provitamin → provitamin
Provitamins are substances in food from which certain vitamins are created in the organism, for example the carotene is the provitamin of vitamin A.
water softener → omekšivač vode
Water softeners are substances which help remove constant water hardness. It reacts with calcium and magnesium salts, creating compounds that do not react with soap.
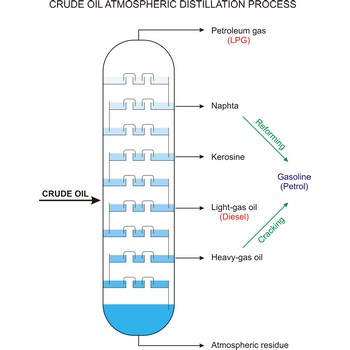
fractional distillation → frakcijska destilacija
Fractional distillation is a procedure in which liquids of close boiling points are separated. It is conducted in fraction or rectification columns in a way that vapour phase created by distillation is condensed and the condensate thus obtained is redistilled. The procedure is repeated several times. Vapour phase always contains more volatile component than the liquid phase, at top of the column vapour of clean volatile component gets out and at the bottom of the column liquid of nonvolatile component.
glass electrode → staklena elektroda
Glass electrode is a hydrogen-ion responsive electrode usually consisting of a bulb, or other suitable form, of special glass attached to a stem of high resistance glass complete with internal reference electrode and internal filling solution system. Glass electrode is also available for the measurement of sodium ions.
The glass electrode, which consists of a thin wall glass bulb, has an extremely high electrical resistance. The membrane of a typical glass electrode (with a thickness of 0.03 mm to 0.1 mm) has an electrical resistance of 30 MΩ to 600 MΩ. The surface of a glass membrane must be hydrated before it will function as a pH electrode. When a glass surface is immersed in an aqueous solution then a thin solvated layer (gel layer) is formed on the glass surface in which the glass structure is softer. This applies to both the outside and inside of the glass membrane.
The simplest explanation for the working of the thin glass electrode is that the glass acts as a weak acid (Glass-H).
The hydrogen ion activity of the internal solution is held constant. When a solution of different pH from the inside comes in contact with the outside of the glass membrane, the glass is either deprotonated or protonated relative to the inside of the glass. The difference in pH between solutions inside and outside the thin glass membrane creates electromotive force in proportion to this difference in pH.
X-ray diffraction pattern → rendgenski difrakcijski uzorci
X-ray diffraction pattern is an interference pattern created by x-rays as they pass through a solid material. Studying X-ray diffraction patterns gives detailed information on the three-dimensional structure of crystals, surfaces, and atoms.
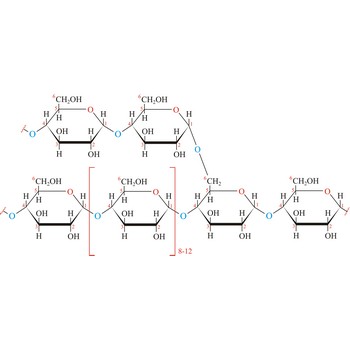
glycogen → glikogen
Glycogen (animal starch) is a polysaccharide that serves the same energy storage function in animals that starch serves in plants. Dietary carbohydrates not needed for immediate energy are converted by the body to glycogen for long term storage (principally in muscle and liver cells). Like amylopectin found in starch, glycogen is a polymer of α(1→4)-linked subunits of glucose, with α(1→6)-linked branches. Glycogen molecules are larger than those of amylopectin (up to 100 000 glucose units) and contain even more branches. Branch points occur about every 10 residues in glycogen and about every 25 residues in amylopectin. The branching also creates lots of ends for enzyme attack and provides for rapid release of glucose when it is needed.
hybrid orbital → hibridne orbitale
Hybrid orbital is an orbital created by mixing together atomic orbitals to form an equal number of new hybrid atomic orbitals. For example, a common hybridization is sp3 where s orbital combine with a three p orbitals to form four new orbitals. After hybridization, all hybrid orbitals have the same energy, lower than p orbitals, but higher than s orbitals.
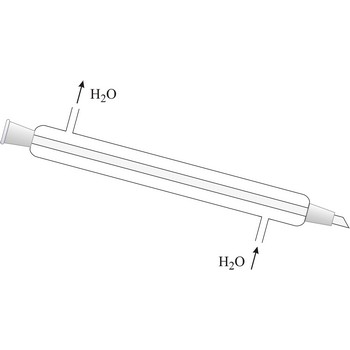
Liebig condenser → Liebigovo hladilo
Liebig condenser is used for condensing of vapours that pass trough the centre tube. It is cooled with water that passes in the outer tube (shell around the centre tube) in the opposite direction than the one of hot vapour. Though named after the German chemist Justus von Liebig (1803-1873), he cannot be given credit for having invented it because it had already been in use for some time before him.
lime → živo vapno
Lime (or quicklime) is the common name for calcium oxide (CaO). It is manufactured from limestone, CaCO3, by heating it to a high temperature (about 1 000 °C). At this temperature carbon dioxide, CO2, is released from the limestone creating calcium oxide, CaO.
A further process involves adding water in a process known as hydrating, which produces hydrated, or slaked lime [Ca(OH)2].
luminescence → luminiscencija
Luminescence (from Latin lumen, light) is the emission of electromagnetic radiation (UV, visible or IR) from atoms or molecules as a result of the transition of an electronically excited state to a lower energy state, usually the ground state. Luminescence can be divided into categories by duration (fluorescence or phosphorescence) or by the mechanism that creates the light (radioluminescence, electroluminescence, photoluminescence, thermoluminescence, triboluminescence, chemiluminescence, bioluminescence). The prefix identifies the energy source responsible for generating or releasing the light.
Phosphorescence is emission of light from a substance exposed to radiation and persisting as an afterglow after the source of excitation has been removed. Fluorescence, on the other hand, is an almost instantaneous effect, ending within about 10-8 second after excitation.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Creo pdf." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. 3 Apr. 2025. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table