mass spectrometry → masena spectrometrija
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique in which ions are separated according to the mass/charge (m/e) ratio and detected by a suitable detector.
In a mass spectrometer a sample is ionised and the positive ions produced are accelerated into a high-vacuum region containing electric and magnetic fields. These fields deflect and focus the ions onto a detector. A mass spectrum is thus obtained, consisting of a series of peaks of variable intensity to which m/e values can be assigned. Different molecules can be identified by their characteristic pattern of lines.
metre → metar
Metre (m) is the SI base unit of length.
The meter is the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of 1/299 792 458 s.
This definition, adopted by the General Conference on Weights and Measure in October 1983, replaced the 1967 definition based on the krypton lamp.
photomultiplier → fotomultiplikator
Photomultiplier (photomultiplier tube or PMT) is a very versatile and sensitive detector of radiant energy in the ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. A typical photomultiplier tube consists of a photoemissive cathode (photocathode) followed by focusing electrodes, an electron multiplier (dynode) and an electron collector (anode) in a vacuum tube.
Soxhlet extractor → Soxhletov ekstraktor
Soxhlet extractor is a laboratory apparatus designed to extract substances with a low solubility in the extracting solvent. The method described by the German chemist Franz von Soxhlet (1848-1926) in 1879 is the most commonly used example of a semi-continuous method applied to extraction of lipids from foods. In the Soxhlet extractor, the sample soaks in hot solvent that is periodically siphoned off, distilled and returned to the sample. During each cycle, a portion of the non-volatile compound dissolves in the solvent. After many cycles the desired compound is concentrated in the distillation flask. The solvent in the flask is then evaporated and the mass of the remaining lipid is measured.
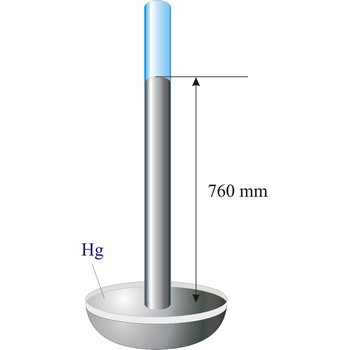
Torricelli, Evangelista → Torricelli, Evangelista
Evangelista Torricelli (1852-1908) is Italian physicist and mathematician. He became the first scientist to create a sustained vacuum and to discover the principle of a barometer. He filled a tube three feet long, and hermetically closed at one end, with mercury and set it vertically with the open end in a basin of mercury, taking care that no air-bubbles should get into the tube. The column of mercury invariably fell to about twenty-eight inches, leaving an empty space above its level. He discovered that the variation of the height of the mercury from day to day was caused by changes in the atmospheric pressure. He also constructed a number of large objectives and small, short focus, simple microscopes.
zirconium → cirkonij
Zirconium was discovered by Martin Heinrich Klaproth (Germany) in 1789. The origin of the name comes from the Arabic word zargun meaning gold colour. It is grey-white, lustrous, corrosion-resistant metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide protective film. Zirconium is found in many minerals such as zircon and baddeleyite. Used in alloys such as zircaloy this is used in nuclear applications since it does not readily absorb neutrons. Also baddeleyite is used in lab crucibles. Used in high-performance pumps and valves. Clear zircon (ZrSiO4) is a popular gemstone.
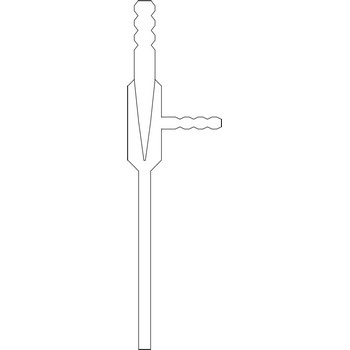
water jet vacuum pump → vodena sisaljka
The water jet vacuum pump or vacuum aspirator is one of the most popular devices that produces vacuum in laboratories. The rapid flow of water through the device creates a vacuum in a side-arm that is connected to a vacuum application such a Buchner flask. The water jet vacuum pump creates a vacuum by means of Venturi effect named after the Italian physicist Giovanni Battista Venturi (1746–1822). The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a fluid flows through a constricted section of pipe. Water jet pumps are manufactured of glass, plastic or metal, depending on the conditions in which they are used.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Vakuum filtracija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table