zwitterion → dipolarni ion
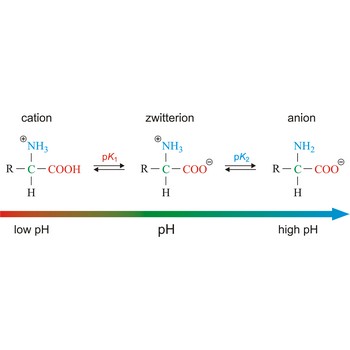
Zwitterion, also known as inner salt or dipolar ion, is an ion with a positive and a negative electrical charge at different locations within a molecule. As the molecule contains two opposite charges, it is electrically neutral. The term zwitterion is derived from the German word zwitter, meaning a hybrid, hermaphrodite. Zwitterions can be formed from compounds that contain both acid groups and base groups in their molecules (ampholytes).
All of the common amino acids found in proteins are ampholytes because they contain a carboxyl group (-COOH) that acts as an acid and an amino group (-NH2) that acts as a base. In the solid state, amino acids exist in the dipolar or zwitterion form. If acid is added to a solution containing the zwitterion, the carboxylate group captures a hydrogen (H+) ion, and the amino acid becomes positively charged. If base is added, ion removal of the H+ ion from the amino group of the zwitterion produces a negatively charged amino acid.
T-S diagram → T-S dijagram
The relationship between the temperature (T) and the salinity (S) of a seawater can be illustrated graphically on a T-S diagram, which is a simple, but powerful tool used in studies of seawater density, mixing, and circulation. In a T-S diagram, temperature is plotted along the vertical axis in degrees Celsius and salinity is measured along the horizontal axis in PSU (Practical Salinity Units). Seawater density is illustrated in the diagram by curved lines of constant density (isopycnals). Water tends to move horizontally throughout the deep ocean, moving along lines of equal density.
CO2 ion selective electrode → CO2 ion selektivna elektroda
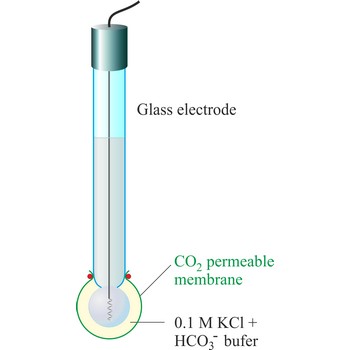
The carbon dioxide ion selective electrode uses a gas-permeable membrane to separate the sample solution from the electrode internal solution. Dissolved carbon dioxide in the sample solution diffuses through the membrane until an equilibrium is reached between the partial pressure of CO2 in the sample solution and the CO2 in the internal filling solution. In any given sample the partial pressure of carbon dioxide will be proportional to the concentration of carbon dioxide. The diffusion across the membrane affects the level of hydrogen ions in the internal filling solution:
The hydrogen level of the internal filling solution is measured by the pH electrode located behind the membrane. The internal filling solution contains a high concentration of sodium bicarbonate (e.g. 0.1 mol/L NaHCO3) so that the bicarbonate level can be considered constant.
Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation → Heyrovsky-Ilkovičeva jednadžba
The Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation describes the entire current-potential curve (polarographic wave) of a reversible redox system in polarography
where R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, F is the Faraday constant, n denotes the number of electrons taking part in the electrode reaction. E1/2 is a unique potential (for a given reaction and supporting electrolyte) termed the half-wave potential.
In order to obtain E1/2 from the above equation, we plot a graph of ln[(id-i)/i] against E. The intercept on the x-axis gives then an accurate value of E1/2. The slope of the obtained straight line is equal to nF/RT from which n is determined.
water jet vacuum pump → vodena sisaljka
The water jet vacuum pump or vacuum aspirator is one of the most popular devices that produces vacuum in laboratories. The rapid flow of water through the device creates a vacuum in a side-arm that is connected to a vacuum application such a Buchner flask. The water jet vacuum pump creates a vacuum by means of Venturi effect named after the Italian physicist Giovanni Battista Venturi (1746–1822). The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a fluid flows through a constricted section of pipe. Water jet pumps are manufactured of glass, plastic or metal, depending on the conditions in which they are used.
