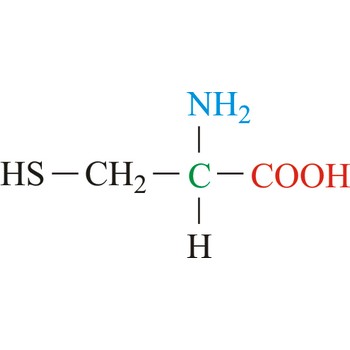
cysteine → cistein
Cysteine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. Because of its high reactivity, the thiol group of cysteine has numerous biological functions. It serves as a potent nucleophile and metal ligand (particularly for iron and zinc), but is best known for its ability to form disulfide bonds, which often make an important contribution to the stability of extracellular proteins. Cysteine is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans.
- Abbreviations: Cys, C
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2S
- Molecular weight: 121.16 g/mol
oligosaccharide → oligosaharid
Oligosaccharides are carbohydrates containing from three to ten monosaccharide units, each joined to the next by a glycoside bond.
organometallic compound → organometalni spoj
Organometallic compounds are compounds in which there is a covalent connection between atoms of carbons and atoms of metal (C-Me).
oxonium ion → oksonijev ion
Oxonuim ion (H3O+) is formed when a molecule of water binds with a proton.
Pauling scale → Paulingova skala
Pauling scale is a numerical scale of electronegativities based on bond-energy calculations for different elements joined by covalent bonds. Electronegativity is the power of an atom when in a molecule to attract eletrons to itself. Fluorine is the most electronegative element with a Pauling electronegativity value of 4.
deoxyribonucleic acid → dezoksiribonukleinska kiselina
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a nucleic acid with 2-deoxy-D-ribose as the sugar in its nucleotides. DNA contains encoded genetic information, specifically templates for the synthesis of all of an organism’s proteins and enzymes.
DNA was first identified in the 1869 by Swiss chemist Friedrich Miescher (1844-1895). In 1953, American biologist James Dewey Watson (1928-) and English physicist Francis Harry Compton Crick (1916–2004) had discovered that DNA occurs in the cell as a double helix, with two long strands of the molecule wound around each other, and further that the chemical structure of the molecule dictates that adenine (A) always aligns or pairs with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) always pairs with guanine (G). It is this base pairing that allows DNA in a cell to copy itself, and transfer its information to a new cell. The diameter of the helix is 2.0 nm and there is a residue on each chain every 0.34 nm in the z direction. The angle between each residue on the same strand is 36°, so that the structure repeats after 10 residues (3.4 nm) on each strand.
diagenesis → dijageneza
Diagenesis is the process that turns sediments into sedimentary rocks. The lithification (literally turning into stone) of the sediments is usually accomplished by a cementing agent. How the weight of the overlying material increases the grains closer together, reducing pore space and eliminating some of the contained water. This water may carry mineral components in solution, and these constituents precipitate as new minerals in the pore spaces. This causes cementation, which will then start to bind the individual particles together. Further compaction and burial may cause recrystallization of the minerals to make the rock even harder.
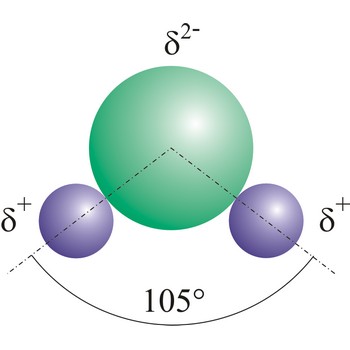
dipole molecule → dipolna molekula
Dipole molecules are created when mutual electronic pair at covalent bond is asymmetrical. If different atoms are bonded by a covalent bond, which can have different electron affinity, then the the atom with greater electron affinity will attract the electron pairs more strongly. In this way an asymmetrical distribution of negative charge appears in a molecule, so one part of the molecule becomes relatively negatively (the one closer to the electron pair) and the other becomes relatively positively charged.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Pi veza." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table