fructose → fruktoza
Fructose (fruit sugar) is a ketohexose (a six-carbon ketonic sugar), which occurs in sweet fruits and honey. Glucose and fructose have the same molecular formula, C6H12O6, but have different structures. Pure, dry fructose is a very sweet, white, odorless, crystalline solid. Fructose is one of the sweetest of all sugars and is combined with glucose to make sucrose, or common table sugar. An older common name for fructose is levulose, after its levorotatory property of rotating plane polarized light to the left (in contrast to glucose which is dextrorotatory). The polysaccharide inulin is a polymer of fructose.
glycogen → glikogen
Glycogen (animal starch) is a polysaccharide that serves the same energy storage function in animals that starch serves in plants. Dietary carbohydrates not needed for immediate energy are converted by the body to glycogen for long term storage (principally in muscle and liver cells). Like amylopectin found in starch, glycogen is a polymer of α(1→4)-linked subunits of glucose, with α(1→6)-linked branches. Glycogen molecules are larger than those of amylopectin (up to 100 000 glucose units) and contain even more branches. Branch points occur about every 10 residues in glycogen and about every 25 residues in amylopectin. The branching also creates lots of ends for enzyme attack and provides for rapid release of glucose when it is needed.
isomorphism → izomorfija
Isomorphism is the existence of two or more substances that have the same crystal structure, so that they form solid solutions.
ligand field theory → teorija ligandnog polja
Ligand field theory is a description of the structure of crystals containing a transition metal ion surrounded by nonmetallic ions (ligands). It is based on the construction of molecular orbitals involving the d-orbitals of the central metal ion and combinations of atomic orbitals of the ligands.
metabolism → metabolizam
Metabolism is a sum of all chemical and physiological processes by which the body builds and maintains itself. It is a process of building the body’s molecular structures from nutrients (anabolism) and breaking them down for energy (catabolism).
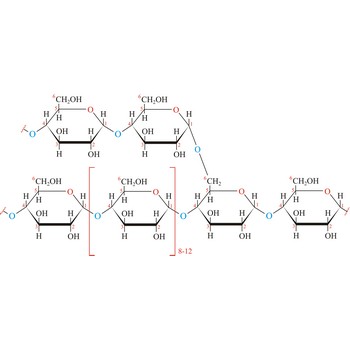
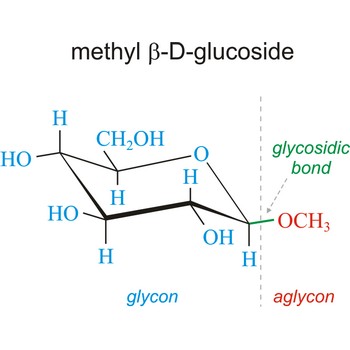
glycosidic bond → glikozidna veza
Glycosidic bond ia a bond between the glycosyl group, the structure obtained by removing the hydroxy group from the hemiacetal function of a monosaccharide, and the -OR group (which itself may be derived from a saccharide and chalcogen replacements thereof (RS–, RSe–). The terms N-glycosides and C-glycosides are misnomers and should not be used. The glycosidic bond can be α or β in orientation, depending on whether the anomeric hydroxyl group was α or β before the glycosidic bond was formed and on the specificity of the enzymatic reaction catalyzing their formation. Once the glycosidic bond is formed, the anomeric configuration of the ring is locked as either α or β. Specific glycosidic bonds therefore may be designated α(1→4), β(1→4), α(1→6), and so on. Cellulose is formed of glucose molecules linked by β(1→4)-glycosidic bonds, whereas starch is composed of α(1→4)-glycosidic bonds.
hexagonal close-packed structure → heksagonska gusta slagalina
In a hexagonal close-packed (hcp) arrangement of atoms, the unit cell consists of three layers of atoms. The top and bottom layers (a) contain six atoms at the corners of a hexagon and one atom at the center of each hexagon. The middle layer (b) contains three atoms nestled between the atoms of the top and bottom layers, hence, the name close-packed. The hexagonal close packed structure can be made by piling layers in the a-b-a-b-a-b... sequence.
homologous series → homologni niz
Series of compounds which have a common general formula and in which each member differs from the next member by a constant unit, which is the methylene group (-CH2-) is called the homologous series. Members of a homologous series are called homolog.
An example of the homologous series with some of their homologs are given below. Straight chain alkanes having general formula CnH2n+2
| Structure | Name |
|---|---|
| CH4 | methane |
| CH3-CH3 | ethane |
| CH3-CH2-CH3 | propane |
| CH3-CH2CH2CH3 | butane |
| CH3-(CH2)3-CH3 | pentane |
| CH3-(CH2)4-CH3 | hexane |
| CH3-(CH2)5-CH3 | heptane |
| CH3-(CH2)6-CH3 | octane |
| CH3-(CH2)7-CH3 | nonane |
| CH3-(CH2)8-CH3 | decane |
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Prstenasta struktura." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table