chromium → krom
Chromium was discovered by Louis-Nicholas Vauquelin (France) in 1797. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word chroma meaning colour. It is very hard, crystalline, steel-grey metal. The pure metal has a blue-white colour. It is hard, brittle and corrosion-resistant at normal temperatures. Hexavalent compounds toxic by skin contact. The most important chromium mineral is chromite [Fe,Mg(CrO4)]. Produced commercially by heating its ore in the presence of silicon or aluminium. Used to make stainless steel. It gives the colour to rubies and emeralds. Iron-nickel-chromium alloys in various percentages yield an incredible variety of the most important metals in modern technology.
cobalt → kobalt
Cobalt was discovered by Georg Brandt (Germany) in 1735. The origin of the name comes from the German word kobald meaning goblin or evil spirit. It is hard, ductile, lustrous bluish-grey metal. Surfaces stable in air. Reacts over time with dilute acids. It has remarkable magnetic properties. Cobalt occurs in compounds with arsenic and sulfur as in cobaltine (CoAsS) and linneite (Co3S4). Pure cobalt is obtained as a by-product of refining nickel, copper and iron. Used in many hard alloys; for magnets, ceramics and special glasses. Radioactive cobalt-60 is used in cancer therapy.
decomposing → raščinjavanje
Decomposing in analytical chemistry means that a certain substance is converted, by melting it with a suitable melting medium (sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide, sodium peroxide, ...) in the kind of compound which will afterwards that dissolve in water, acid or base very easily.
effervescence → pjenušanje
Effervescence is the formation of gas bubbles in a liquid by a chemical reaction. An example of effervescence is the release of carbon dioxide which bubbles as a gas from the liquid when limestone chips, which are composed of calcium carbonate, are added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
contact procedure → kontaktni postupak
Contact procedure is an industrial procedure used for the production of sulphuric acid, where a dry and clean sulphur dioxide and air go over a catalyst made of vanadium pentoxide at 450 °C by which sulphur trioxide is gained, then we add concentrated sulphuric acid by which we obtain smoking sulphuric acid which is now diluted to sulphuric acid.
copolymer → kopolimer
Copolymers are also known as heteropolymers. They are made from two (or more) different monomers, which usually undergo a condensation reaction with the elimination of a simple molecule, such as ammonia or water. A typical example is the condensation of 1,6-diaminohexane (hexamethylenediamine) with hexanedioic acid (adipic acid) to form nylon 6,6.
The properties of a polymeric plastic can most easily be modified if it is a copolymer of two or more different monomers, e.g. acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer (ABS). Varying the proportions of the component monomers can preselect its properties.
copper → bakar
Copper has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word cuprum meaning the island of Cyprus famed for its copper mines. It is malleable, ductile, reddish-brown metal. Resistant to air and water. Exposed surfaces form greenish carbonate film. Pure copper occurs rarely in nature. Usually found in sulfides as in chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), coveline (CuS), chalcosine (Cu2S) or oxides like cuprite (Cu2O). Most often used as an electrical conductor. Also used in the manufacture of water pipes. Its alloys are used in jewellery and for coins.
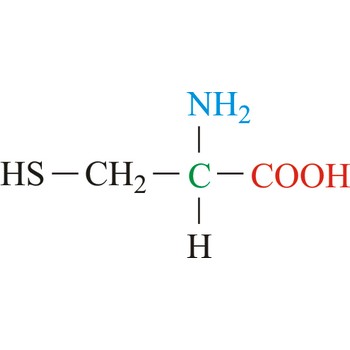
cysteine → cistein
Cysteine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. Because of its high reactivity, the thiol group of cysteine has numerous biological functions. It serves as a potent nucleophile and metal ligand (particularly for iron and zinc), but is best known for its ability to form disulfide bonds, which often make an important contribution to the stability of extracellular proteins. Cysteine is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans.
- Abbreviations: Cys, C
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2S
- Molecular weight: 121.16 g/mol
heat of crystallization → toplina kristalizacije
Heat of crystallization or enthalpy of crystallization is the heat evolved or absorbed when one mole of given substance crystallises from a saturated solution of the same substance.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Zasićena masna kiselina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table