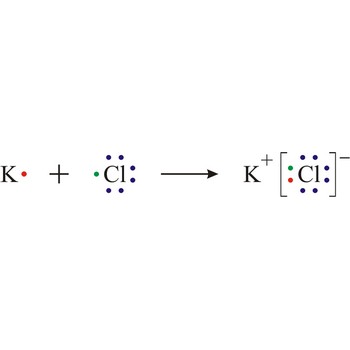hydrogen bond → vodikova veza
Hydrogen is a bond formed by a hydrogen atom to an electronegative atom, and is denoted by dashed lines H-X---H-B. A hydrogen atom covalently bound to an oxygen (electronegative atom) has a significant positive charge and can form a weak bond to another electronegative atom.
conjugated bond → konjugirana veza
Conjugated bonds describe the alternating pattern of double and single bonds, or triple bonds and single bonds, in a molecule. In such molecules, there is some delocalisation of electrons into the pi orbitals of the carbon atoms linked by the single bond.
conjugated double bond → konjugirana dvostruka veza
Conjugated double bond in organic compounds is a system of double bonds between atoms which are separated by one single bond (1,3-butene, H2C=CH-CH=CH2).
cumulated double bond → kumulirana dvostruka veza
Cumulated double bond in organic compounds is a system of two double bonds on the same atom of carbon (C=C=C)
covalent bond → kovalentna veza
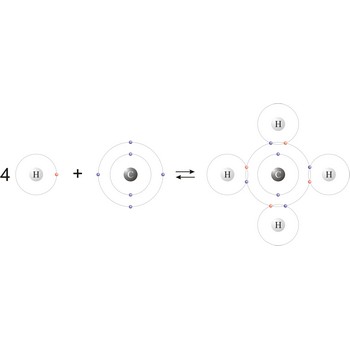
Covalent bond is a chemical bond between two atoms whose stability results from the sharing of two electrons, one from each atom (H· + ·H = H:H or H-H).
metallic bond → metalna veza
Metallic bond is a electrostatic attraction binding the positive ions of a solid metal together by means of a "sea" of delocalised valence electrons
polar covalent bond → polarna kovalentna veza
Polar covalent bond is a covalent bond in which the electrons are not equally shared because one atom attracts them more strongly than the other
valence bond → valentna veza
In the valence bond theory, a valence bond is a chemical bond formed by overlap of half-filled atomic orbitals on two different atoms.
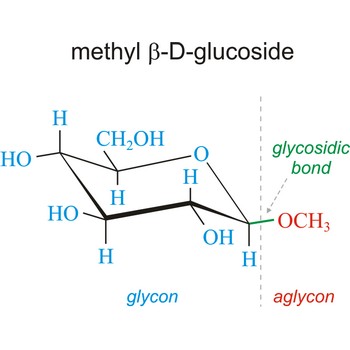
glycosidic bond → glikozidna veza
Glycosidic bond ia a bond between the glycosyl group, the structure obtained by removing the hydroxy group from the hemiacetal function of a monosaccharide, and the -OR group (which itself may be derived from a saccharide and chalcogen replacements thereof (RS–, RSe–). The terms N-glycosides and C-glycosides are misnomers and should not be used. The glycosidic bond can be α or β in orientation, depending on whether the anomeric hydroxyl group was α or β before the glycosidic bond was formed and on the specificity of the enzymatic reaction catalyzing their formation. Once the glycosidic bond is formed, the anomeric configuration of the ring is locked as either α or β. Specific glycosidic bonds therefore may be designated α(1→4), β(1→4), α(1→6), and so on. Cellulose is formed of glucose molecules linked by β(1→4)-glycosidic bonds, whereas starch is composed of α(1→4)-glycosidic bonds.
ionic bond → ionska veza
Ionic bond is a strong force of attraction holding atoms together in a molecule or crystal. Typically chemical bonds have energies of about 100 kJ mol-1. Ionic bond is a bond at which one of the participants, during the procedure of bonding, gives away its unpaired electrons to another atom so that both can achieve electron arrangement of the closest noble gas. In order to form an ionic bond one of the atoms must cross to the positively charged ion by losing certain number of electrons and the other atom must receive those electrons and cross to the negatively charged ion.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Vodikova veza." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table