logarithmic scale → logaritamska skala
Logarithmic scale is the one in which values of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, in fact represents values of 1, 10, 100, 1 000, 10 000. Logarithmic scales are often used to simplify graphs and tables, where otherwise changes of data at the lower end of the scale would be difficult to distinguish (e.g. a graph axis which would normally have values from 1 - 1 000 000 is shown by values of 1 - 7). An example of a logarithmic scale is the pH scale.
luminescence → luminiscencija
Luminescence (from Latin lumen, light) is the emission of electromagnetic radiation (UV, visible or IR) from atoms or molecules as a result of the transition of an electronically excited state to a lower energy state, usually the ground state. Luminescence can be divided into categories by duration (fluorescence or phosphorescence) or by the mechanism that creates the light (radioluminescence, electroluminescence, photoluminescence, thermoluminescence, triboluminescence, chemiluminescence, bioluminescence). The prefix identifies the energy source responsible for generating or releasing the light.
Phosphorescence is emission of light from a substance exposed to radiation and persisting as an afterglow after the source of excitation has been removed. Fluorescence, on the other hand, is an almost instantaneous effect, ending within about 10-8 second after excitation.
magnetic permeability → magnetska permeabilnost
Magnetic permeability (μ), also called permeability, is a constant of proportionality that exists between magnetic induction and magnetic field intensity. This constant is equal to approximately μo = 1.257×10-6 H/m in a vacuum.
Magnetic permeability is often expressed in relative, rather than in absolute, terms. If μ represents the permeability of the substance in question, then the relative permeability, μr, is given by:
mineral → mineral
Minerals are compounds in which metals can be found in nature. Metals in nature can appear as:
| autochthonous | Au, Cu, Pt, Ag, Pd, Hg, Ir |
| oxides | Fe, Al, Sn, Cr, Mn, W, Cu |
| sulphides | Cu, Pb, Zn, Ni, Ag, Co, Sb, Hg, Mo, Cd, Bi |
| carbonates | Fe, Zn, Cu, Mg, Mn, Pb |
| silicates | Ni, Cu, Zn, Mn |
| chlorides | Ag, Cu, Mg, Na, K |
| sulphates | Ca, Ba, Sr, Cu |
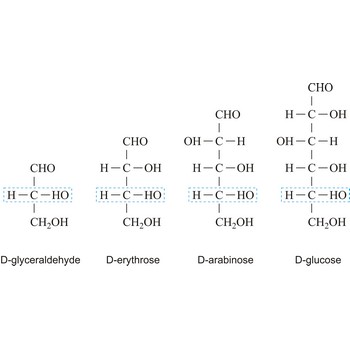
monosaccharide → monosaharid
Monosaccharides are carbohydrates, with the general formula Cn(H2O)n, that cannot be decomposed to a simpler carbohydrates by hydrolysis.
Depending on whether the molecule contains an aldehyde group (-CHO) or a ketone group (-CO-) monosaccharide can be a polyhydroxy aldehyde (aldose) or a polyhydroxy ketone (ketose). These aldehyde and ketone groups confer reduction properties on monosaccharides. They are also classified according to the number of carbon atoms they contain: trioses have three carbon atoms, tetroses four, pentoses five, hexoses six, heptoses seven, etc. These two systems of classification are often combined. For example, a six-carbon polyhydroxy aldehyde such as D-glucose is an aldohexose, whereas a six-carbon polyhydroxy ketone such as D-fructose is a ketohexose.
The notations D and L are used to describe the configurations of carbohydrates. In Fischer projections of monosaccharides, the carbonyl group is always placed on top (in the case of aldoses) or as close to the top as possible (in the case of ketoses). If the OH group attached to the bottom-most asymmetric carbon (the carbon that is second from the bottom) is on the right, then the compound is a D-sugar. If the OH group is on the left, then the compound is an L-sugar. Almost all sugars found in nature are D-sugars.
