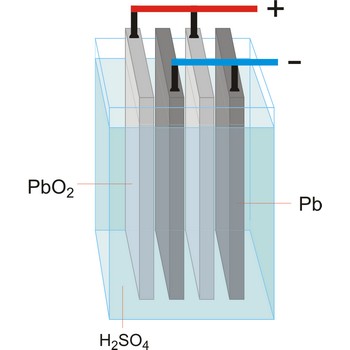
battery → baterija
Battery a device that converts chemical energy to electrical energy. The process underlying the operation of a battery involves a chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred from one chemical species to another. This process is carried out in two half-reactions, one that involves the loss of electrons and one that involves their gain. The battery is an electrochemical cell divided in two half-cells, and reaction proceeds when these are connected together by an electrically conducting pathway. The passage of electrons from one half-cell to the other corresponds to an electric current. Each half-cell contains an electrode in contact with the reacting species. The electrode which passes electrons into the circuit when battery discharges is called anode and is negative terminal. The electrode which receives electrons is called cathode, and is the battery’s positive terminal. The electrical circuit is completed by an electrolyte, an electrically conducting substance placed between the two electrodes which carriers a flow of charge between them. In wet cells, the electrolyte is a liquid containing dissolved ions, whose motion generates an electrical current; in dry cells the electrolyte is basely solid, for example, a solid with mobile ions or porous solid saturated with an ionic solution.
copper → bakar
Copper has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word cuprum meaning the island of Cyprus famed for its copper mines. It is malleable, ductile, reddish-brown metal. Resistant to air and water. Exposed surfaces form greenish carbonate film. Pure copper occurs rarely in nature. Usually found in sulfides as in chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), coveline (CuS), chalcosine (Cu2S) or oxides like cuprite (Cu2O). Most often used as an electrical conductor. Also used in the manufacture of water pipes. Its alloys are used in jewellery and for coins.
electrochemical cell → elektrokemijski članak
Electrochemical cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy or vice versa when a chemical reaction is occurring in the cell. It consist of two electronically conducting phases (e.g., solid or liquid metals, semiconductors, etc) connected by an ionically conducting phase (e.g. aqueous or non-aqueous solution, molten salt, ionically conducting solid). As an electric current passes, it must change from electronic current to ionic current and back to electronic current. These changes of conduction mode are always accompanied by oxidation/reduction reactions.
An essential feature of the electrochemical cell is that the simultaneously occurring oxidation-reduction reactions are spatially separated. E.g., in a spontaneous chemical reaction during the oxidation of hydrogen by oxygen to water, electrons are passed directly from the hydrogen to the oxygen.
In contrast, in the spontaneous electrochemical reaction in a galvanic cell the hydrogen is oxidised at the anode by transferring electrons to the anode and the oxygen is reduced at the cathode by accepting electrons from the cathode. The ions produced in the electrode reactions, in this case positive hydrogen ions and the negative hydroxyl (OH-) ions, will recombine in the solution to form the final product of the reaction: water. During this process the electrons are conducted from the anode to the cathode through an outside electric circuit where the electric current can drive a motor, light a light bulb, etc. The reaction can also be reversed: water can be decomposed into hydrogen and oxygen by the application of electrical power in an electrolytic cell.
electrolytic cell → elektrolitska ćelija
Electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that converts electrical energy into chemical energy. The chemical reactions do not occur spontaneously at the electrodes when they are connected through an external circuit. The reaction must be forced by applying an external electric current. It is used to store electrical energy in chemical form (rechargeable battery). It is also used to decompose or produce (synthesise) new chemicals by the application of electrical power. This process is called electrolysis, e.g., water can be decomposed into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. The free energy change of the overall cell reaction is positive.
ferrite → ferit
Ferrites are ceramic materials of the nominal formula MO·Fe2O3, where M is a divalent metal (Co, Mn, NI, or Zn). The ferrites show either ferrimagnetism or ferromagnetism, but are not electrical conductors, and they are used in high-frequency circuits as magnetic cores, in rectifiers on memory and record tapes, and various related uses in radio, television, radar, computers, and automatic control systems.
galvanic celll → galvanski članak
Galvanic cell (voltaic cell) is a simple device with which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. Galvanic cells consist of two separate compartments called half cells containing electrolyte solutions and electrodes that can be connected in a circuit. Two dissimilar metals (e.g., copper and zinc) are immersed in an electrolyte. If the metals are connected by an external circuit, one metal is reduced (i.e., gains electrons) while the other metal is oxidized (i.e., loses electrons).
In the example above, copper is reduced and zinc is oxidized. The difference in the oxidation potentials of the two metals provides the electric power of the cell.
A voltaic cell can be diagrammed using some simple symbols. In the diagram the electrodes are on the outer side of the diagram and a vertical line (|) is used to separate the electrode from the electrolyte solution found in the compartment. A double vertical line (||) is used to separate the cell compartments and is symbolic of the salt bridge. Usually in a diagram the species oxidized is written to the left of the double slash. Here is an example of the Daniell cell:
The names refer to the 18th-century Italian scientists Alessandro Volta (1745-1827) and Luigi Galvani (1737-1798).
mercury → živa
Mercury has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word hydrargyrum meaning liquid silver. It is heavy, silver-white metal, liquid at ordinary temperatures. Stable in air and water. Unreactive with alkalis and most acids. Gives off poisonous vapour. Chronic cumulative effects. Mercury only rarely occurs free in nature. The chief ore is cinnabar or mercury sulfide (HgS). Used in thermometers, barometers and batteries. Also used in electrical switches and mercury-vapour lighting products.
xenon → ksenon
Xenon was discovered by Sir William Ramsay, Morris W. Travers (England) in 1898. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word xenos meaning stranger. It is heavy, colourless, odourless, noble gas. Reacts only with fluorine. Xenon is obtain from the small quantities in liquid air. Used for filling flash lamps and other powerful lamps. Electrical excitation of xenon produces a burst of brilliant white light. Also used in bubble chambers and modern nuclear power reactors.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Electrical circuit words." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. 5 Apr. 2025. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table