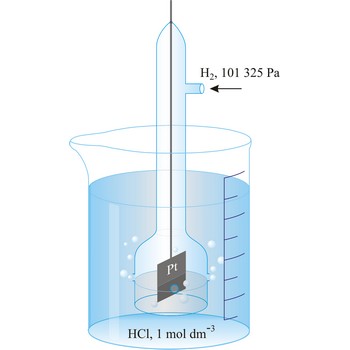
standard hydrogen electrode → standardna vodikova elektroda
Standard hydrogen electrode is a system in which hydrogen ion and gaseous hydrogen are present in their standard states. The convention is to designate the cell so that the standard hydrogen electrode is written first.
The electrode is used as a reference (of zero) for the values of other standard electrode potentials.
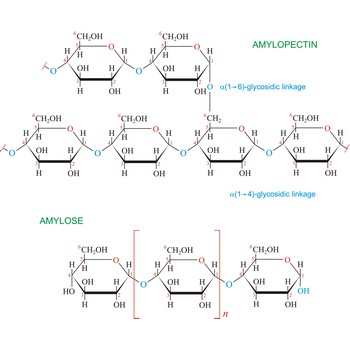
starch → škrob
Starch (C6H10O5)x is a polysaccharide used by plants to stockpile glucose molecules. It is the major component of flour, potatoes, rice, beans, corn, and peas. Starch is a mixture of two different polysaccharides: amylose (about 20 %), which is insoluble in cold water, and amylopectin (about 80 %), which is soluble in cold water. Amylose is composed of unbranched chains of D-glucose units joined by α(1→4)-glycosidic linkages. Unlike amylose, which are linear polymers, amylopectin contains α(1→6)-glycoside branches approximately every 25 glucose units.
Starch digestion begins in the mouth via the action of amylase, a digestive enzyme present in saliva. The process is completed in the small intestine by the pancreatic amylase. The final products of starch digestion, glucose molecules, are absorbed into the intestinal bloodstream and transported to the liver. Like most enzymes, glycosidases are highly selective in their action. They hydrolyze only the α-glycoside links in starch and leave the β-glycoside links in cellulose untouched. Starch is important food stuff and is used in adhesives, and sizes, in laundering, pharmacy and medicine.
strontium → stroncij
Strontium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1808. Named after the village of Strontian in Scotland. It is soft, malleable, silvery-yellow metal. Combustible in air, will react with water. Exposed surfaces form protective oxide film. Metal ignites and burns readily. Strontium is found in minerals celestite and strontianite. Used in flares and fireworks for crimson colour. Strontium-90 is a long lived highly radioactive fallout product of atomic-bomb explosions.
thorium → torij
Thorium was discovered by Jöns Jakob Berzelius (Sweden) in 1828. Named after Thor, the mythological Scandinavian god of war. It is heavy, grey, soft, malleable, ductile, radioactive metal. Tarnishes in air; reacts with water. Reacts violently with oxidants. Thorium is found in various minerals like monazite and thorite. Used in making strong alloys. Also in ultraviolet photoelectric cells. It is a common ingredient in high-quality lenses. Bombarded with neutrons make uranium-233, a nuclear fuel.
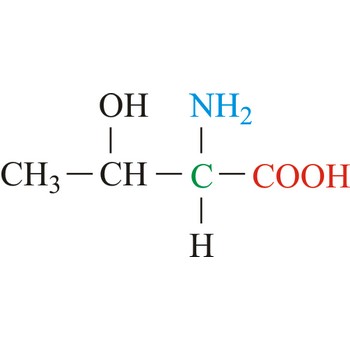
threonine → treonin
Threonine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It differs from serine by having a methyl substituent in place of one of the hydrogens on the β carbon. Threonine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Thr, T
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H9NO3
- Molecular weight: 119.12 g/mol
triclinic lattice → triklinska rešetka
Triclinic lattice has one lattice point at the each corner of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a≠b≠c and interaxial angles α≠β≠γ≠90°.
tyrosine → tirozin
Tyrosine is hydrophobic amino acids with aromatic side chain. Tyrosine is large aromatic residue that is normally found buried in the interior of a protein and is important for protein stability. Tyrosine has special properties since its hydroxyl side chain may function as a powerful nucleophile in an enzyme active site (when ionized) and is a common site for phosphorylation in cell signaling cascades. Tyrosine absorbs ultraviolet radiation and contributes to the absorbance spectra of proteins. It is not essential (or semi-essential) to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites.
- Abbreviations: Tyr, Y
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C9H11NO3
- Molecular weight: 181.19 g/mol
ultraviolet light → ultraljubičasto svjetlo
Ultraviolet light (UV light or UV radiation) is an electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of x-rays, but shorter than that of visible light. Ultraviolet light can break some chemical bonds and cause cell damage.
T-S diagram → T-S dijagram
The relationship between the temperature (T) and the salinity (S) of a seawater can be illustrated graphically on a T-S diagram, which is a simple, but powerful tool used in studies of seawater density, mixing, and circulation. In a T-S diagram, temperature is plotted along the vertical axis in degrees Celsius and salinity is measured along the horizontal axis in PSU (Practical Salinity Units). Seawater density is illustrated in the diagram by curved lines of constant density (isopycnals). Water tends to move horizontally throughout the deep ocean, moving along lines of equal density.
Chitin → Hitin
Chitin is a nitrogen-containing linear polysaccharide of ß(1->4) linked units of N-acetyl-ß-d-glucosamine. The structure of chitin is similar to cellulose except for the replacement hydroxyl group (-OH) at the carbon 2 with an acetyl amine group (–NH–CO–CH3). Chitin is the main component of the exoskeleton, or outer covering of insects, crustaceans, and arachnids. It is also found in the cell walls of certain fungi and algae. After cellulose, chitin is the second most abundant biopolymer in nature. It is insoluble in water, organic solvents, weak acids and lyes.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Galvanic cell." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table