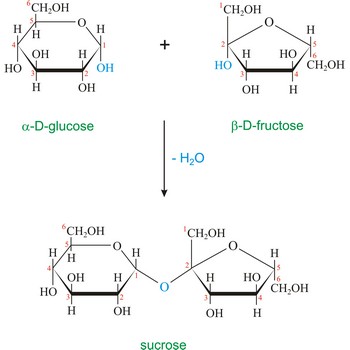
sucrose → saharoza
Sucrose (saccharose), or ordinary table sugar, is a disaccharide in which α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-fructofuranose are joined at their anomeric carbons by a glycosidic bond. There are no hemiacetals remaining in the sucrose and therefore sucrose is not a reducing sugar and does not exhibit mutarotation. Sugar is a white crystalline sweet compound found in many plants and extracted from sugar cane and sugar beet. It is used as a sweetening agent in food and drinks. If heated to 200 °C, sucrose becomes caramel. When sucrose is hydrolyzed it forms an equimolar mixture of glucose and fructose. This mixture of monosaccharides is called invert sugar. Honeybees have enzymes called invertases that catalyze the hydrolysis of sucrose. Honey, in fact, is primarily a mixture of glucose, fructose, and sucrose.
Chitin → Hitin
Chitin is a nitrogen-containing linear polysaccharide of ß(1->4) linked units of N-acetyl-ß-d-glucosamine. The structure of chitin is similar to cellulose except for the replacement hydroxyl group (-OH) at the carbon 2 with an acetyl amine group (–NH–CO–CH3). Chitin is the main component of the exoskeleton, or outer covering of insects, crustaceans, and arachnids. It is also found in the cell walls of certain fungi and algae. After cellulose, chitin is the second most abundant biopolymer in nature. It is insoluble in water, organic solvents, weak acids and lyes.
addition reactions → reakcije adicije
Addition reactions are normally occur with unsaturated compounds and involve the addition of one molecule (called the reactant) across the unsaturated bond (i.e. the double bond or the triple bond) of another molecule (called the substrate) to give a single product, formed by the combination of both reacting molecules.
For example, bromine adds across the double bond of ethene in an addition reaction to form dibromoethane.
aldehydes → aldehidi
Aldehydes are a broad class of organic compounds having the generic formula RCHO, and characterized by an unsaturated carbonyl group (C=O). They are formed from alcohols by either dehydrogenation or oxidation. Their chemical derivation is indicated by the name al(cohol) + dehyd(rogenation). An example of these distinct aromatic compounds is formaldehyde.
amino acids → aminokiseline
Amino acids are compounds containing both a carboxylic acid group (-COOH) and an amino group (-NH2 ). The most important are the α-amino acids, in which the -NH2 group in attached to the C atom adjacent to the -COOH group. In the β-amino acids, there is an intervening carbon atom.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Glikozidna veza." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table