bismuth → bizmut
Bismuth was discovered by Claude Geoffroy (France) in 1753. The origin of the name comes from the German words Weisse Masse meaning white mass; now spelled wismut and bisemutum. It is hard, brittle, steel-grey metal with a pink tint. Stable in oxygen and water. Dissolves in concentrated nitric acid. Bismuth can be found free in nature and in minerals like bismuthine (Bi2S3) and in bismuth ochre (Bi2O3) Main use is in pharmaceuticals and low melting point alloys used as fuses.
chlorosity → klorocitet
Chlorosity is the quantity determined by volumetric methods and is defined in the same manner as chlorinity except that the sample unit is 1 L of sea water rather than 1 kg of sea water weighed in vacuo.
coal gas → ugljeni plin
Coal gas is a gas produced by the destructive distillation of coal, and contains approximately 50 % hydrogen, 35 % methane and 8 % carbon monoxide. The by-products of the production of coal gas are coal tar and coke.
coal tar → ugljeni katran
Coal tar is a material obtained from the destructive distillation of coal in the production of coal gas. The crude tar contains a large number of organic compounds (e.g. benzene, naphthalene, methylbenzene, etc.), which can be separated by fractional distillation.
concentration of ore → koncentriranje ruda
Concentration of ores is important industrial processes and is the first steps to the extraction of the metals. Normally, the ore is concentrated by separating it from the clay body in which it occurs either by gravity, sedimentation, or by a floatation process, before the extraction of the metal from the ore is started.
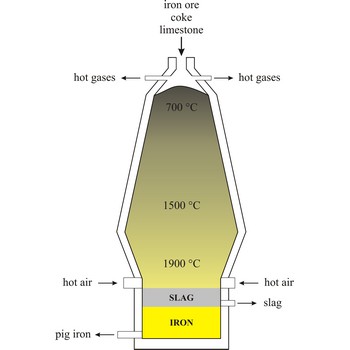
blast furnace → visoka peć
Blast furnace is a furnace for smelting of iron from iron oxide ores (hematite, Fe2O3 or magnetite, Fe3O4). Coke, limestone and iron ore are poured in the top, which would normally burn only on the surface. The hot air blast to the furnace burns the coke and maintains the very high temperatures that are needed to reduce the ore to iron. The reaction between air and the fuel generates carbon monoxide. This gas reduces the iron(III) oxide in the ore to iron.
Because the furnace temperature is in the region of 1500 °C, the metal is produced in a molten state and this runs down to the base of the furnace.
The production of iron in a blast furnace is a continuous process. The furnace is heated constantly and is re-charged with raw materials from the top while it is being tapped from the bottom. Iron making in the furnace usually continues for about ten years before the furnace linings have to be renewed.
body-centered cubic lattice → prostorno centrirana kubična rešetka
Body-centered cubic lattice (bcc or cubic-I), like all lattices, has lattice points at the eight corners of the unit cell plus an additional points at the center of the cell. It has unit cell vectors a = b = c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
The simplest crystal structures are those in which there is only a single atom at each lattice point. In the bcc structures the spheres fill 68 % of the volume. The number of atoms in a unit cell is two (8 × 1/8 + 1 = 2). There are 23 metals that have the bcc lattice.
conductometry → konduktometrija
Conductometry is a volumetric analytic method in which the end of titration (equivalent point) is defined by an electric conductivity appliance.
coulometry → kulometrija
Coulometry is a quantitative electrochemical analytical method which is based on measuring the quantity of electricity that has passed and on Faraday’s laws.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Meta položaj." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table