white light → bijela svjetlost
White light is a mixture of lights of all colours. If white light is passed through a glass prism or an optical lattice, it is separated into several colours (the visible light spectrum).
high fructose corn syrup → visoko fruktozni kukuruzni sirup
High fructose corn syrup (HFCS) is commonly used in place of sugar in foods and drinks. Corn starch is hydrolyzed to glucose, which is then treated with glucose isomerase to produce a fructose-rich mixture. HFCS is available in a number of forms, named according to the percentage of fructose they contain, HFCS-55 for instance contains 55 % fructose and 45 % glucose. The enhanced sweetness, low cost and ease of use are the main reasons why manufacturers now prefer to use high fructose corn syrup instead of sugar.
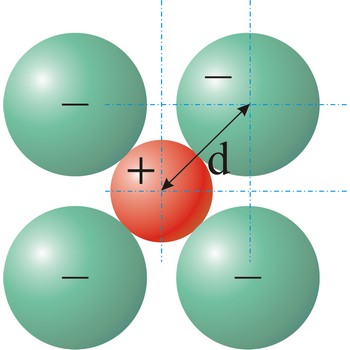
ionic radius → ionski radijus
Ionic radius is the radius of anions and cations in crystalline ionic compounds, as determined by consistently partitioning the center-to-center distance of ions in those compounds. In general, negative ions have larger ionic radii than positive ions.
ionisation → ionizacija
Ionisation is the process of producing ions. Certain molecules ionise in a solution; for example, acids ionise when dissolved in water.
Electron transfer also causes ionisation in certain reactions, for example sodium and chlorine react by transfer of a valence electron from the sodium atom to the chlorine atom to form the ions that constitute a sodium chloride crystal.
metallic glass → metalno staklo
Certain alloys can solidify by extremely rapid cooling out of melt without formation of a crystal lattice, that is in the amorphous form - such, amorphous alloys are so called metallic glasses. The alloy of zirconium, beryllium, titanium, copper, and nickel is one of the first metallic glasses that can be made in bulk and formed into strong, hard, useful objects.
Unlike pure metals and most metal alloys, metallic glasses have no regular crystalline structure. This lack of long range order or microstructure is related to such desirable features as strength and low damping which is one reason why the premier use for zirconium-based metallic glass is in the manufacture of expensive golf club heads. Metallic glasses can be quite strong yet highly elastic, and they can also be quite tough (resistant to fracture). Even more interesting are the thermal properties; for instance, just like an oxide glass, there is a temperature (called the glass transition temperature) above which a metallic glass becomes quite soft and flows easily. This means that there are lots of opportunities for easily forming metallic glasses into complex shapes.
nerve poison → živčani bojni otrov
Nerve poison (nerve gas, agents) have had an entirely dominant role since the Second World War. Nerve poisons acquired their name because they affect the transmission of nerve impulses in the nervous system. All nerve poisons belong chemically to the group of organo-phosphorus compounds. They are stable and easily dispersed, highly toxic and have rapid effects both when absorbed through the skin and via respiration. Nerve poisons can be manufactured by means of fairly simple chemical techniques. The raw materials are inexpensive and generally readily available.
The most important nerve agents included in modern chemical weapons arsenals are:
| Tabun | (o-ethyl dimethylamidophosphorylcyanide) |
| Sarin | (isopropyl methylphosphonofluoridate) |
| Soman | (pinacolyl methylphosphonofluoridate) |
| GF | (cyclohexyl methylphosphonofluoridate) |
| VX | (o-ethyl S-diisopropylaminomethyl methylphosphonothiolate) |
Nerve poisons are colorless, odorless, tasteless liquids of low volatility. Antidotes are atropine sulfate and pralidoxime iodide.
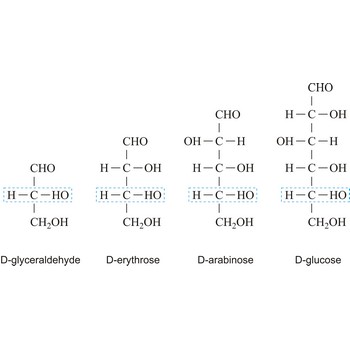
monosaccharide → monosaharid
Monosaccharides are carbohydrates, with the general formula Cn(H2O)n, that cannot be decomposed to a simpler carbohydrates by hydrolysis.
Depending on whether the molecule contains an aldehyde group (-CHO) or a ketone group (-CO-) monosaccharide can be a polyhydroxy aldehyde (aldose) or a polyhydroxy ketone (ketose). These aldehyde and ketone groups confer reduction properties on monosaccharides. They are also classified according to the number of carbon atoms they contain: trioses have three carbon atoms, tetroses four, pentoses five, hexoses six, heptoses seven, etc. These two systems of classification are often combined. For example, a six-carbon polyhydroxy aldehyde such as D-glucose is an aldohexose, whereas a six-carbon polyhydroxy ketone such as D-fructose is a ketohexose.
The notations D and L are used to describe the configurations of carbohydrates. In Fischer projections of monosaccharides, the carbonyl group is always placed on top (in the case of aldoses) or as close to the top as possible (in the case of ketoses). If the OH group attached to the bottom-most asymmetric carbon (the carbon that is second from the bottom) is on the right, then the compound is a D-sugar. If the OH group is on the left, then the compound is an L-sugar. Almost all sugars found in nature are D-sugars.
Monosaccharides can exist as either straight-chain or ring-shaped molecules. During the conversion from straight-chain form to cyclic form, the carbon atom containing the carbonyl oxygen, called the anomeric carbon, becomes a chiral center with two possible configurations (anomers), α and β. When the stereochemistry of the first carbon matches the stereochemistry of the last stereogenic center the sugar is the α-anomer when they are opposite the sugar is the β-anomer.
organic → organski
1. Organic refers to any chemical compound based on carbon (C) with the exception of some of the simple compounds of carbon, such as carbon dioxide, which are frequently classified as inorganic compounds. Additional elements that are commonly found in organic compounds are hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), phosphorus (P) and sulfur (S).
2. Organic or organically-grown foods are grown or raised without synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, growth stimulators, or antibiotics and other drugs. Pests are controlled by cultivation techniques and the use of pesticides derived from natural sources and the use of natural fertilizers. In addition, organically grown foods must also be stored without the use of chemicals such as artificial additives and preservatives, and without food irradiation.
polymorphism → polimorfija
Polymorphism is the ability of a solid substance to crystallise into more than one different crystal structure. Different polymorphs have different arrangements of atoms within the unit cell, and this can have a profound effect on the properties of the final crystallised compound. The change that takes place between crystal structures of the same chemical compound is called polymorphic transformation.
The set of unique crystal structures a given compound may form are called polymorphs. Calcium carbonate is dimorphous (two forms), crystallizing as calcite or aragonite. Titanium dioxide is trimorphous; its three forms are brookite, anatase, and rutile. The prevailing crystal structure depends on both the temperature and the external pressure.
Iron is a metal with polymorphism structure. Each structure stable in the range of temperature, for example, when iron crystallizes at 1 538 °C it is bcc (δ-iron), at 1 394 °C the structure changes to fcc (γ-iron or austenite), and at 912 °C it again becomes bcc (α-iron or ferrite).
Polymorphism of an element is called allotropy.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Jednostavna ortorompska rešetka." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table