scandium → skandij
Scandium was discovered by Lars Fredrik Nilson (Sweden) in 1879. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word Scandia meaning Scandinavia. It is fairly soft, silvery-white metal. Burns easily. Tarnishes readily in air. Reaction with water releases hydrogen. Reacts with air and halogens. Scandium occurs mainly in the minerals thortveitile (~34 % scandium) and wiikite. Also in some tin and tungsten ores. Pure scandium is obtained as a by-product of uranium refining. Scandium metal is used in some aerospace applications. Scandium oxide (Sc2O2) is used in the manufacture of high-intensity electric lamps. Scandium iodide (ScI3) is used in lamps that produce light having a colour closely matching natural sunlight.
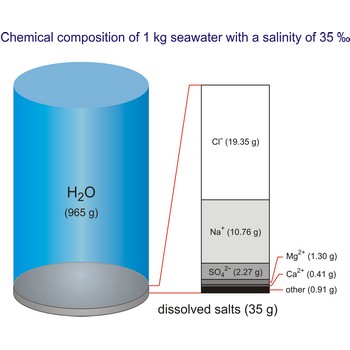
seawater → more
Seawater is a complex mixture of 96.5 % water, 3.5 % salts, and smaller amounts of other substances, including dissolved inorganic and organic materials, particulates, and a few atmospheric gases. The world's oceans cover nearly 71 % (361 840 000 km2) of the Earth's surface (510 100 000 km2), with an average depth of 3 682.2 m.
The density of seawater is higher than that of fresh water because of its higher salinity. Seawater's freezing point is lower than that of pure water and its boiling point is higher. The average salinity of the ocean is 35 ‰, which means that for every kilograms of water, there are 35 g of salt. The relative abundance of the major salts in seawater are constant regardless of the ocean. Only six elements and compounds comprise about 99 % of sea salts: chlorine (Cl-), sodium (Na+), sulfur (SO42-), magnesium (Mg2+), calcium (Ca2+), and potassium (K+).
sediment → sediment
1. Sediment is a fragmental material that originates from weathering of rocks and is transported by, suspended in, or deposited by water or air or is accumulated in beds by other natural agencies. When solidified, sediments form sedimentary rocks.
2. Strictly, sediment is a solid material that has settled down from a state of suspension in a liquid.
sedimentary rocks → sedimentne stijene
Sedimentary Rocks are formed by the accumulation and subsequent consolidation of sediments into various types of rock. There are three major types of sedimentary rocks:
Biogenic sedimentary rocks are formed from organic processes when organisms use materials dissolved in water to build a shell or other skeletal structure.
Clastic sedimentary rocks are composed directly of the sediments or fragments from other rocks.
Chemical sedimentary rocks are formed through evaporation of a chemical rich solution.
Based on their sizes, sediment particles are classified, based on their size, into six general categories:
- boulder (>256 mm)
- cobble (64 - 256 mm)
- gravel (2 - 64 mm)
- sand (1/16 - 2 mm)
- silt (1/256 - 1/16 mm)
- clay (<1/256 mm)
selenium → selenij
Selenium was discovered by Jöns Jakob Berzelius (Sweden) in 1817. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word selene meaning moon. It is soft metalloid similar to sulfur. Ranges from grey metallic to red glassy appearance. Unaffected by water. Soluble in alkalis and nitric acid. Burns in air. Toxic by inhalation or ingestion. Selenium is obtained from lead, copper and nickel refining. Conducts electricity when struck by light. Light causes it to conduct electricity more easily. It is used in photoelectric cells, TV cameras, xerography machines and as a semiconductor in solar batteries and rectifiers. Also colours glass red.
silicon → silicij
Silicon was discovered by Jöns Jacob Berzelius (Sweden) in 1824. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word silicis meaning flint. Amorphous form of silicon is brown powder; crystalline form has grey metallic appearance. Solid form unreactive with oxygen, water and most acids. Dissolves in hot alkali. Silica dust is a moderately toxic acute irritant. Silicon makes up major portion of clay, granite, quartz and sand. Commercial production depends on a reaction between sand (SiO2) and carbon at a temperature of around 2200 °C. Used in glass as silicon dioxide (SiO2). Silicon carbide (SiC) is one of the hardest substances known and used in polishing. Also the crystalline form is used in semiconductors.
silver → srebro
Silver has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word argentum meaning silver. It is silvery-ductile and malleable metal. Stable in water and oxygen. Reacts with sulfur compounds to form black sulfides. Silver is found in ores called argentite (AgS), light ruby silver (Ag3AsS3), dark ruby silver (Ag3SbS3) and brittle silver. Used in alloys for jewellery and in other compounds for photography. It is also a good conductor, but expensive.
smoke → dim
Smoke is a fine suspension of solid particles in a gas. In general smoke particles range downward from about 5 μm in diameter to less than 01 μm in diameter. Smoke generally refers to a visible mixture of products given off by the incomplete combustion of an organic substance such as wood, coal, fuel oil etc. This airborne mixture general contains small particles (dusts) of carbon, hydrocarbons, ash etc. as well as vapors such as carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and water vapor.
sodium → natrij
Sodium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1807. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word natrium meaning sodium carbonate. It is soft silvery-white metal. Fresh surfaces oxidize rapidly. Reacts vigorously, even violently with water. Reacts with water to give off flammable gas. Burns in air with a brilliant white flame. Sodium is obtained by electrolysis of melted sodium chloride (salt), borax and cryolite. Metallic sodium is vital in the manufacture of organic compounds. Sodium chloride (NaCl) is table salt. Liquid sodium is used to cool nuclear reactors.
sol → sol
Sols are dispersions of small solid particles in a liquid. The particles may be macromolecules or may be clusters of small molecules. Lyophobic sols are those in which there is no affinity between the dispersed phase and the liquid (e.g. silver chloride dispersed in water). Lyophobic sols are inherently unstable, in time the particles aggregate, and form a precipitate. Lyiophilic sols, on the other hand, are more like true solutions in which the solute molecules are large and have an affinity for the solvent (e.g. starch in water). Association colloids are systems in which the dispersed phase consists of clusters of molecules that have lyophobic and lyophilic parts (e.g. soap in water).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Permanent hardness in water." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table