Buchner flask → Buchnerova tikvica
Büchner flask (also known as a vacuum flask, filter flask, side-arm flask or Kitasato flask) is a thick-walled Erlenmeyer flask with a side arm to which a vacuum can be applied.
Fermi level → Fermijev nivo
Fermi level is the highest energy of occupied states in a solid at zero temperature. The Fermi level in conductors lies in the conduction band, in insulators it lies in the valence band, and in semiconductors it falls in the gap between the conduction band and the valence band. It was named after the Italian physicst Enrico Fermi (1901 - 1954).
fire-damp → plin praskavac
Fire-damp is a mixture of two volume parts of hydrogen and one volume part of oxygen which, if set on fire, strongly explodes, the flame giving of a very high temperature (2 000 °C).
freezing → smrzavanje
Freezing is the change of a liquid into a solid state as the temperature decreases. For water, the freezing point is 0 °C (or 273.16 K).
Bunsen burner → Bunsenov plamenik
Bunsen burner is a standard source of heat in the laboratory. German chemist Roberts Bunsen (1811-1899) improved the burner's design, which had been invented by Faraday, to aid his endeavors in spectroscopy. The Bunsen burner has a vertical metal tube through which a fine jet of fuel gas is directed. Air is drawn in through airholes near the base of the tube and the mixture is ignited and burns at the tube’s upper opening. The flow of this air is controlled by an adjustable collar on the side of the metal tube. When the whole is closed a yellow safety flame is displayed. Where as when the whole is open it displays a power dull blue flame with a faint blue outer flame with a vibrant blue core used u for combustion and hearting. The flame can reach temperatures of 1 500 °C.
caesium → cezij
Caesium was discovered by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff (Germany) in 1860. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word caesius meaning sky blue or heavenly blue. It is very soft, light grey, ductile metal. Reacts readily with oxygen. Reacts explosively with water. Caesium is found in pollucite [(Cs4Al4Si9O26)·H2O] and as trace in lepidolite. Used as a ’getter’ to remove air traces in vacuum and cathode-ray tubes. Also used in producing photoelectric devices and atomic clocks. Since it ionises readily, it is used as an ion rocket motor propellant.
calcium → kalcij
Calcium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1808. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word calix meaning lime. It is fairly hard, silvery-white metal. Exposed surfaces form oxides and nitrides. Reacts with water and oxygen. Occurs only in compounds. Calcium is obtained from minerals like chalk, limestone and marble. Pure metal is produced by replacing the calcium in lime (CaCO3) with aluminium in hot, low pressure retorts. Used by many forms of life to make shells and bones. Virtually no use for the pure metal, however two of its compounds are, lime (CaO) and gypsum (CaSO4), are in great demand by a number of industries.
calomel electrode → kalomel elektroda
Calomel electrode is a type of half cell in which the electrode is mercury coated with calomel (Hg2Cl2) and the electrolyte is a solution of potassium chloride and saturated calomel. In the calomel half cell the overall reaction is
Table: Dependence of potential of calomel electrode upon temperature and concentration of KCl according to standard hydrogen electrode
| Potential vs. SHE / V | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| t / °C | 0.1 mol dm-3 | 3.5 mol dm-3 | sat. solution |
| 15 | 0.3362 | 0.254 | 0.2511 |
| 20 | 0.3359 | 0.252 | 0.2479 |
| 25 | 0.3356 | 0.250 | 0.2444 |
| 30 | 0.3351 | 0.248 | 0.2411 |
| 35 | 0.3344 | 0.246 | 0.2376 |
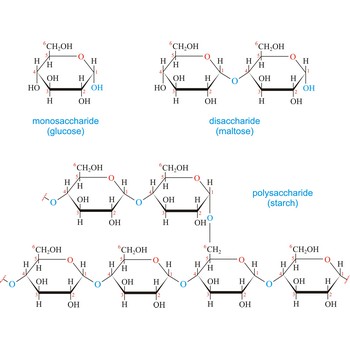
carbohydrate → ugljikohidrat
Carbohydrates (often called carbs for short) are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, or substances that yield such compounds on hydrolysis. They are also known as saccharides, a term derived from the Latin word saccharum for sugar. Carbohydrates are the most abundant class of compounds in the biological world, making up more than 50 % of the dry weight of the Earth’s biomass. Every type of food we eat can have its energy traced back to a plant. Plants use carbon dioxide and water to make glucose, a simple sugar, in photosynthesis. Other carbohydrates such as cellulose and starch are made from the glucose. Light from the sun is absorbed by chlorophyll and this is converted to the energy necessary to biosynthesize carbohydrates
The term carbohydrate was applied originally to monosaccharides, in recognition of the fact that their empirical composition can be expressed as Cx(H2O)y. Later structural studies revealed that these compounds were not hydrates but the term carbohydrate persists.
Carbohydrates are generally classed as either simple or complex. Simple sugars, or monosaccharides, are carbohydrates that can’t be converted into smaller subunits by hydrolysis. Complex carbohydrates are made of two (disaccharides) or more (oligosaccharides, polysaccharides) simple sugars linked together by acetal (glycosidic) bonds and can be split into the former by hydrolysis.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Slana voda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table