convection → konvekcija
Convection is the process by which heat is transferred from one part of a fluid to another by movement of the fluid itself. There are two methods by which this can be carried out.
Natural convection, in which movement occurs as a result of gravity. Heat transferred through a fluid medium, such as air or water, by currents that result from the rising of less dense, warm fluid and the sinking of heavier, cooler fluid.
Forced convection is where hot fluid is transferred from one region to another by a mechanical means (fans or pumps).
copper → bakar
Copper has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word cuprum meaning the island of Cyprus famed for its copper mines. It is malleable, ductile, reddish-brown metal. Resistant to air and water. Exposed surfaces form greenish carbonate film. Pure copper occurs rarely in nature. Usually found in sulfides as in chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), coveline (CuS), chalcosine (Cu2S) or oxides like cuprite (Cu2O). Most often used as an electrical conductor. Also used in the manufacture of water pipes. Its alloys are used in jewellery and for coins.
dysprosium → disprozij
Dysprosium was discovered by Paul Emile Lecoq de Boisbaudran (France) in 1886. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word dysprositos meaning hard to obtain. It is soft, lustrous, silvery metal. Reacts with oxygen. Reacts rapidly with water; dissolves in acids. Metal ignites and burns readily. Reductant. Dysprosium usually found with erbium, holmium and other rare earths in some minerals such as monazite sand. Dysprosium uses are limited to the experimental and esoteric. Some isotopes of dysprosium are effective absorbers of thermal neutrons and are being considered for use in the control rods in nuclear reactors.
equilibrium constant → konstanta ravnoteže
The equilibrium constant (K) was originally introduced in 1863 by Norwegian chemists C.M. Guldberg and P. Waage using the law of mass action. For a reversible chemical reaction represented by the equation
chemical equilibrium occurs when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the back reaction, so that the concentrations of products and reactants reach steady-state values.
The equilibrium constant is the ratio of chemical activities of the species A, B, C, and D at equilibrium.
To a certain approximation, the activities can be replaced by concentrations.
For gas reactions, partial pressures are used rather than concentrations
The units of Kp and Kc depend on the numbers of molecules appearing in the stoichiometric equation (a, b, c, and d).
The value equilibrium constant depends on the temperature. If the forward reaction is exothermic, the equilibrium constant decreases as the temperature rises. The equilibrium constant shows the position of equilibrium. A low value of K indicates that [C] and [D] are small compared to [A] and [B]; i.e. that the back reaction predominates.
The equilibrium constant is related to ΔrG°, the standard Gibbs free energy change in the reaction, by
fluorine → fluor
Fluorine was discovered by Henri Moissan (France) in 1886. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word fluere meaning to flow. It is pale yellow to greenish gas, with an irritating pungent odour. Extremely reactive, flammable gas. Reacts violently with many materials. Toxic by inhalation or ingestion. Does not occur uncombined in nature. Fluorine is found in the minerals fluorite (CaF2) and cryolite (Na3AlF6). Electrolysis of hydrofluoric acid (HF) or potassium acid fluoride (KHF2) is the only practical method of commercial production. Used in refrigerants and other fluorocarbons. Also in toothpaste as sodium fluoride (NaF).
gallium → galij
Gallium was discovered by Lecoq de Boisbaudran (France) in 1875. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word Gallia meaning France. It is soft, blue-white metal. Stable in air and water. Reacts violently with chlorine and bromine. Gallium is found throughout the crust in minerals like bauxite, germanite and coal. Used in semiconductor production. It us used in making LED’s (light-emitting diodes) and GaAs laser diodes.
germanium → germanij
Germanium was discovered by Clemens Winkler (Germany) in 1886. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word Germania meaning Germany. It is greyish-white semi-metal. Unaffected by alkalis and most (except nitric) acids. Stable in air and water. Germanium is obtained from refining copper, zinc and lead. Widely used in semiconductors. It is a good semiconductor when combined with tiny amounts of phosphorus, arsenic, gallium and antimony.
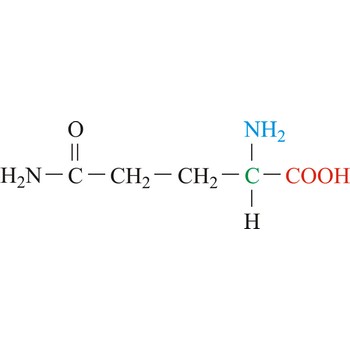
glutamine → glutamin
Glutamine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It serves as an important carrier of ammonia and contributes it to the formation of urea and purines. Glutamine is not recognized as an essential amino acid but may become conditionally essential in certain situations, including intensive athletic training or certain gastrointestinal disorders. It is synthesized by the enzyme glutamine synthetase from glutamate and ammonia.
- Abbreviations: Gln, Q
- IUPAC name: 2,5-diamino-5-oxopentanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H10N2O3
- Molecular weight: 146.14 g/mol
gold → zlato
Gold has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word aurum meaning gold. It is soft, malleable, bright yellow metal. Unaffected by air, water, alkalis and most acids. Gold is found in veins in the crust, with copper ore and native. Used in electronics, jewellery and coins. It is a good reflector of infrared radiation, so a thin film of gold is applied to the glass of skyscrapers to reduce internal heating from sunlight.
Gratzel solar cell → Gratzelova sunčeva ćelija
Grätzel solar cell is photoelectrochemical cell, developed by Michael Grätzel and collaborators, simulates some characteristics of the natural solar cell, which enables photosynthesis take place. In natural solar cell the chlorophyll molecules absorb light (most strongly in the red and blue parts of the spectrum, leaving the green light to be reflected). The absorbed energy is sufficient to knock an electron from the excited chlorophyll. In the further transport of electron, other molecules are involved, which take the electron away from chlorophyll. In Grätzel cell, the tasks of charge-carrier generation and transport are also assigned to different species.
His device consists of an array of nanometre-sized crystallites of the semiconductor titanium dioxide, welded together and coated with light-sensitive molecules that can transfer electrons to the semiconductor particles when they absorb photons. So, light-sensitive molecules play a role equivalent to chlorophyll in photosynthesis. In Grätzel cell, the light-sensitive molecule is a ruthenium ion bound to organic bipyridine molecules, which absorb light strongly in the visible range; titanium dioxide nanocrystals carry the received photoexcited electrons away from electron donors. On the other hand, a donor molecule must get back an electron, so that it can absorb another photon. So, this assembly is immersed in a liquid electrolyte containing molecular species (dissolved iodine molecules) that can pick up an electron from an electrode immersed in the solution and ferry it to the donor molecule. These cells can convert sunlight with efficiency of 10 % in direct sunlight and they are even more efficient in diffuse daylight.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Balance carried forward meaning." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table