air stripping → zračni striping
Air stripping is a process for the removal of volatile organic contaminants from groundwater. The groundwater flows downward inside a tower filled with materials (the packing) over a large surface area. Air is introduced at the bottom of the tower and is forced upward past the falling water. The volatiles evaporate from the water and are collected in air filters or released to the atmosphere.
ampere → amper
Ampere (A) is the SI base unit of electric current.
The ampere is that constant current which, if maintained in two straight parallel conductors of infinite length, of negligible circular cross-section, and placed 1 metre apart in vacuum, would produce between these conductors a force equal to 2×10-7 newton per metre of length.
asbestos → azbest
Asbestos is any one of a group of fibrous amphibole minerals (from the silicate group). It has widespread commercial uses because of its resistance to heat, chemical inertness., and high electrical resistance. Since 1970s short asbestos fibres have been recognized as a cause of asbestosis, a serious lung disorder, and mesothelioma, a fatal form of lung cancer. These concerns have limited its use and imposed many safety procedures when it is used.
atmosphere → atmosfera
1. Atmosphere is the column of air which is extending several hundred kilometers above the surface the Earth's surface. The density of this air decreases as you proceed up from the surface. The air in the atmosphere consists of 78 % nitrogen, 21 % oxygen, and 0.9 % argon. The remaining 0.1 % of the atmosphere consists of ozone, water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, helium, and neon. The atmosphere is divided into different regions. The lowest two layers are the troposphere (the layer closest to the earth) and the stratosphere respectively. These two layers contain more than 99 % of the atmospheric molecules.
2. Standard atmosphere (atm) is an obsolete pressure and stress unit which should be discontinued. It is unit of pressure equal to the air pressure measured at mean sea level.
1 atm = 101 325 Pa
Technical atmosphere (at) is an obsolete MKpS pressure and sttress derived unit.
1 at = 98 066.5 Pa
1 atm = 1.033 227 453 at
battery → baterija
Battery a device that converts chemical energy to electrical energy. The process underlying the operation of a battery involves a chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred from one chemical species to another. This process is carried out in two half-reactions, one that involves the loss of electrons and one that involves their gain. The battery is an electrochemical cell divided in two half-cells, and reaction proceeds when these are connected together by an electrically conducting pathway. The passage of electrons from one half-cell to the other corresponds to an electric current. Each half-cell contains an electrode in contact with the reacting species. The electrode which passes electrons into the circuit when battery discharges is called anode and is negative terminal. The electrode which receives electrons is called cathode, and is the battery’s positive terminal. The electrical circuit is completed by an electrolyte, an electrically conducting substance placed between the two electrodes which carriers a flow of charge between them. In wet cells, the electrolyte is a liquid containing dissolved ions, whose motion generates an electrical current; in dry cells the electrolyte is basely solid, for example, a solid with mobile ions or porous solid saturated with an ionic solution.
Bessemer, Henry → Bessemer, Henry
Sir Henry Bessemer (1813-1898) is the British engineer who first introduced a process for converting pig iron from a blast furnace into steel
biogas → bioplin
Biogas is a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide resulting from the anaerobic decomposition of such waste materials as domestic, industrial, and agricultural sewage. Methanogenic bacteria carry out the decomposition; these obligate anaerobes produce methane, the main component of biogas, which can be collected and used as an energy source for domestic processes, such as heating, cooking, and lighting.
blanching → blanširanje
1. Blanching is a heat treatment of foodstuffs to partially or completely inactivate the naturally occurring enzymes prior to freezing.
2. Blanching is a washing process for coins cleaning. The black surface layer of cupric oxide is removing by dipping the coins in hot dilute sulphuric acid (w(H2SO4) = 10 %).
blank determination → slijepa proba
Blank determination is a procedure of determining which follows all steps of analysis but in the absence of a sample. It is used for detection and compensation of systematic analysis mistakes.
Bravais lattice → Bravaisova rešetka
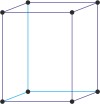
Bravais lattice is a set of points constructed by translating a single point in discrete steps by a set of basis vectors. The French crystallographer Auguste Bravais (1811-1863) established that in three-dimensional space only fourteen different lattices may be constructed. All crystalline materials recognised till now fit in one of these arrangements. The fourteen three-dimensional lattices, classified by crystal system, are shown to the bottom.
|
Crystal system
|
Bravais lattices
|
|||
|
cubic a=b=c α=β=γ=90° |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
simple cubic
|
body-centered cubic
|
face-centered cubic
|
|
|
tetragonal a=b≠c α=β=γ=90° |
 |
 |
||
|
|
simple tetragonal
|
body-centered tetragonal
|
||
|
orthorhombic a≠b≠c α=β=γ=90° |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
simple orthorhombic
|
base-centered orthorhombic
|
body-centered orthorhombic
|
face-centered orthorhombic
|
|
monoclinic a≠b≠c α=γ=90°≠β |
 |
 |
||
|
|
simple monoclinic
|
base-centered monoclinic
|
||
|
hexagonal a=b≠c α=β=90° γ=120° |
 |
|||
|
|
hexagonal
|
|||
|
rhombohedral a=b=c α=β=γ≠90° |
 |
|||
|
|
rhombohedral
|
|||
|
triclinic a≠b≠c α≠β≠γ≠90° |
 |
|||
|
triclinic
|
||||
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Born-Haberov kružni proces." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table


