polarimetry → polarimetrija
Polarimetry measures the overall turning of the flat of polarised light. It is used when analysing optically active substances and compounds.
sedimentary rocks → sedimentne stijene
Sedimentary Rocks are formed by the accumulation and subsequent consolidation of sediments into various types of rock. There are three major types of sedimentary rocks:
Biogenic sedimentary rocks are formed from organic processes when organisms use materials dissolved in water to build a shell or other skeletal structure.
Clastic sedimentary rocks are composed directly of the sediments or fragments from other rocks.
Chemical sedimentary rocks are formed through evaporation of a chemical rich solution.
Based on their sizes, sediment particles are classified, based on their size, into six general categories:
- boulder (>256 mm)
- cobble (64 - 256 mm)
- gravel (2 - 64 mm)
- sand (1/16 - 2 mm)
- silt (1/256 - 1/16 mm)
- clay (<1/256 mm)
serine → serin
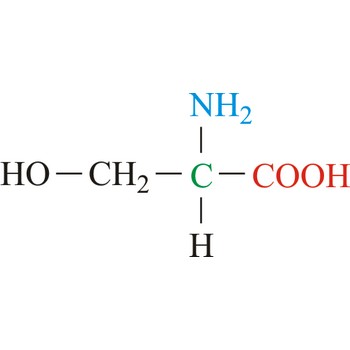
Serine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It is one of two hydroxyl amino acids. Both are commonly considered to by hydrophilic due to the hydrogen bonding capacity of the hydroxyl group. Serine often serves as a nucleophile in many enzyme active sites, and is best known for its role in the serine proteases. Serine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine.
- Abbreviations: Ser, S
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO3
- Molecular weight: 105.09 g/mol
smoke → dim
Smoke is a fine suspension of solid particles in a gas. In general smoke particles range downward from about 5 μm in diameter to less than 01 μm in diameter. Smoke generally refers to a visible mixture of products given off by the incomplete combustion of an organic substance such as wood, coal, fuel oil etc. This airborne mixture general contains small particles (dusts) of carbon, hydrocarbons, ash etc. as well as vapors such as carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and water vapor.
tyrosine → tirozin
Tyrosine is hydrophobic amino acids with aromatic side chain. Tyrosine is large aromatic residue that is normally found buried in the interior of a protein and is important for protein stability. Tyrosine has special properties since its hydroxyl side chain may function as a powerful nucleophile in an enzyme active site (when ionized) and is a common site for phosphorylation in cell signaling cascades. Tyrosine absorbs ultraviolet radiation and contributes to the absorbance spectra of proteins. It is not essential (or semi-essential) to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites.
- Abbreviations: Tyr, Y
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C9H11NO3
- Molecular weight: 181.19 g/mol
valence electron → valentni elektron
Valence electrons are electrons that can be actively involved in a chemical change, usually electrons in the outermost (valent) shell. For example, sodium’s ground state electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1; the 3s electron is the only valence electron in the atom. Germanium (Ge) has the ground state electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p2; the 4s and 4p electrons are the valence electrons.
water gas → vodeni plin
Water gas (blue gas, synthesis gas) is a fuel gas used in industrial synthesis of organic chemicals, and in welding, glassmaking, and other high-temperature industrial applications. Water gas is made by passing steam over a bed of hot coal or coke. It mainly consists of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2), contaminated with small amounts of CO2, N2, CH4, and O2.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Aktivni ugljen." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table