ligand field theory → teorija ligandnog polja
Ligand field theory is a description of the structure of crystals containing a transition metal ion surrounded by nonmetallic ions (ligands). It is based on the construction of molecular orbitals involving the d-orbitals of the central metal ion and combinations of atomic orbitals of the ligands.
liquid crystal → tekući kristal
Liquid crystals or crystalline liquids are a physical state between crystals and melts. The liquid crystalline phase - the so-called mesophase - is formed at the melting point. The most important (usable) mesophases are nematic, cholesteric and smectic phase, having different molecular orientations.
Erlenmeyer flask → Erlenmeyerova tikvica
Erlenmeyer flask is a glass container which has a narrow, cylindrical mouth and a cone-shaped main body that ends in a wide, flat bottom. It was named after its inventor, a German chemist Richard Erlenmeyer (1825-1909). Erlenmeyer flasks are most often used in titrations to hold the liquid that is being titrated.
free radical → slobodni radikal
Free radical is a molecular fragment having one or more unpaired electrons, usually short-lived and highly reactive. They can be produced by photolysis or pyrolysis in which a bond is broken without forming ions. In formulas, a free radical is conventionally indicated by a dot (·CH3, ·SnH3, ·Cl). Free radicals are known to be formed by ionising radiation and thus play a part in deleterious degradation effects that occur in irradiated tissue. They also act as initiators or intermediates in oxidation, combustion, photolysis, and polymerisation.
fructose → fruktoza
Fructose (fruit sugar) is a ketohexose (a six-carbon ketonic sugar), which occurs in sweet fruits and honey. Glucose and fructose have the same molecular formula, C6H12O6, but have different structures. Pure, dry fructose is a very sweet, white, odorless, crystalline solid. Fructose is one of the sweetest of all sugars and is combined with glucose to make sucrose, or common table sugar. An older common name for fructose is levulose, after its levorotatory property of rotating plane polarized light to the left (in contrast to glucose which is dextrorotatory). The polysaccharide inulin is a polymer of fructose.
glutamic acid → glutaminska kiselina
Glutamic acid is an electrically charged amino acids. It is one of the two amino acids that contain a carboxylic acid group in its side chains. These acids play important roles as general acids in enzyme active centers, as well as in maintaining the solubility and ionic character of proteins. Glutamic acid is commonly referred to as glutamate, because its carboxylic acid side chain will be deprotonated and thus negatively charged in its anionic form at physiological pH. Glutamic acid is referred to as a non-essential amino acid because a healthy human can synthesize all the glutamic acid needed for normal body function from other amino acids.
- Abbreviations: Glu, E
- IUPAC name: 2-aminopentanedioic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H9NO4
- Molecular weight: 147.13 g/mol
malleability → kovkost
Malleability is a property of something that can be worked or hammered or shaped under pressure without breaking.
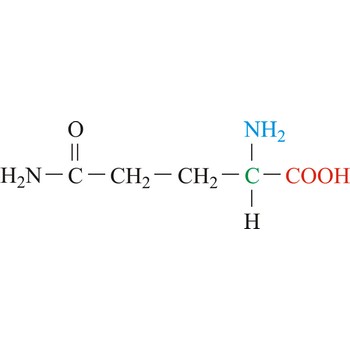
glutamine → glutamin
Glutamine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It serves as an important carrier of ammonia and contributes it to the formation of urea and purines. Glutamine is not recognized as an essential amino acid but may become conditionally essential in certain situations, including intensive athletic training or certain gastrointestinal disorders. It is synthesized by the enzyme glutamine synthetase from glutamate and ammonia.
- Abbreviations: Gln, Q
- IUPAC name: 2,5-diamino-5-oxopentanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H10N2O3
- Molecular weight: 146.14 g/mol
glycine → glicin
Glycine is the smallest amino acid and is unique because it lacks a side chain. This gives it more conformational freedom than any other amino acid. Glycine is often found in turns and loops where other amino acids would be sterically unacceptable. Although it is formally nonpolar, it’s very small side chain makes no real contribution to hydrophobic interactions. Glycine is not essential to the human diet, as it is biosynthesized in the body from the amino acid serine.
- Abbreviations: Gly, G
- IUPAC name: 2-aminoacetic acid
- Molecular formula: C2H5NO2
- Molecular weight: 75.07 g/mol
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Linear molecular shape." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table