cadmium → kadmij
Cadmium was discovered by Friedrich Strohmeyer (Germany) in 1817. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word cadmia meaning calamine (zinc carbonate, ZnCO3), or from the Greek word kadmeia with the same meaning. It is soft, malleable, blue-white metal. Tarnishes in air, soluble in acids, insoluble in alkalis. Boiling cadmium gives off a weird, yellow-colored vapour that is poisonous. Cadmium can cause a variety of health problems, including kidney failure and high blood pressure. Cadmium is obtained as a by product of zinc refining. The mayor use of cadmium is in electroplating of steel to protect it from corrosion. Also used to make nickel-cadmium batteries. The ability of cadmium to adsorb neutrons has made it of great importance in the design of nuclear reactors. Its compounds are found in paint pigments and a wide variety of intense colours.
point-like object → materijalna točka
Point-like object is an expression, usual in kinematics: a point-like object (or a particle) is an object with dimensions, which can be neglected while considering its motion.
caesium → cezij
Caesium was discovered by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff (Germany) in 1860. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word caesius meaning sky blue or heavenly blue. It is very soft, light grey, ductile metal. Reacts readily with oxygen. Reacts explosively with water. Caesium is found in pollucite [(Cs4Al4Si9O26)·H2O] and as trace in lepidolite. Used as a ’getter’ to remove air traces in vacuum and cathode-ray tubes. Also used in producing photoelectric devices and atomic clocks. Since it ionises readily, it is used as an ion rocket motor propellant.
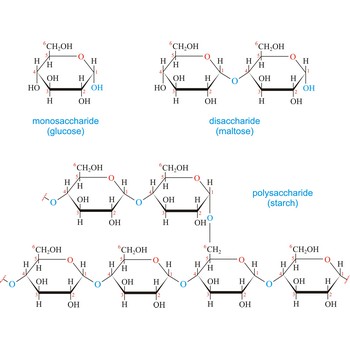
carbohydrate → ugljikohidrat
Carbohydrates (often called carbs for short) are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, or substances that yield such compounds on hydrolysis. They are also known as saccharides, a term derived from the Latin word saccharum for sugar. Carbohydrates are the most abundant class of compounds in the biological world, making up more than 50 % of the dry weight of the Earth’s biomass. Every type of food we eat can have its energy traced back to a plant. Plants use carbon dioxide and water to make glucose, a simple sugar, in photosynthesis. Other carbohydrates such as cellulose and starch are made from the glucose. Light from the sun is absorbed by chlorophyll and this is converted to the energy necessary to biosynthesize carbohydrates
The term carbohydrate was applied originally to monosaccharides, in recognition of the fact that their empirical composition can be expressed as Cx(H2O)y. Later structural studies revealed that these compounds were not hydrates but the term carbohydrate persists.
Carbohydrates are generally classed as either simple or complex. Simple sugars, or monosaccharides, are carbohydrates that can’t be converted into smaller subunits by hydrolysis. Complex carbohydrates are made of two (disaccharides) or more (oligosaccharides, polysaccharides) simple sugars linked together by acetal (glycosidic) bonds and can be split into the former by hydrolysis.
preservative → konzervans
Preservatives are substances that will prevent the development of wood-destroying fungi, borers of various kinds, and other harmful insects that deteriorate wood.
Schiff base → Schiffova baza
Schiff base is a class of compounds derived by the chemical reaction (condensation) of aldehydes or ketones with aromatic amines, for example
They were named after the German chemist Hugo Schiff (1834-1915).
temperature → temperatura
Temperature is a measure to the average kinetic energy of its molecules. The SI unit in which thermodynamic temperature is expressed is the kelvin (K).
toxicology → toksikologija
Toxicology is a science which studies all kinds of poisons and their effects on live organisms.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Alicikli�ki spojevi." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table