Lennard-Jones potential → Lennard-Jonesov potencijal
The Lennard-Jones potential (or 12-6 potential) is a mathematically simple model that describes the interaction between two non-bonded and uncharged atoms (known as the van der Waals interaction). It was first proposed in 1924 by British physicist Sir John Edward Lennard-Jones (1894-1954). The Lennard-Jones Potential is given by the following equation
V(r) = 4e[(sigma/r)12-(sigma/r)6)]
where V is the intermolecular potential between the two atoms or molecules, ε is the well depth and a measure of how strongly the two particles attract each other, σ is the distance at which the intermolecular potential between the two particles is zero, r is the distance of separation between centres of both particles.
Chitosan → Kitozan
Chitosan is a linear polysaccharide composed of randomly distributed N-acetyl D-glucosamine and D-glucosamine units. It can be easily derived from partial deacetylation of natural polymer chitin. At a minimum deacetylization level of 60 % (amount of free amino groups in the polymer) it is considered to be chitosan. Thanks to the amino groups of D-glucosamine, chitosan can be protonated and turned into polycation, which is one of the sources of unique properties of chitosan as biopolymer, like aqueous solubility, antibacterial properties, biodegradability with non-toxic residues and biocompatibility.
Chitin → Hitin
Chitin is a nitrogen-containing linear polysaccharide of ß(1->4) linked units of N-acetyl-ß-d-glucosamine. The structure of chitin is similar to cellulose except for the replacement hydroxyl group (-OH) at the carbon 2 with an acetyl amine group (–NH–CO–CH3). Chitin is the main component of the exoskeleton, or outer covering of insects, crustaceans, and arachnids. It is also found in the cell walls of certain fungi and algae. After cellulose, chitin is the second most abundant biopolymer in nature. It is insoluble in water, organic solvents, weak acids and lyes.
Schrotter apparatus for determination of CO2 → Schrotterova aparatura za određivanje CO2
Schrötter decomposition apparatus (Schrötter's alkalimeter) is used to determining the carbonate content in samples of limestone, gypsum, dolomite, or baking powder by loss of weight. The apparatus is named after the Austrian chemist Anton Schrötter von Kristelli (1802-1875), who devised it in 1871. The size of the filled apparatus (apparatus is 16 cm high) is such that it weights less than 75 g, and can be placed on the pan of an analytical balance.
Procedure: Weigh about 0.5 g of the powdered carbonate sample and introduce it into the decomposition flask C. Pour into the drying tube A 2-3 mL of concentrated sulphuric acid (H2SO4), and to the dropping funnel B add about 10-15 mL of hydrochloric acid (w(HCl) = 15 %). Weigh the whole apparatus. Open the upper taps of both parts and allow the hydrochloric acid from B to run slowly down on to the powdered sample. The evolved CO2 escapes through the strong sulphuric acid and is thus thoroughly dried. When further addition of acid produces no more evolution of CO2, warm the apparatus up to 80 °C so as to expel the CO2 from the solution. Connect the upper tap of the drying tube A to a water pump and draw a slow current of air through the apparatus until completely cool. Open the upper taps for a moment to equalize the internal and external pressure and weight the apparatus again. The weight loss is equal to the weight of carbon dioxide liberated from the carbonates.
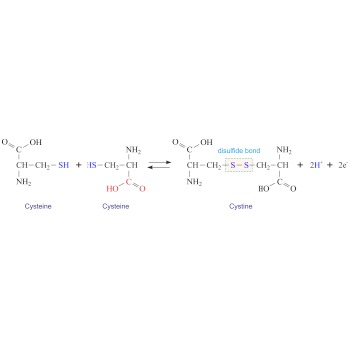
Cystine → Cistin
Cystine (C6H12N2O4S2) is a dimer of cysteine. It is formed by the oxidation of the thiol groups (-SH) of two cysteines generating a disulphide bridge (-S-S-). Cystine is a white crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water. Cystine is particularly abundant in skeletal and connective tissues and in hair, horn, and wool.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Curtain rod width." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table