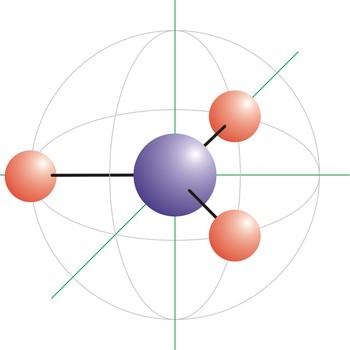
trigonal planar molecular geometry → trigonska planarna geometrija molekule
Trigonal planar is a molecular shape that results when there are three bonds and no lone pairs around the central atom in the molecule. The pairs are arranged along the central atom’s equator, with 120° angles between them. Molecules with an trigonal planar electron pair geometries have sp2d hybridization at the central atom. The carbonate ion (CO32-) has a trigonal planar geometry.
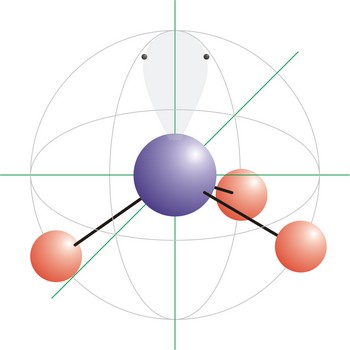
trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry → trigonska piramidalna geometrija molekule
Trigonal pyramidal is a molecular shape that results when there are three bonds and one lone pair on the central atom in the molecule. Molecules with an tetrahedral electron pair geometries have sp3 hybridization at the central atom. Ammonia (NH3) is a trigonal pyramidal molecule.
chiral centre → kiralno središte
Chiral centre in organic chemistry is most often an asymmetrically substituted carbon atom (C*).
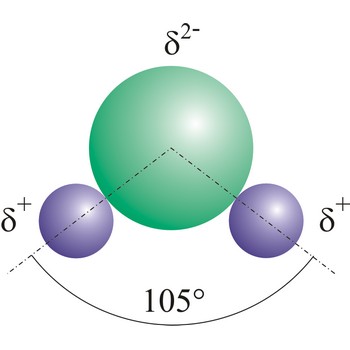
dipole molecule → dipolna molekula
Dipole molecules are created when mutual electronic pair at covalent bond is asymmetrical. If different atoms are bonded by a covalent bond, which can have different electron affinity, then the the atom with greater electron affinity will attract the electron pairs more strongly. In this way an asymmetrical distribution of negative charge appears in a molecule, so one part of the molecule becomes relatively negatively (the one closer to the electron pair) and the other becomes relatively positively charged.
molecular formula → molekularna formula
Molecular formula is a formula which represents one molecule of an element or a compound, and the number of atoms in each one of them.
molecular lattice → molekularna rešetka
Molecular lattice is a crystal lattice made molecules bonded together by intermolecular forces.
percentage composition of atom in the molecule → postotni sastav atoma u molekuli
Percentage composition of atom in the molecule is a structure of compound presented in the shape of a percentage of its mass, which comes from every element.
polyvalent molecule → polivalentna molekula
Polyvalent molecule is a molecule which having multiple binding sites. The antibodies of our immune system are one example.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kiralne molekule." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table