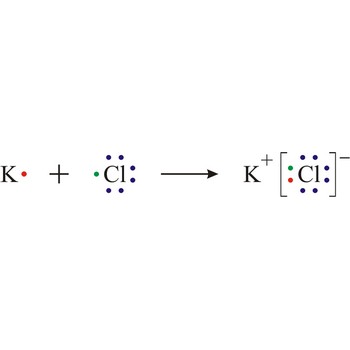ionic bond → ionska veza
Ionic bond is a strong force of attraction holding atoms together in a molecule or crystal. Typically chemical bonds have energies of about 100 kJ mol-1. Ionic bond is a bond at which one of the participants, during the procedure of bonding, gives away its unpaired electrons to another atom so that both can achieve electron arrangement of the closest noble gas. In order to form an ionic bond one of the atoms must cross to the positively charged ion by losing certain number of electrons and the other atom must receive those electrons and cross to the negatively charged ion.
peptide bond → peptidna veza
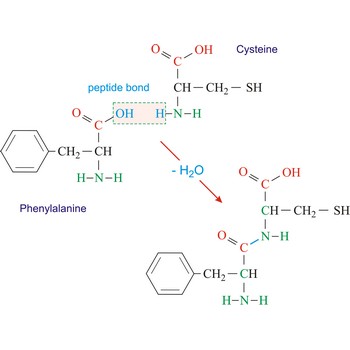
Peptide bond emerges when two amino acid join in a way that the carbon atom from one connects with the nitrogen atom from the other (creating a C-N bond).
sigma bond → sigma veza
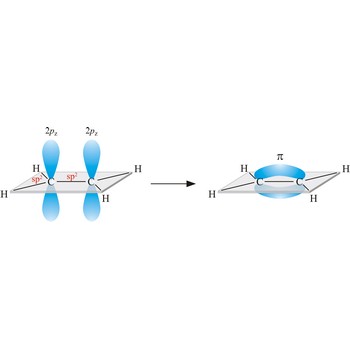
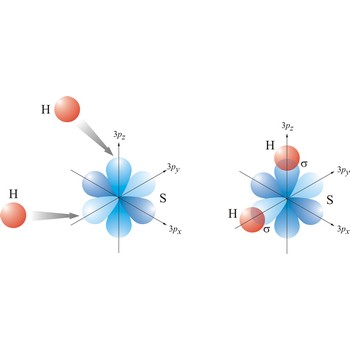
Most single bonds are sigma bonds (σ-bond). In the valence bond theory, a sigma bond is a valence bond that is symmetrical around the imaginary line between the bonded atoms.
covalent compound → kovalentni spoj
Covalent compound is a compound made of molecules - not ions, such as H2O, CH4, Cl2. The atoms in the compound are bound together by shared electrons. Also called a molecular compound.
covalentity → kovalentnost
Covalentity is a maximum number of covalent bond that one atom can make, it is equal to the number of hydrogen atoms that are combined with other atoms. It is usually constant.
valence bond theory → teorija valentne veze
Valence bond theory is a theory that explains the shapes of molecules in terms of overlaps between half-filled atomic orbitals, or half filled hybridised orbitals.
atom radius → radijus atoma
Atoms and molecules have no strict boundaries. The volume of a free atom is usually defined as that volume that contains 90 % of electron cloud. The radius of an atom represents half of interatom distance of two identical atoms which are in touch but are not interconnected either by a covalent or an ionic bond, but with a very weak van der Waals’s bond.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kovalentna veza." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table