graduated pipette → graduirana pipeta
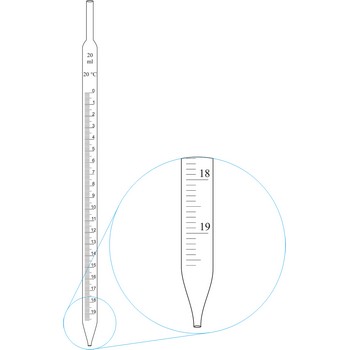
Graduated pipettes (Mohr pipette) have a scale divided into units of one and of 1/10th of a millilitre. Because of their wide necks it is less accurate than the volumetric pipette. They are used when taking volume of solutions in which accuracy does not have to be very high. By sucking in (with mouth, propipette or a water pump) the liquid is pulled in a little bit above the mark and the opening of the pipet is closed with a forefingertip. Outer wall of pipet is wiped and, with a slight forefinger loosening, the liquid is released until it reaches the mark 0. A pipette is emptied out by lifting the forefinger off and letting the liquid flow out of the pipette freely.
Kjeldahl’s method → Kjeldahlov postupak
Kjeldahl’s method is an analytical method for determination of nitrogen in certain organic compounds. The method was developed by the Danish chemist Johan Kjeldahl (1849-1900).
It involves addition of a small amount of anhydrous potassium sulphate to the test compound, followed by heating the mixture with concentrated sulphuric acid, often with a catalyst such as copper sulphate. As a result ammonia is formed. After alkalyzing the mixture with sodium hydroxyde, the ammonia is separated by distillation, collected in standard acid, and the nitrogen determined by back-titration.
- Kjeldahl flask for decomposition (500 ml – macro or 100 ml - micro)
- funnel for alkaline solution
- Wagner tube (drop catcher)
- condenser
- absorption flask with known volume of standard acid
krypton → kripton
Krypton was discovered by Sir William Ramsay and Morris W. Travers (England) in 1898. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word kryptos meaning hidden. It is colourless, odourless rare noble gas. Reacts only with fluorine. Krypton is obtained from production of liquid air. Used in lighting products. Some is used as inert filler-gas in incandescent bulbs. Some is mixed with argon in fluorescent lamps. The most important use is in flashing stroboscopic lamps that outline airport runways.
parallax → paralaksa
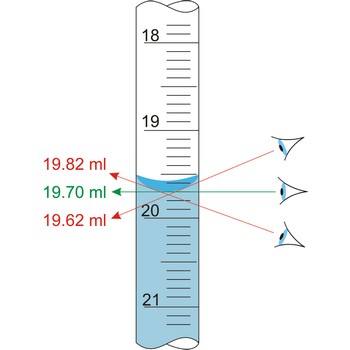
Parallax is a deceptive change of the position of an object which is observed while the position of the observer changes. Position of eye at all volumetric vessels must be at the same level as the meniscus. If not, the parallax will cause an error while reading the position of the meniscus of a liquid in a burette. It will be a positive mistake if the eye is lower, and negative if the eye is higher than the meniscus plane.
picnometer → piknometar
Picnometer is a special glass flask which is used for determining a relative density of liquids using the weight of a known volume. It usually has a glass faceted cork which is pierced in the centre like a thin capillary through which surplus of liquid runs out.
polarography → polarografija
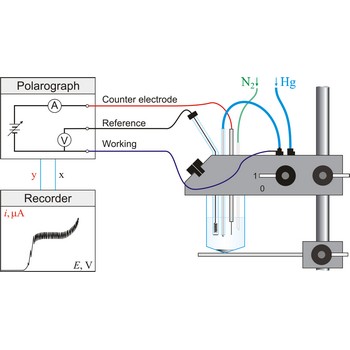
Polarography is a volumetric technique which is based on a diffusion controlled analyte travel to the surface of dropping mercury electrode (DME). The surface of the working electrode (dropping mercury electrode) is constantly renewed under dropping conditions and, thus, the conditions under which reaction takes place are readily reproducible. Depolarisation potential enables identification of ions present in the solution, and by measuring the diffusion current their concentration is calculated. Polarography was discovered in 1922 by the Czech chemist Jaroslav Heyrovský (1890-1967).
potentiometric titration → potenciometrijska titracija
Potentiometric titration is a volumetric method in which the potential between two electrodes is measured (referent and indicator electrode) as a function of the added reagent volume. Types of potentiometric titrations for the determination of analytes in photoprocessing solutions include acid-base, redox, precipitation, and complexometric.
Potentiometric titrations are preferred to manual titrations, since they are more accurate and precise. They are also more easily adapted to automation, where automated titration systems can process larger volumes of samples with minimal analyst involvement.
A titration curve has a characteristic sigmoid curve. The part of the curve that has the maximum change marks the equivalence point of the titration. The first derivative, ΔE/ΔV, is the slope of the curve, and the endpoint occurs at the volume, V', where ΔE/ΔV has the maximum value.
pipette → pipeta
Pipettes are glass tubes which are tapers towards at both ends into narrow opened tubes. According to their design two types of pipettes can be distinguished:
Volumetric pipettes
Volumetric pipettes (transfer or belly pipette) are used in volumetric analysis, when there is a need for taking exact smaller volume of a sample solution or reagent. The upper tube of volumetric pipette has a ringlike marking (mark) which marks its calibrated volume. Pipettes calibrated to deliver (TD or Ex) the indicated volume. By sucking in (with mouth, propipette or a water pump) the liquid is pulled in a little bit above the mark and the opening of the pipet is closed with a forefingertip. Outer wall of pipet is wiped and, with a slight forefinger loosening, the liquid is released until it reaches the mark. Mark must figure as a tangent on a lower edge of the liquid meniscus. A pipette is emptied out by lifting the forefinger off and letting the liquid flow out of the pipette freely. After another 15 s and the tip of the pipette is pulled onto the inner wall of the vessel. It is absolutely forbidden to blow out the contents of the pipette
Graduated pipettes
Graduated pipettes (Mohr pipette) have a scale divided into units of one and of 1/10th of a millilitre. Because of their wide necks it is less accurate than the volumetric pipette. They are used when taking volume of solutions in which accuracy does not have to be very high. They are filled in the same way as volumetric ones and liquid can be gradually released.
Soxhlet extractor → Soxhletov ekstraktor
Soxhlet extractor is a laboratory apparatus designed to extract substances with a low solubility in the extracting solvent. The method described by the German chemist Franz von Soxhlet (1848-1926) in 1879 is the most commonly used example of a semi-continuous method applied to extraction of lipids from foods. In the Soxhlet extractor, the sample soaks in hot solvent that is periodically siphoned off, distilled and returned to the sample. During each cycle, a portion of the non-volatile compound dissolves in the solvent. After many cycles the desired compound is concentrated in the distillation flask. The solvent in the flask is then evaporated and the mass of the remaining lipid is measured.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Volumetric+flask." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table