Archimedes law → Arhimedov zakon
The upward force (buoyancy force) is exerted on a body floating in a fluid. It equals the weight of the displaced fluid.
Avogadro, Amadeo → Avogadro, Amadeo
Amadeo Avogadro (1776-1856) is an Italian chemist and physicist that proposed a correct molecular explanation for Gay-Lussac’s law of combining volumes. His work provided a simple way to determine atomic weights and molecular weights of gases. He is published a theory about the movement of particles in gases that became known as Avogadro’s Law.
Avogadro’s law → Avogadrov zakon
Avogadro’s law: Equal volumes of all gases contain equal numbers of molecules at the same pressure and temperature. The law, often called Avogadro’s hypothesis, is true only for ideal gases. It was proposed in 1811 by Italian chemist Amadeo Avogadro (1776-1856).
argon → argon
Argon was discovered by Lord Raleigh and Sir William Ramsay (Scotland) in 1894. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word argos meaning inactive. It is colourless and odourless noble gas. Chemically inert. It is the third most abundant element in the earth’s atmosphere and makes up about 1 %. Argon is continuously released into the air by decay of radioactive potassium-40. Pure form is obtained from fractional distillation of liquid air. Used in lighting products. It is often used in filling incandescent light bulbs. Some is mixed with krypton in fluorescent lamps. Crystals in the semiconductor industry are grown in argon atmospheres.
Arrhenius equation → Arheniusova jednadžba
In 1889, Svante Arrhenius explained the variation of rate constants with temperature for several elementary reactions using the relationship
where the rate constant k is the total frequency of collisions between reaction molecules A times the fraction of collisions exp(-Ea/RT) that have an energy that exceeds a threshold activation energy Ea at a temperature of T (in kelvin). R is the universal gas constant.
Boltzmann constant → Boltzmannova konstanta
The Boltzmann constant (k or kB) is the physical constant describing the relationship between the thermodynamic temperature and the average kinetic energy of particles in a gas. It equals the molar gas constant R divided by the Avogadro constant NA and has the value 1.380 648 52(79)×10-23 J/K. It is named after the Austrian physicist Ludwig Eduard Boltzmann (1844-1906).
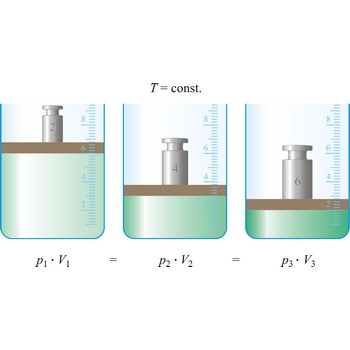
Boyle’s law → Boyleov zakon
Boyle’s law (sometimes referred to as the Boyle-Mariott’s law) is the empirical law, exact only for an ideal gas, which states that the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at constant temperature.
Bunsen burner → Bunsenov plamenik
Bunsen burner is a standard source of heat in the laboratory. German chemist Roberts Bunsen (1811-1899) improved the burner's design, which had been invented by Faraday, to aid his endeavors in spectroscopy. The Bunsen burner has a vertical metal tube through which a fine jet of fuel gas is directed. Air is drawn in through airholes near the base of the tube and the mixture is ignited and burns at the tube’s upper opening. The flow of this air is controlled by an adjustable collar on the side of the metal tube. When the whole is closed a yellow safety flame is displayed. Where as when the whole is open it displays a power dull blue flame with a faint blue outer flame with a vibrant blue core used u for combustion and hearting. The flame can reach temperatures of 1 500 °C.
butane → butan
Butane is a gaseous hydrocarbon C4H10 obtained from petroleum (refinery gas or by cracking higher hydrocarbons). The fourth member of the alkane series, it has a straight chain of carbon atoms and is isomeric with 2-methylpropane, formerly called isobutene. It can easily be liquefied under pressure and is supplied into cylinders for use as a fuel gas. It is also a raw material for making buta-1, 3-diene for synthetic rubber.
catalyst → katalizator
Catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change. Catalysts that have the same phase as the reactants are homogenous catalysts (e.g. enzymes in biochemical reactions). Those that have a different phase are heterogeneous catalyst (e.g. metals or oxides used in gas reactions).
The catalyst provides an alternative pathway by which the reaction can proceed, in which the activation energy is lower. In thus increases the rate at which the reaction comes to an equilibrium, although it does not alter the position of the equilibrium.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Plin." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table