critical point → kritična točka
In general, critical point is the point on the phase diagram of a two-phase system at which the two coexisting phases have identical properties and therefore represent a single phase. At the liquid-gas critical point of a pure substance, the distinction between liquid and gas vanishes, and the vapour pressure curve ends. The coordinates of this point are called the critical temperature and critical pressure. Above the critical temperature it is not possible to liquefy the substance.
critical mass → kritična masa
Critical mass is the minimum mass of a fissionable material (235U or 239Pu) that will initiate an uncontrolled chain reaction as in an atomic bomb. The critical mass of pure 239Pu is about 4.5 kg, and of 235U about 15 kg.
equivalence point → točka ekvivalencije
Eequivalence point is the point in a titration when enough titrant has been added to react completely with the analyte.
critical temperature → kritična temperatura
Critical temperature is the temperature of the liquid-vapour critical point, that is, the temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied by an increase of pressure.
point-like object → materijalna točka
Point-like object is an expression, usual in kinematics: a point-like object (or a particle) is an object with dimensions, which can be neglected while considering its motion.
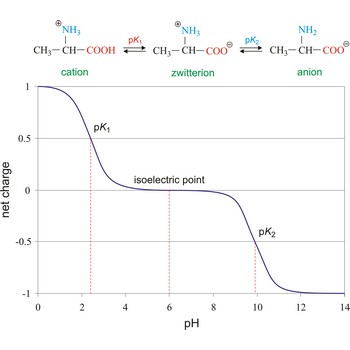
isoelectric point → izoelektrična točka
Isoelectric point (pI or IEP) is the pH of a solution or dispersion at which the net charge on the molecules or colloidal particles is zero. In electrophoresis there is no motion of the particles in an electric field at the isoelectric point. The net charge (the algebraic sum of all the charged groups present) of any amino acid, peptide or protein, will depend upon the pH of the surrounding aqueous environment. For example, alanine can have a charge of +1, 0, or -1, depending on the pH of the solution in which it is dissolved.
triple point → trojna točka
Triple point is the point in p,T space where the solid, liquid, and gas phases of a substance are in thermodynamic equilibrium.
critical pressure → kritični tlak
Critical pressure is the pressure of a fluid in its critical point; i.e. when it is at its critical temperature and critical volume.
critical volume → kritični volumen
Critical volume is the volume of a fixed mass of a fluid at critical temperature and pressure.
phase diagram → fazni dijagram
Phase diagram is a graphic representation of the equilibrium relationships between phases (such as vapour-liquid, liquid-solid) of a chemical compound, mixture of compounds, or solution.
The figure shows a typical phase diagram of an element or a simple compound. The stability of solid, liquid and gas phases depends on the temperature and the pressure. The three phases are in equilibrium at the triple point. The gas and liquid phases are separated by a phase transition only below the temperature of the critical point.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kritična točka." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table