cosmic rays → kozmičke zrake
Cosmic rays are high energy (1015 eV- 1017 eV) nuclear particles, electrons, and photons, originating mostly outside the solar system, which continually bombard the Earth’s atmosphere.
argon → argon
Argon was discovered by Lord Raleigh and Sir William Ramsay (Scotland) in 1894. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word argos meaning inactive. It is colourless and odourless noble gas. Chemically inert. It is the third most abundant element in the earth’s atmosphere and makes up about 1 %. Argon is continuously released into the air by decay of radioactive potassium-40. Pure form is obtained from fractional distillation of liquid air. Used in lighting products. It is often used in filling incandescent light bulbs. Some is mixed with krypton in fluorescent lamps. Crystals in the semiconductor industry are grown in argon atmospheres.
atmosphere → atmosfera
1. Atmosphere is the column of air which is extending several hundred kilometers above the surface the Earth's surface. The density of this air decreases as you proceed up from the surface. The air in the atmosphere consists of 78 % nitrogen, 21 % oxygen, and 0.9 % argon. The remaining 0.1 % of the atmosphere consists of ozone, water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, helium, and neon. The atmosphere is divided into different regions. The lowest two layers are the troposphere (the layer closest to the earth) and the stratosphere respectively. These two layers contain more than 99 % of the atmospheric molecules.
2. Standard atmosphere (atm) is an obsolete pressure and stress unit which should be discontinued. It is unit of pressure equal to the air pressure measured at mean sea level.
1 atm = 101 325 Pa
Technical atmosphere (at) is an obsolete MKpS pressure and sttress derived unit.
1 at = 98 066.5 Pa
1 atm = 1.033 227 453 at
cerium → cerij
Cerium was discovered by Martin Heinrich Klaproth (Germany) and by Jöns Jacob Berzelius (Sweden) in 1803 and Wilhelm von Hisinger (Germany) in 1814. Named after the asteroid Ceres this discovered two years before the element. It is malleable, ductile, iron-grey metal. Tarnishes in air; reacts easily with water. Dissolves in acids; ignites when heated. Metal ignites and burns readily. Strong reductant. Cerium is most abundant rare earth metal. Found in many minerals like monazite sand [Ce(PO4)]. Its oxides are used in the optics and glass-making industries. Its salts are used in the photography and textile industry. Used in high-intensity carbon lamps and as alloying agents in special metals.
geochemistry → geokemija
Geochemistry is the scientific study of the chemical composition of the Earth. It includes the study of the abundance of the Earth’s elements and their isotopes and the distribution of the elements in environments of the Earth (lithosphere, atmosphere, biosphere, and hydrosphere).
mineral water → mineralna voda
Mineral water is a groundwater that rises to the surface through a natural opening in the earth or rock and contains a relatively high concentration of mineral ions and trace of elements which can be radioactive or thermal.
carbohydrate → ugljikohidrat
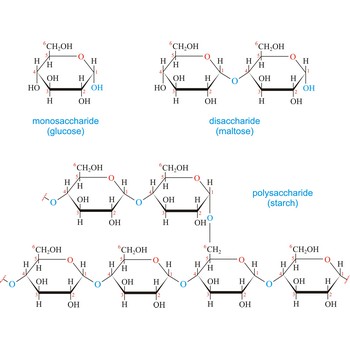
Carbohydrates (often called carbs for short) are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, or substances that yield such compounds on hydrolysis. They are also known as saccharides, a term derived from the Latin word saccharum for sugar. Carbohydrates are the most abundant class of compounds in the biological world, making up more than 50 % of the dry weight of the Earth’s biomass. Every type of food we eat can have its energy traced back to a plant. Plants use carbon dioxide and water to make glucose, a simple sugar, in photosynthesis. Other carbohydrates such as cellulose and starch are made from the glucose. Light from the sun is absorbed by chlorophyll and this is converted to the energy necessary to biosynthesize carbohydrates
The term carbohydrate was applied originally to monosaccharides, in recognition of the fact that their empirical composition can be expressed as Cx(H2O)y. Later structural studies revealed that these compounds were not hydrates but the term carbohydrate persists.
Carbohydrates are generally classed as either simple or complex. Simple sugars, or monosaccharides, are carbohydrates that can’t be converted into smaller subunits by hydrolysis. Complex carbohydrates are made of two (disaccharides) or more (oligosaccharides, polysaccharides) simple sugars linked together by acetal (glycosidic) bonds and can be split into the former by hydrolysis.
crude oil → sirova nafta
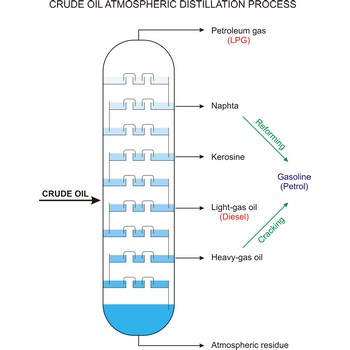
Crude oil (petroleum) is a fossil fuel formed from plant and animal remains many million of years ago. It is occasionally found in springs or pools but is usually drilled from wells beneath the earth’s surface. Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons with small quantities of other chemicals such as sulphur, nitrogen and oxygen. Crude is the raw material which is refined into petrol, heating oil, jet fuel, propane, petrochemicals, and other products.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Earth overshoot day." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table