crucible → lončić za žarenje
Crucible is used for heating small amounts of solid in an oven to very high temperatures. Crucibles are usually made out of porcelain, platinum, nickel or iron.
crude oil → sirova nafta
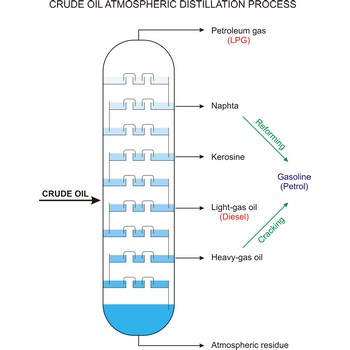
Crude oil (petroleum) is a fossil fuel formed from plant and animal remains many million of years ago. It is occasionally found in springs or pools but is usually drilled from wells beneath the earth’s surface. Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons with small quantities of other chemicals such as sulphur, nitrogen and oxygen. Crude is the raw material which is refined into petrol, heating oil, jet fuel, propane, petrochemicals, and other products.
cubic close-packed structure → kubična gusta slagalina
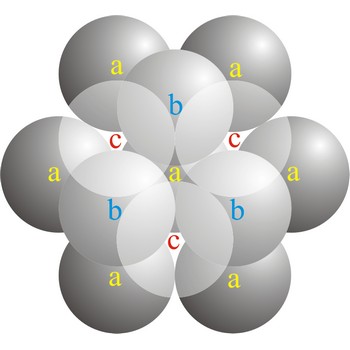
In a cubic close-packed (ccp) arrangement of atoms, the unit cell consists of four layers of atoms. The top and bottom layers (a) contain six atoms at the corners of a hexagon and one atom at the center of each hexagon. The atoms in the second layer (b) fit into depressions in the first layer. The atoms in the third layer (c) occupy a different set of depressions than those in the first. The cubic close packed structure can be made by piling layers in the a-b-c-a-b-c-a-b-c... sequence.
cubic crystal system → kubični kristalni sustav
Cubic crystal system is also known as the isometric system. The Isometric crystal system characterizes itself by its three equivalent crystallographic axes perpendicular to each other.
a = b = c
α = β = γ = 90°
cyclic compound → ciklički spoj
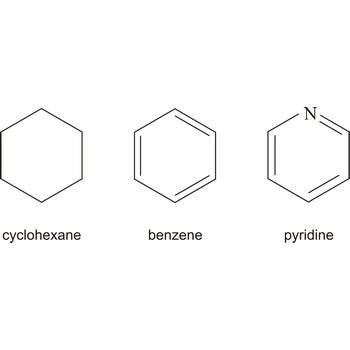
Cyclic describing a compound that has a ring of atoms in its molecules. In homocyclic compounds all the atoms in the ring are of the same type, e.g. benzene (C6H6) and cyclohexane (C6H12). These two examples are also examples of carbocyclic compounds; i.e. the rings are made of carbon atoms. If different atoms occur in the ring, as in pyridine (C5H5N), the compound is said to be heterocyclic.
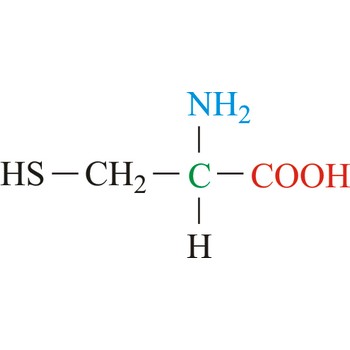
cysteine → cistein
Cysteine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. Because of its high reactivity, the thiol group of cysteine has numerous biological functions. It serves as a potent nucleophile and metal ligand (particularly for iron and zinc), but is best known for its ability to form disulfide bonds, which often make an important contribution to the stability of extracellular proteins. Cysteine is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans.
- Abbreviations: Cys, C
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2S
- Molecular weight: 121.16 g/mol
decay series → raspadni niz
Decay series is a series of decay in which radioactive element is decomposed in different elements until it produces one stable atom.
deoxyribonucleic acid → dezoksiribonukleinska kiselina
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a nucleic acid with 2-deoxy-D-ribose as the sugar in its nucleotides. DNA contains encoded genetic information, specifically templates for the synthesis of all of an organism’s proteins and enzymes.
DNA was first identified in the 1869 by Swiss chemist Friedrich Miescher (1844-1895). In 1953, American biologist James Dewey Watson (1928-) and English physicist Francis Harry Compton Crick (1916–2004) had discovered that DNA occurs in the cell as a double helix, with two long strands of the molecule wound around each other, and further that the chemical structure of the molecule dictates that adenine (A) always aligns or pairs with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) always pairs with guanine (G). It is this base pairing that allows DNA in a cell to copy itself, and transfer its information to a new cell. The diameter of the helix is 2.0 nm and there is a residue on each chain every 0.34 nm in the z direction. The angle between each residue on the same strand is 36°, so that the structure repeats after 10 residues (3.4 nm) on each strand.
Daniell cell → Daniellov članak
In 1836 the British chemist John Frederic Daniell (1790-1845) proposed an improved electric cell that supplied an even current during continuous operation. Daniell cell consisted of a glass jar containing copper and zinc electrodes, each immersed in their respective acidic sulphate solutions. The two solutions were separated by a porous clay cylinder separator. It was a galvanic cell in which the spontaneous electrodissolution of zinc and electroplating of copper provided the electrical current.
Zn(s) |
→ | Zn2+ + 2e- |
+0.763 V |
Cu2+ + 2e- |
→ | Cu(s) |
+0.337 V |
Zn(s) + Cu2+ |
→← | Zn2+ + Cu(s) |
+1.100 V |
desiccator → eksikator
Desiccator is a glass container with dry atmosphere due to the presence of some dehydrating agent. It is used for protecting the samples, reagents or precipitates from humidity. As dehydrating agent usually waterless calcium chloride (CaCl2) is used.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Periodni_sustav_elemenata." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table