potentiometric titration → potenciometrijska titracija
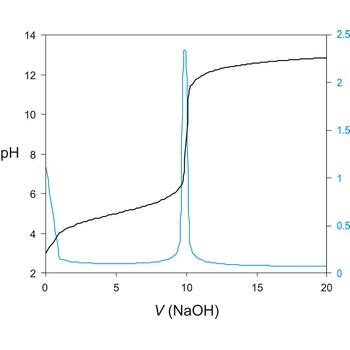
Potentiometric titration is a volumetric method in which the potential between two electrodes is measured (referent and indicator electrode) as a function of the added reagent volume. Types of potentiometric titrations for the determination of analytes in photoprocessing solutions include acid-base, redox, precipitation, and complexometric.
Potentiometric titrations are preferred to manual titrations, since they are more accurate and precise. They are also more easily adapted to automation, where automated titration systems can process larger volumes of samples with minimal analyst involvement.
A titration curve has a characteristic sigmoid curve. The part of the curve that has the maximum change marks the equivalence point of the titration. The first derivative, ΔE/ΔV, is the slope of the curve, and the endpoint occurs at the volume, V', where ΔE/ΔV has the maximum value.
referent electrode → referentna elektroda
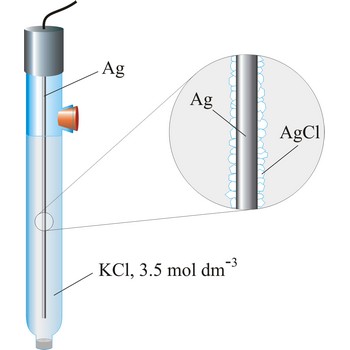
Referent electrode is an electrode whose potential is known and completely independent of analyte concentration. Mostly used referent electrodes are calomel and silver/silver chloride electrode.
Table: Dependence of referent electrodes potentials on KCl concentration
| Potential vs. SHE / V | |||||
| calomel electrode | Ag/AgCl electrode | ||||
| t / °C | 0.1 mol dm-3 | 3.5 mol dm-3 | sat. solution | 3.5 mol dm-3 | sat. solution |
| 15 | 0.3362 | 0.254 | 0.2511 | 0.212 | 0.209 |
| 20 | 0.3359 | 0.252 | 0.2479 | 0.208 | 0.204 |
| 25 | 0.3356 | 0.250 | 0.2444 | 0.205 | 0.199 |
| 30 | 0.3351 | 0.248 | 0.2411 | 0.201 | 0.194 |
| 35 | 0.3344 | 0.246 | 0.2376 | 0.197 | 0.189 |
salt bridge → solni most
Salt bridge is a permeable material soaked in a salt solution that allows ions to be transferred from one container to another. The salt solution remains unchanged during this transfer.
Schrodinger equation → Schrodingerova jednadžba
Schrödinger equation is the basic equation of wave mechanics which, for systems not dependent on time, takes the form:
where Ψ is the wavefunction, V is the potential energy expressed as a function of the spatial coordinates, E its total energy, ![]() 2 is the Laplacian operator, h is Planck’s constant, and m is the mass.
2 is the Laplacian operator, h is Planck’s constant, and m is the mass.
silver/silver-chloride electrode → srebro/srebrov klorid elektroda
Silver/silver-chloride electrode is by far the most common reference type used today because it is simple, inexpensive, very stable and non-toxic. It is mainly used with saturated potassium chloride electrolyte, but can be used with lower concentrations such as 3.5 mol dm-3 or 1 mol dm-3 potassium chloride. Silver/silver-chloride electrode is a referent electrode based on the following halfreaction
| Potential vs. SHE / V | ||
|---|---|---|
| t / °C | 3.5 mol dm-3 | sat. solution |
| 15 | 0.212 | 0.209 |
| 20 | 0.208 | 0.204 |
| 25 | 0.205 | 0.199 |
| 30 | 0.201 | 0.194 |
| 35 | 0.197 | 0.189 |
supercritical carbon dioxide → superkritični ugljikov dioksid
Supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) is a powerful, cheap, non-toxic and environmental friendly solvent. When used at a supercritical state (over 74 bar and 31 °C), it achieves similar solvating power as its organic competitors, such as hydrocarbons and chlorinated solvents. Supercritical carbon dioxide is one of few solvents that can be unrestrictedly used for food processing.
Tafel plot → Tafelov dijagram
Tafel plot is the graph of the logarithm of the current density j against the overpotential η in electrochemistry in the high overpotential limit. An electrode when polarised frequently yields a current potential relationship over a region which can be approximated by:
where η is change in open circuit potential, i is the current density, B and i0 is constants. B is known as the Tafel Slope. If this behaviour is observed a plot of the semilogarithmic components is known as the Tafel line and the diagram is called the Tafel diagram.
Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation → Heyrovsky-Ilkovičeva jednadžba
The Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation describes the entire current-potential curve (polarographic wave) of a reversible redox system in polarography
where R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, F is the Faraday constant, n denotes the number of electrons taking part in the electrode reaction. E1/2 is a unique potential (for a given reaction and supporting electrolyte) termed the half-wave potential.
In order to obtain E1/2 from the above equation, we plot a graph of ln[(id-i)/i] against E. The intercept on the x-axis gives then an accurate value of E1/2. The slope of the obtained straight line is equal to nF/RT from which n is determined.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Potencijal članka." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table