Monosaccharides can exist as either straight-chain or ring-shaped molecules. During the conversion from straight-chain form to cyclic form, the carbon atom containing the carbonyl oxygen, called the anomeric carbon, becomes a chiral center with two possible configurations (anomers), α and β. When the stereochemistry of the first carbon matches the stereochemistry of the last stereogenic center the sugar is the α-anomer when they are opposite the sugar is the β-anomer.
mutarotation → mutarotacija
Mutarotation is the change in optical rotation accompanying epimerization. In carbohydrate chemistry this term usually refers to epimerization at the hemiacetal carbon atom. In general α- and β-form are stable solids, but in solution they rapidly equilibrate. For example, D-glucose exists in an equilibrium mixture of 36 % α-D-glucopyranose and 64 % β-D-glucopyranose, with only a tiny fraction in the open-chain form. The equilibration occurs via the ring opening of the cyclic sugar at the anomeric center with the acyclic form as the intermediate. Mutarotation was discovered by French chemist Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut (1797-1881) in 1846.
neodymium → neodimij
Neodymium was discovered by Carl F. Auer von Welsbach (Austria) in 1885. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words neos didymos meaning new twin. It is silvery-white, rare-earth metal that oxidizes easily in air. Reacts slowly in cold water, more rapidly as heated. Metal ignites and burns readily. Neodymium is made from electrolysis of its halide salts, which are made from monazite sand. Used in making artificial ruby for lasers. Also in ceramics and for a special lens with praseodymium. Also to produce bright purple glass and special glass that filters infrared radiation. Misch metal, used in the manufacture of pyrophoric alloys for cigarette lighters, contains about 18 % neodymium metal. (Typically composition of misch metal are Ce:Nd:Pr:La:Other rare earth=50:18:6:22:4). Neodymium is used to create some of the most powerful permanent magnets on Earth, known as NIB magnets they consist of neodymium, iron, and boron.
nerve poison → živčani bojni otrov
Nerve poison (nerve gas, agents) have had an entirely dominant role since the Second World War. Nerve poisons acquired their name because they affect the transmission of nerve impulses in the nervous system. All nerve poisons belong chemically to the group of organo-phosphorus compounds. They are stable and easily dispersed, highly toxic and have rapid effects both when absorbed through the skin and via respiration. Nerve poisons can be manufactured by means of fairly simple chemical techniques. The raw materials are inexpensive and generally readily available.
The most important nerve agents included in modern chemical weapons arsenals are:
| Tabun | (o-ethyl dimethylamidophosphorylcyanide) |
| Sarin | (isopropyl methylphosphonofluoridate) |
| Soman | (pinacolyl methylphosphonofluoridate) |
| GF | (cyclohexyl methylphosphonofluoridate) |
| VX | (o-ethyl S-diisopropylaminomethyl methylphosphonothiolate) |
Nerve poisons are colorless, odorless, tasteless liquids of low volatility. Antidotes are atropine sulfate and pralidoxime iodide.
niobium → niobij
Niobium was discovered by Charles Hatchett (England) in 1801. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word Niobe meaning daughter of Tantalus in Greek mythology (tantalum is closely related to niobium in the periodic table). It is shiny white, soft, ductile metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide film. Niobium occurs in a mineral columbite. It is used in stainless steel alloys for nuclear reactors, jets and missiles. Used as an alloy with iron and nickel. It can be used in nuclear reactors and is known to be superconductive when alloyed with tin, aluminium or zirconium.
noble gas → plemeniti plin
Noble gas refers to any element of the group of six elements in group 18 of the periodic table. They are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn). Unlike most elements, the noble gases are monoatomic. The atoms have stable configurations of electrons. Therefore, under normal conditions they do not form compounds with other elements.
They were generally called inert gases until about 1962 when xenon tetrafluoride, XeF4, was produced in the laboratory. This was the first report of a stable compound of a noble gas with another single element.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Create table if not exists postgresql." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table