beta-glucan → beta-glukan
Beta-glucans are are naturally occurring polysaccharides that contain only glucose as structural components, and are linked with β-glycosidic bonds. They is the most known powerful immune stimulant. The most active forms of β-glucans are those comprising D-glucose units with β(1→3) links and with short side-chains of D-glucose attached at the β(1→6) position. These are referred to as beta-1,3/1,6 glucan. They are a major component of soluble dietary fiber, which can be found in cereal grains (oats, barley, wheat), yeast, and certain mushrooms (shiitake, maitake).
bidentate ligand → bidentatni ligand
Bidentate ligand is a ligand that has two "teeth" or atoms that coordinate directly to the central atom in a complex. An example of a bidentate ligand is ethylenediamine. A single molecule of ethylenediamine can form two bonds to a metal ion. The bonds form between the metal ion and the nitrogen atoms of ethylenediamine.
computational chemistry → kompjutacijska kemija
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry concerned with the prediction or simulation of chemical properties, structures, or processes using numerical techniques.
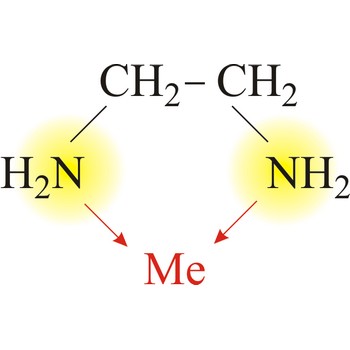
condensational polymerisation → kondenzacijska polimerizacija
Condensational polymerisation is a reaction of polymerisation in which monomers together create a polymer by losing small molecules like water.
conduction → kondukcija
This process occurs most significantly in solids. The atoms or molecules in a solid state do not leave their mean positions, but continue to vibrate about their mean positions. They transfer heat energy from one atom to another. This happens because of the coupling between them due to mutually attractive forces.
body-centered cubic lattice → prostorno centrirana kubična rešetka
Body-centered cubic lattice (bcc or cubic-I), like all lattices, has lattice points at the eight corners of the unit cell plus an additional points at the center of the cell. It has unit cell vectors a = b = c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
The simplest crystal structures are those in which there is only a single atom at each lattice point. In the bcc structures the spheres fill 68 % of the volume. The number of atoms in a unit cell is two (8 × 1/8 + 1 = 2). There are 23 metals that have the bcc lattice.
carboxylic acids → karboksilne kiseline
Carboxylic acids are organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more RC(=O)OH groups (the carboxyl group). In the systematic chemical nomenclature carboxylic acids names end in the suffix -oic (e.g. ethanoic acids, CH3COOH). The carbon of the terminal group being counted as part of the chain. They are generally weak acids. Carboxylic acids include a large and important class of fatty acids and may be either saturated or unsaturated. There are also some natural aromatic carboxylic acids (benzoic, salicylic).
catalyst → katalizator
Catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change. Catalysts that have the same phase as the reactants are homogenous catalysts (e.g. enzymes in biochemical reactions). Those that have a different phase are heterogeneous catalyst (e.g. metals or oxides used in gas reactions).
The catalyst provides an alternative pathway by which the reaction can proceed, in which the activation energy is lower. In thus increases the rate at which the reaction comes to an equilibrium, although it does not alter the position of the equilibrium.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Planarna struktura molekule." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table