threonine → treonin
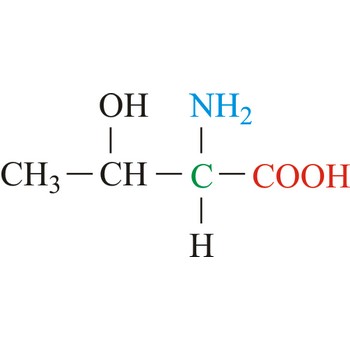
Threonine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It differs from serine by having a methyl substituent in place of one of the hydrogens on the β carbon. Threonine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Thr, T
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H9NO3
- Molecular weight: 119.12 g/mol
toxin → toksin
Toxins are effective and specific poisons produced by living organisms. They usually consist of an amino acid chain which can vary in molecular weight between a couple of hundred (peptides) and one hundred thousand (proteins). They may also be low-molecular organic compounds. Toxins are produced by numerous organisms, e.g., bacteria, fungi, algae and plants. Many of them are extremely poisonous, with a toxicity that is several orders of magnitude greater than the nerve agents. Botulinum toxin, produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum, is the most poisonous substance known.
tryptophan → triptofan
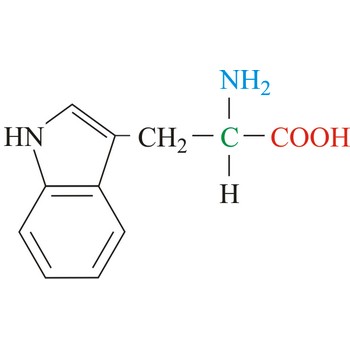
Tryptophan is hydrophobic amino acids with aromatic side chain. Tryptophan is large aromatic residue that is normally found buried in the interior of a protein and is important for protein stability. Tryptophan has the largest side chain and is the least common amino acid in proteins. It has spectral properties that make it the best inherent probe for following protein folding and conformational changes associated with biochemical processes. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Trp, W
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C11H12N2O2
- Molecular weight: 204.23 g/mol
tyrosine → tirozin
Tyrosine is hydrophobic amino acids with aromatic side chain. Tyrosine is large aromatic residue that is normally found buried in the interior of a protein and is important for protein stability. Tyrosine has special properties since its hydroxyl side chain may function as a powerful nucleophile in an enzyme active site (when ionized) and is a common site for phosphorylation in cell signaling cascades. Tyrosine absorbs ultraviolet radiation and contributes to the absorbance spectra of proteins. It is not essential (or semi-essential) to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites.
- Abbreviations: Tyr, Y
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C9H11NO3
- Molecular weight: 181.19 g/mol
valine → valin
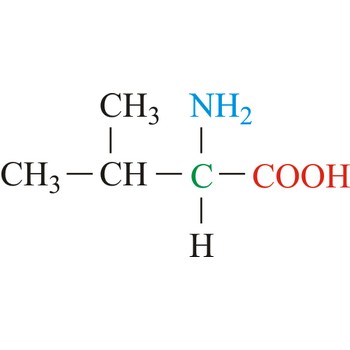
Valine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It is a member of the branched-chain amino acid family, along with leucine and isoleucine. Valine differs from threonine by replacement of the hydroxyl group with a methyl substituent, but they are of roughly the same shape and volume. The nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions. Valine is an essential amino acid, which means that it cannot be synthesized in the body and must be obtained through dietary sources.
- Abbreviations: Val, V
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-methylbutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H11NO2
- Molecular weight: 117.15 g/mol
water → voda
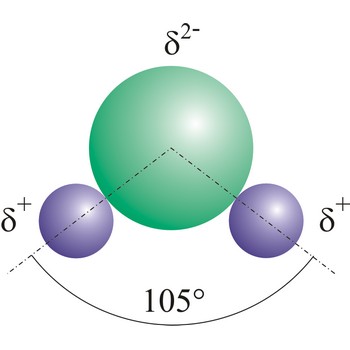
Water (H2O) (dihydrogen oxide) is a binary compound that occurs at room temperature as a clear colorless odorless tasteless liquid; freezes into ice below 0 °C and boils above 100 °C. Water is a chemical compound which is essential for living organisms and it is widely used as a solvent.
Wilson’s chamber → Wilsonova komora
Wilson’s chamber is used for detection of radioactive radiation. Wilson’s chamber has a glass cylinder filled with air that has been saturated with water vapour. Radioactive radiation in its way ionises molecules of gas which then function as centres on which water vapour condenses into very small drops, thereupon showing Tyndall’s effect, i.e. is they are visible as a bright trail.
zeolite → zeolit
Zeolite is a natural or synthetic hydrated aluminosilicate with an open three-dimensional crystal structure, in which water molecules are held in cavites in the latice. The water can be driven off by heating and the zeolite can then absorb other molecules of suitable size. Zeolites are used for separating mixtures by selective absorption.
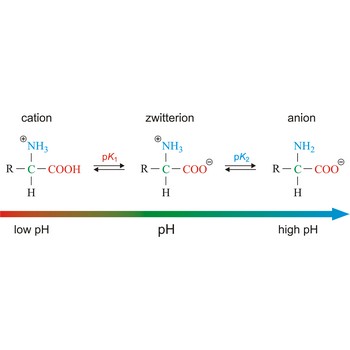
zwitterion → dipolarni ion
Zwitterion, also known as inner salt or dipolar ion, is an ion with a positive and a negative electrical charge at different locations within a molecule. As the molecule contains two opposite charges, it is electrically neutral. The term zwitterion is derived from the German word zwitter, meaning a hybrid, hermaphrodite. Zwitterions can be formed from compounds that contain both acid groups and base groups in their molecules (ampholytes).
All of the common amino acids found in proteins are ampholytes because they contain a carboxyl group (-COOH) that acts as an acid and an amino group (-NH2) that acts as a base. In the solid state, amino acids exist in the dipolar or zwitterion form. If acid is added to a solution containing the zwitterion, the carboxylate group captures a hydrogen (H+) ion, and the amino acid becomes positively charged. If base is added, ion removal of the H+ ion from the amino group of the zwitterion produces a negatively charged amino acid.
Lennard-Jones potential → Lennard-Jonesov potencijal
The Lennard-Jones potential (or 12-6 potential) is a mathematically simple model that describes the interaction between two non-bonded and uncharged atoms (known as the van der Waals interaction). It was first proposed in 1924 by British physicist Sir John Edward Lennard-Jones (1894-1954). The Lennard-Jones Potential is given by the following equation
V(r) = 4e[(sigma/r)12-(sigma/r)6)]
where V is the intermolecular potential between the two atoms or molecules, ε is the well depth and a measure of how strongly the two particles attract each other, σ is the distance at which the intermolecular potential between the two particles is zero, r is the distance of separation between centres of both particles.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Oktaedarska geometrija molekule." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table