polyprotonic acids → poliprotonske kiseline
Polyprotonic acids are acids which dissolve in more than one degree.
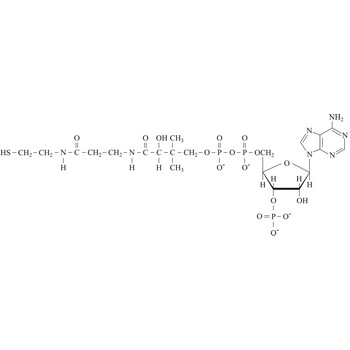
coenzyme a → koenzim a
Coenzyme A (CoA) is an essential metabolic cofactor synthesized from cysteine, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and ATP. CoA plays important roles in many metabolic pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, and the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids. One of the main functions of CoA is the carrying and transfer of acyl groups. Acylated derivatives (acetyl-CoA) are critical intermediates in many metabolic reactions.
glyceride → glicerid
Glycerides are esters of glycerol (propane-1,2,3-triol) with fatty acids, widely distributed in nature. They are by a long-established custom subdivided into triglycerides, 1,2- or 1,3-diglycerides, and 1- or 2- monoglycerides, according to the number and positions of acyl groups.
saponification → saponifikacija
Saponification is a proces of hydrolysis of esters using hot sodium hydroxide solution to produce the salt of a carboxylic acid. Saponification usually refers to the hydrolysis of esters of fatty acids to manufacture soaps.
tryglyceride → triglicerid
Triglyceride is an ester of glycerol and three fatty acids. It is the main constituent of vegetable oil and animal fats. The fatty acids attached to the glycerol can be the same or different. Natural fatty acids found in plants and animals are typically composed only of even numbers of carbon atoms (usually from 16 to 20) due to the way they are bio-synthesized from acetyl CoA.
acid halide → kiselinski halogenid
Acid halide is organic compound containing the group -COX where X is a halogen atom.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Nezasićena masna kiselina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table