accelerated corrosion test → ubrzana korozija
Accelerated corrosion test is method designed to approximate, in a short time, the deteriorating effect under normal long-term service conditions.
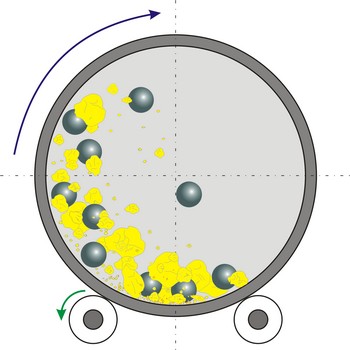
ball mill → kuglični mlin
Ball mill is a grinder for reducing hard materials to powder. The grinding is carried out by the pounding and rolling of a charge of steel or ceramic balls carried within the cylinder. The cylinder rotates at a relatively slow speed, allowing the balls to cascade through the mill base, thus grinding or dispersing the materials.
Type of ball mills, centrifugal and planetary mills, are devices used to rapidly grind materials to colloidal fineness (approximately 1 μm and below) by developing high grinding energy via centrifugal and/or planetary action.
colloid mill → koloidni mlin
Colloid mills are machines used to grind aggregates into very fine particles or to apply very high shearing within a fluid to produce colloid suspensions or emulsions in which the particle sizes are less than 1 micrometer. One type of colloid mill is called a disc mill, in which a mixture of a solid and liquid (or two liquids) is passed between two discs a small distance apart, which rotate very rapidly relative to each other. Applications of colloid mills occur in food processing, in paint manufacture, and in the pharmaceutical industry.
standard mean ocean water → standardna prosječna oceanska voda
Standard mean ocean water (SMOW) is a standard sample of pure water of accurately known isotopic composition which is maintained by the International Atomic Energy Agency. It is used for precise calibration of density and isotopic composition measurements.
Fehling’s test → Fehlingova otopina
Fehling’s test is a chemical test to detect reducing sugars and aldehydes in a solution, devised by the German chemist Hermann Christian von Fehling (1812-1885). Fehling’s solution consists of Fehling’s A (copper(II) sulphate solution) and Fehling’s B (sodium tartarate solution), equal amounts of which are added to the test solution. After boiling, a positive result is indicated by the formation of a brick-red precipitate of copper(I) oxide. Methanal, being a strong reducing agent, also produces copper metal; ketones do not react. The test is now rarely used, having been replaced by Benedict’s test.
salt fog test → ispitivanje u slanoj komori
Salt fog test is an accelerated corrosion test in which specimens are exposed to a fine mist of a solution usually containing sodium chloride (typically 5 %). Other contaminants can be added according to desired conditions. It is mainly used to determine the effectiveness of material finishes and protective coatings on materials. Salt-fog testing is also used to determine the effects of salt deposits on the electrical functions of electronic assemblies.
standard → standard
Standards are materials containing a known concentration of an analyte. They provide a reference to determine unknown concentrations or to calibrate analytical instruments.
The accuracy of an analytical measurement is how close a result comes to the true value. Determining the accuracy of a measurement usually requires calibration of the analytical method with a known standard. This is often done with standards of several concentrations to make a calibration or working curve.
A primary standard is a reagent that is extremely pure, stable, has no waters of hydration, and has a high molecular weight.
A secondary standard is a standard that is prepared in the laboratory for a specific analysis. It is usually standardised against a primary standard.
standard deviation → standardna devijacija
Standard deviation (σ) is a measure of the dispersion of a set of data from its mean. Standard deviation is a statistical term that measures the amount of variability or dispersion around an average
Suppose there are many measurements of a quantity presumed to be similar, like the size of peas in a pod. If the number of readings for each size were plotted, a bell-shaped curve would probably result, with a few small and large peas and most clustered around the average size. Around two-thirds of all measurements fall in the range spanned by the standard deviation, a measure of the spread.
standard electrode potential → standardni elektrodni potencijal
Standard electrode potential (E°) (standard reduction potentials) are defined by measuring the potential relative to a standard hydrogen electrode using 1 mol solution at 25 °C. The convention is to designate the cell so that the oxidised form is written first. For example,
The e.m.f. of this cell is -0.76 V and the standard electrode potential of the Zn2+|Zn half cell is -0.76 V.
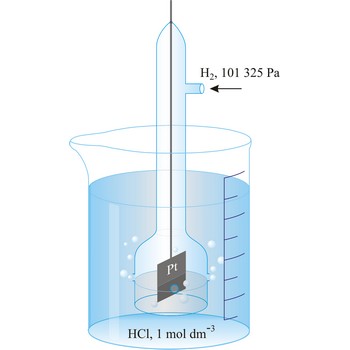
standard hydrogen electrode → standardna vodikova elektroda
Standard hydrogen electrode is a system in which hydrogen ion and gaseous hydrogen are present in their standard states. The convention is to designate the cell so that the standard hydrogen electrode is written first.
The electrode is used as a reference (of zero) for the values of other standard electrode potentials.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Engine mill standard test." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table