distillation → destilacija
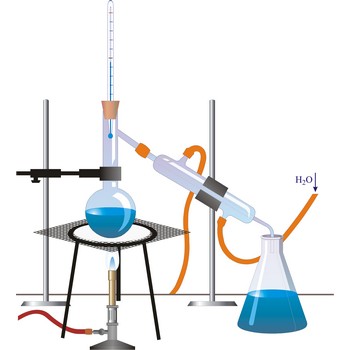
Distillation is a process of boiling a liquid and condensing and collecting the vapour. The liquid collected is the distillate. The usual purpose of distillation is purification or separation of the components of a mixture. This is possible because the composition of the vapour is usually different from that of liquid mixture from which it is obtained. Petrol, kerosene, fuel oil, and lubricating oil are produced from petroleum by distillation.
elastic collision → elastični sudar
Elastic collision is a collision in which the total kinetic energy of the colliding bodies after collision is equal to their total kinetic energy before collision. Elastic collisions occur only if there is no conversion of kinetic energy into other forms, as in the collision of atoms. In the case of macroscopic bodies this will not be the case as some of the energy will become heat. In a collision between polyatomic molecules, some kinetic energy may be converted into vibrational and rotational energy of the molecules.
energy → energija
Energy (E, U) is the characteristic of a system that enables it to do work. Like work itself, it is measured in joules (J).
The internal energy of a body is the sum of the potential energy and the kinetic energy of its component atoms and molecules.
Potential energy is the energy stored in a body or system as a consequence of its position, shape, or state (this includes gravitation energy, electrical energy, nuclear energy, and chemical energy).
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion and is usually defined as the work that will be done by a body possessing the energy when it is brought to rest. For a body of mass m having a speed v, the kinetic energy is mv2/2. Kinetic energy is most clearly exhibited in gases, in which molecules have much greater freedom of motion than in liquids and solids.
In an isolated system energy can be transferred from one form to another but the total energy of the system remains constant.
equal-arm balance → vaga s jednakim krakovima
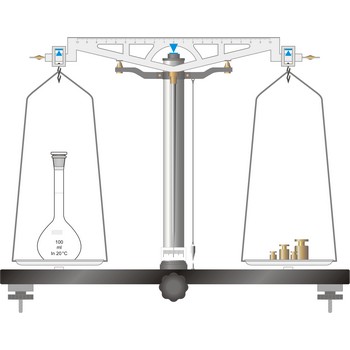
The simplest type of balance, the equal-arm balance, is an application of a first class lever. The beam of the balance is supported on a central knife-edge, usually of agate, which rests upon a plane agate plate. The point of support is called the fulcrum. Two pans of equal weight are suspended from the beam, one at each end, at points equidistant from the fulcrum. A long pointer attached at right angles to the beam at the fulcrum indicates zero on a scale when the beam is at rest parallel to a level surface.
To prevent the knife-edge from becoming dull under the weight of the beam and pans the balance is equipped with a special device called an arrest. The arrest is operated by means of milled knob underneath the base plate in the middle and in front of the balance (sometimes the arrest knob is at one side of the balance).
The object to be weighed is placed on one pan, and standard weights are added to the other until the balance of the beam is established again. When not in use and during loading or unloading of the pans, the balance should be arrested.
Fajans’ rules → Fajansova pravila
Fajans’ rules, formulated by American chemist of Polish origin. Kazimierz Fajans (1887-1975), indicating the extent to which an ionic bond has covalent character caused by polarisation of the ions. Covalent character is more likely if:
1. the charge of the ions is high;
2. the positive ion is small or the negative ion is large;
3. the positive ion has an outer electron configuration that is not a noble- gas configuration.
Fehling’s test → Fehlingova otopina
Fehling’s test is a chemical test to detect reducing sugars and aldehydes in a solution, devised by the German chemist Hermann Christian von Fehling (1812-1885). Fehling’s solution consists of Fehling’s A (copper(II) sulphate solution) and Fehling’s B (sodium tartarate solution), equal amounts of which are added to the test solution. After boiling, a positive result is indicated by the formation of a brick-red precipitate of copper(I) oxide. Methanal, being a strong reducing agent, also produces copper metal; ketones do not react. The test is now rarely used, having been replaced by Benedict’s test.
filter paper → filtar papir
Filter paper is a quantitative paper used for filtering and made of pure cellulose treated with hydrochloric and hydrofluoric acid. This kind of paper burns out practically without any remains (less than 0.0001 g ashes). Different types of paper are marked with numbers; qualitative bears marking 595 or 597 and quantitative 589 or 590. Dependable upon precipitate character, different types of filter paper are used:
- black band (5891) - 100 mL of fluid flows through it in 20 s to 30 s. It is used for filtering of gelatinous precipitates.
- white band (5892) - 100 mL of fluid flows through it in 40 s to 60 s. It is used for coarse crystalline precipitates filtration.
- blue band (5893) - 100 mL of fluid flows through it in 200 s to 400 s. It is used for fine crystalline precipitates.
Fischer-Tropsch process → Fischer-Tropschov postupak
Fischer-Tropsch process is an industrial method of making hydrocarbon fuels from carbon monoxide and hydrogen. The process was introduced in 1933. and used by Germany in World War II. to produce motor fuel. Hydrogen and carbon monoxide are mixed in the ratio 2:1 (water gas was used with added hydrogen) and passed at 200 °C over a nickel or cobalt catalyst. The resulting hydrocarbon mixture can be separated into a higher-boiling fraction for Diesel engines and a lower-boiling petrol fraction. The petrol fraction contains a high proportion of straight-chain hydrocarbons and has to be reformed for use in motor fuel. Alcohols, aldehydes, and ketones are also present. The process is also used in the manufacture of SNG from coal. It is named after the German chemist Franz Fischer (1852-1932) and the Czech Hans Tropsch (1839-1935).
fructose → fruktoza
Fructose (fruit sugar) is a ketohexose (a six-carbon ketonic sugar), which occurs in sweet fruits and honey. Glucose and fructose have the same molecular formula, C6H12O6, but have different structures. Pure, dry fructose is a very sweet, white, odorless, crystalline solid. Fructose is one of the sweetest of all sugars and is combined with glucose to make sucrose, or common table sugar. An older common name for fructose is levulose, after its levorotatory property of rotating plane polarized light to the left (in contrast to glucose which is dextrorotatory). The polysaccharide inulin is a polymer of fructose.
gasoline → motorni benzin
Gasoline is a complex mixture of volatile hydrocarbons that may have between 5 to 12 carbons. The major components are branched-chain paraffins, cycloparaffins, and aromatics. Gasoline is most often produced by the fractional distillation of crude oil as the fraction of hydrocarbons in petroleum boiling between 30 °C and 200 °C. The quality of a fuel is measured with its octane number. Octane number is the measure of the resistance of gasoline against detonation or preignition of the fuel in the engine. The higher the octane number, the more compression the fuel can withstand before detonating. The octane number is determined by comparing the characteristics of a gasoline to isooctane with good knocking properties (octane number of 100) and heptane with bad (octane number of 0).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Alicikli�ki spojevi." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table