serine → serin
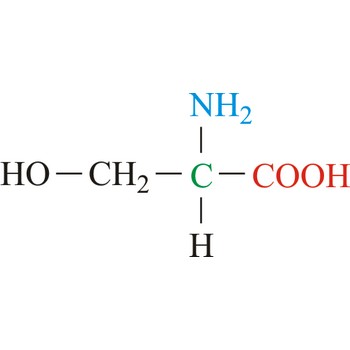
Serine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It is one of two hydroxyl amino acids. Both are commonly considered to by hydrophilic due to the hydrogen bonding capacity of the hydroxyl group. Serine often serves as a nucleophile in many enzyme active sites, and is best known for its role in the serine proteases. Serine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine.
- Abbreviations: Ser, S
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO3
- Molecular weight: 105.09 g/mol
solid state → čvrsto agregatno stanje
Solid state is characterised by a constant shape and volume. Particles are placed very close to one another and have efect one on another with great attraction forces. Solid bodies do not assume the shape of the container in which they are put.
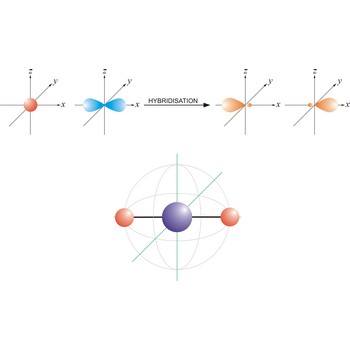
sp hybrid orbital → sp hibridna orbitala
An sp hybrid orbital is an orbital formed by the linear combination of one s and one p orbital of comparable energy (such 2s and 2p orbitals) on a same atom. The two sp hybrid orbitals are aligned in a straight line in opposite direction (bond angles are 180°). The remaining two p orbitals are at right angles to one another and to the line formed by the two sp orbitals.
sp2 hybrid orbital → sp2 hibridna orbitala
An sp2 hybrid orbital is an orbital formed by the linear combination of one s and two p orbitals of comparable energy (such 2s and 2p orbitals) on a same atom. The three sp2 hybrid orbitals lie in a plane with angle of 120°. The remaining p orbital remains unchanged and is perpendicular to the plane of the three sp2 orbitals.
sp3 hybrid orbital → sp3 hibridna orbitala
An sp3 hybrid orbital is an orbital formed by the linear combination of one s and three p orbitals of comparable energy (such 2s and 2p orbitals) on a same atom. The four sp3 hybrid orbitals point toward the corners of a regular tetrahedron with the bond angle of 109.5°.
standard → standard
Standards are materials containing a known concentration of an analyte. They provide a reference to determine unknown concentrations or to calibrate analytical instruments.
The accuracy of an analytical measurement is how close a result comes to the true value. Determining the accuracy of a measurement usually requires calibration of the analytical method with a known standard. This is often done with standards of several concentrations to make a calibration or working curve.
A primary standard is a reagent that is extremely pure, stable, has no waters of hydration, and has a high molecular weight.
A secondary standard is a standard that is prepared in the laboratory for a specific analysis. It is usually standardised against a primary standard.
standard deviation → standardna devijacija
Standard deviation (σ) is a measure of the dispersion of a set of data from its mean. Standard deviation is a statistical term that measures the amount of variability or dispersion around an average
Suppose there are many measurements of a quantity presumed to be similar, like the size of peas in a pod. If the number of readings for each size were plotted, a bell-shaped curve would probably result, with a few small and large peas and most clustered around the average size. Around two-thirds of all measurements fall in the range spanned by the standard deviation, a measure of the spread.
starch → škrob
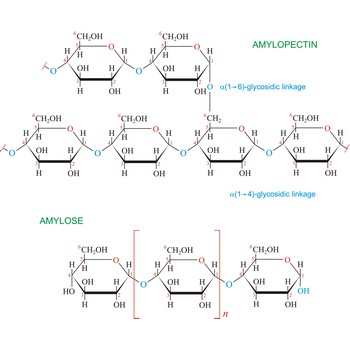
Starch (C6H10O5)x is a polysaccharide used by plants to stockpile glucose molecules. It is the major component of flour, potatoes, rice, beans, corn, and peas. Starch is a mixture of two different polysaccharides: amylose (about 20 %), which is insoluble in cold water, and amylopectin (about 80 %), which is soluble in cold water. Amylose is composed of unbranched chains of D-glucose units joined by α(1→4)-glycosidic linkages. Unlike amylose, which are linear polymers, amylopectin contains α(1→6)-glycoside branches approximately every 25 glucose units.
Starch digestion begins in the mouth via the action of amylase, a digestive enzyme present in saliva. The process is completed in the small intestine by the pancreatic amylase. The final products of starch digestion, glucose molecules, are absorbed into the intestinal bloodstream and transported to the liver. Like most enzymes, glycosidases are highly selective in their action. They hydrolyze only the α-glycoside links in starch and leave the β-glycoside links in cellulose untouched. Starch is important food stuff and is used in adhesives, and sizes, in laundering, pharmacy and medicine.
sugar → šećer
Sugar is any of a group of water-soluble carbohydrates of relatively low molecular weight and typically having a sweet taste. The group comprises mainly monosaccharides (glucose, fructose, galactose), disaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose), and trisaccharides (raffinose). Many monosaccharides and disaccharides fairly commonly found in nature bear names reflecting the source from which they were first isolated. For example, glucose is also known as grape sugar, lactose as milk sugar, and maltose as malt sugar. In everyday usage, the name is often used to refer specifically to sucrose (table sugar, cane sugar, beet sugar).
thermal expansion → toplinsko rastezanje
Thermal expansion is a change in dimensions of a material resulting from a change in temperature. All objects change size with changes in temperature. The change ΔL in any linear dimension L is given by
in which α is the thermal coefficient of linear expansion, Lo is the initial or reference dimension at temperature To (reference temperature) and ΔT is change in temperature which causes the change in dimension.
The change ΔV in the volume of a sample of solid or liquid is
Here γ is coefficient of volume expansion, Vo is the volume of the sample at temperature To and ΔV is the change in volume over the temperature range ΔT. With isotropic substances, the coefficient of volume expansion can be calculated from the coefficient of linear expansion: γ = 3α.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Linear molecular shape." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table