Results 1–4 of 4 for kelat
chelate → kelat
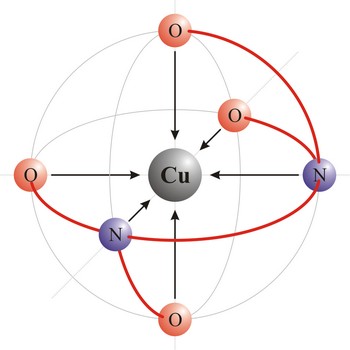
Chelate is a compound characterized by the presence of bonds from two or more bonding sites within the same ligand to a central metal atom. For example, copper complexes with EDTA to form a chelate. Chelate complexes are more stable than complexes with the corresponding monodentate ligands.
chelating agent → kelatni agens
Chelating agent is ligand that binds to a metal using more than one atom; a polydentate ligand.
ligand → ligand
Ligand is an ion (F-, Cl-, Br-, I-, S2-, CN-, NCS-, OH-, NH2-) or molecule (NH3, H2O, NO, CO) that donates a pair of electrons to a metal atom or ion in forming a coordination complex. The main way of classifying ligands is by the number of points at which they are attached to, or bound to, the metal center. This is the denticity. Ligands with one potential donor atom are monodentate. Polydentate ligand is a ligand that is attached to a central metal ion by bonds from two or more donor atoms. Ligands with more than one potential donor atom are known as ambidentate, such as the thiocyanate ion, NCS-, which can bind to the metal center with either the nitrogen or sulphur atoms. Chelating ligands are those polydentate ligands which can form a ring including the metal atom.
polydentant ligand → polidentantni liganad
Polydentant ligands contain more co-ordination points (can give more electron pairs) and they form complex ringlike structures (celate complexes) by replacing two or more monodentant ligands. That kind of ligand is EDTA which has 6 co-ordinational points and with metals it creates complexes, always in 1:1 ratio.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kelat." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table