retardation factor → faktor zaostajanja
Retardation factor, RF, (in planar chromatography) is a ratio of the distance travelled by the centre of the spot to the distance simultaneously travelled by the mobile phase:
The RF value is characteristic for any given compound on the same stationary phase using the same mobile phase for development of the plates. Hence, known RF values can be compared to those of unknown substances to aid in their identifications.
reversible process → reverzibilan proces
Reversible process or reaction is those that can be reversed by an infinitesimally small change in conditions. For example, ice and water coexist at 101 325 Pa and 0 °C; a very slight temperature increase causes the ice to melt; a tiny temperature decrease causes the water to freeze. Melting or freezing under these conditions can be considered reversible.
reversible reaction → reverzibilna reakcija
Reversible reaction is a chemical reaction that can proceed in both the forward and backward directions. When reversible reactions reach equilibrium the forward and reverse reactions are still happening but at the same rate, so the concentrations of reactants and products do not change. A reversible reaction is denoted by a double arrow pointing both directions in a chemical equation.
samarium → samarij
Samarium was discovered by Paul Emile Lecoq de Boisbaudran (France) in 1879. Named after the mineral samarskite. It is silvery rare earth metal. Stable in dry air. Oxide coating forms on surfaces exposed to moist air. Metal ignites and burns readily. Reacts with water. Samarium is found with other rare earths in monazite sand. It is used in the electronics and ceramics industries. It is easily magnetized and very difficult to demagnetise. This suggests important future applications in solid-state and superconductor technologies.
sediment → sediment
1. Sediment is a fragmental material that originates from weathering of rocks and is transported by, suspended in, or deposited by water or air or is accumulated in beds by other natural agencies. When solidified, sediments form sedimentary rocks.
2. Strictly, sediment is a solid material that has settled down from a state of suspension in a liquid.
solar cell → sunčeva ćelija
Solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is a device that captures sunlight and transforms it directly to electricity. All solar cells make use of photovoltaic effect, so often they are called photovoltaic cells. Almost all solar cells are built from solid-state semiconducting materials, and in the vast majority of these the semiconductor is silicon.
The photovoltaic effect involves the generation of mobile charge carriers-electrons and positively charged holes-by the absorption of a photon of light. This pair of charge carriers is produced when an electron in the highest filled electronic band of a semiconductor (the valence band) absorbs a photon of sufficient energy to promote it into the empty energy band (the conduction band). The excitation process can be induced only by a photon with an energy corresponding to the width of the energy gap that separates the valence and the conduction band. The creation of an electron-hole pair can be converted into the generation of an electrical current in a semiconductor junction device, wherein a layer of semiconducting material lies back to back with a layer of either a different semiconductor or a metal. In most photovoltaic cells, the junction is p-n junction, in which p-doped and n-doped semiconductors are married together. At the interface of the two, the predominance of positively charged carriers (holes) in the p-doped material and of negatively charged carriers (electrons) in the n-doped material sets up an electric field, which falls off to either side of the junction across a space-charge region. When absorption of a photon in this region generates an electron-hole pair, these charge carriers are driven in opposite directions by the electric field, i.e. away from the interface and toward the top and bottom of the two-layer structure, where metal electrodes on these faces collect the current. The electrode on the top layer (through which light is absorbed) is divided into strips so as not to obscure the semiconducting layers below. In most widely used commercial solar cells, the p-doped and n-doped semiconductive layers are formed within a monolithic piece of crystalline silicon. Silicon is able to absorb sunlight at those wavelengths at which it is most intense-from the near-infrared region (wavelengths of around 1200 nm) to the violet (around 350 nm).
standard deviation → standardna devijacija
Standard deviation (σ) is a measure of the dispersion of a set of data from its mean. Standard deviation is a statistical term that measures the amount of variability or dispersion around an average
Suppose there are many measurements of a quantity presumed to be similar, like the size of peas in a pod. If the number of readings for each size were plotted, a bell-shaped curve would probably result, with a few small and large peas and most clustered around the average size. Around two-thirds of all measurements fall in the range spanned by the standard deviation, a measure of the spread.
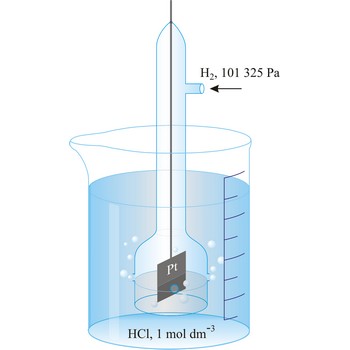
standard hydrogen electrode → standardna vodikova elektroda
Standard hydrogen electrode is a system in which hydrogen ion and gaseous hydrogen are present in their standard states. The convention is to designate the cell so that the standard hydrogen electrode is written first.
The electrode is used as a reference (of zero) for the values of other standard electrode potentials.
supercritical carbon dioxide → superkritični ugljikov dioksid
Supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) is a powerful, cheap, non-toxic and environmental friendly solvent. When used at a supercritical state (over 74 bar and 31 °C), it achieves similar solvating power as its organic competitors, such as hydrocarbons and chlorinated solvents. Supercritical carbon dioxide is one of few solvents that can be unrestrictedly used for food processing.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Change of state." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table